- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support

Overview of the Problem-Solving Mental Process
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Rachel Goldman, PhD FTOS, is a licensed psychologist, clinical assistant professor, speaker, wellness expert specializing in eating behaviors, stress management, and health behavior change.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Rachel-Goldman-1000-a42451caacb6423abecbe6b74e628042.jpg)
- Identify the Problem
- Define the Problem
- Form a Strategy
- Organize Information
- Allocate Resources
- Monitor Progress
- Evaluate the Results
Frequently Asked Questions
Problem-solving is a mental process that involves discovering, analyzing, and solving problems. The ultimate goal of problem-solving is to overcome obstacles and find a solution that best resolves the issue.
The best strategy for solving a problem depends largely on the unique situation. In some cases, people are better off learning everything they can about the issue and then using factual knowledge to come up with a solution. In other instances, creativity and insight are the best options.
It is not necessary to follow problem-solving steps sequentially, It is common to skip steps or even go back through steps multiple times until the desired solution is reached.
In order to correctly solve a problem, it is often important to follow a series of steps. Researchers sometimes refer to this as the problem-solving cycle. While this cycle is portrayed sequentially, people rarely follow a rigid series of steps to find a solution.
The following steps include developing strategies and organizing knowledge.
1. Identifying the Problem
While it may seem like an obvious step, identifying the problem is not always as simple as it sounds. In some cases, people might mistakenly identify the wrong source of a problem, which will make attempts to solve it inefficient or even useless.
Some strategies that you might use to figure out the source of a problem include :
- Asking questions about the problem
- Breaking the problem down into smaller pieces
- Looking at the problem from different perspectives
- Conducting research to figure out what relationships exist between different variables
2. Defining the Problem
After the problem has been identified, it is important to fully define the problem so that it can be solved. You can define a problem by operationally defining each aspect of the problem and setting goals for what aspects of the problem you will address
At this point, you should focus on figuring out which aspects of the problems are facts and which are opinions. State the problem clearly and identify the scope of the solution.
3. Forming a Strategy
After the problem has been identified, it is time to start brainstorming potential solutions. This step usually involves generating as many ideas as possible without judging their quality. Once several possibilities have been generated, they can be evaluated and narrowed down.
The next step is to develop a strategy to solve the problem. The approach used will vary depending upon the situation and the individual's unique preferences. Common problem-solving strategies include heuristics and algorithms.
- Heuristics are mental shortcuts that are often based on solutions that have worked in the past. They can work well if the problem is similar to something you have encountered before and are often the best choice if you need a fast solution.
- Algorithms are step-by-step strategies that are guaranteed to produce a correct result. While this approach is great for accuracy, it can also consume time and resources.
Heuristics are often best used when time is of the essence, while algorithms are a better choice when a decision needs to be as accurate as possible.
4. Organizing Information
Before coming up with a solution, you need to first organize the available information. What do you know about the problem? What do you not know? The more information that is available the better prepared you will be to come up with an accurate solution.
When approaching a problem, it is important to make sure that you have all the data you need. Making a decision without adequate information can lead to biased or inaccurate results.
5. Allocating Resources
Of course, we don't always have unlimited money, time, and other resources to solve a problem. Before you begin to solve a problem, you need to determine how high priority it is.
If it is an important problem, it is probably worth allocating more resources to solving it. If, however, it is a fairly unimportant problem, then you do not want to spend too much of your available resources on coming up with a solution.
At this stage, it is important to consider all of the factors that might affect the problem at hand. This includes looking at the available resources, deadlines that need to be met, and any possible risks involved in each solution. After careful evaluation, a decision can be made about which solution to pursue.
6. Monitoring Progress
After selecting a problem-solving strategy, it is time to put the plan into action and see if it works. This step might involve trying out different solutions to see which one is the most effective.
It is also important to monitor the situation after implementing a solution to ensure that the problem has been solved and that no new problems have arisen as a result of the proposed solution.
Effective problem-solvers tend to monitor their progress as they work towards a solution. If they are not making good progress toward reaching their goal, they will reevaluate their approach or look for new strategies .
7. Evaluating the Results
After a solution has been reached, it is important to evaluate the results to determine if it is the best possible solution to the problem. This evaluation might be immediate, such as checking the results of a math problem to ensure the answer is correct, or it can be delayed, such as evaluating the success of a therapy program after several months of treatment.
Once a problem has been solved, it is important to take some time to reflect on the process that was used and evaluate the results. This will help you to improve your problem-solving skills and become more efficient at solving future problems.
A Word From Verywell
It is important to remember that there are many different problem-solving processes with different steps, and this is just one example. Problem-solving in real-world situations requires a great deal of resourcefulness, flexibility, resilience, and continuous interaction with the environment.
Get Advice From The Verywell Mind Podcast
Hosted by therapist Amy Morin, LCSW, this episode of The Verywell Mind Podcast shares how you can stop dwelling in a negative mindset.
Follow Now : Apple Podcasts / Spotify / Google Podcasts
You can become a better problem solving by:
- Practicing brainstorming and coming up with multiple potential solutions to problems
- Being open-minded and considering all possible options before making a decision
- Breaking down problems into smaller, more manageable pieces
- Asking for help when needed
- Researching different problem-solving techniques and trying out new ones
- Learning from mistakes and using them as opportunities to grow
It's important to communicate openly and honestly with your partner about what's going on. Try to see things from their perspective as well as your own. Work together to find a resolution that works for both of you. Be willing to compromise and accept that there may not be a perfect solution.
Take breaks if things are getting too heated, and come back to the problem when you feel calm and collected. Don't try to fix every problem on your own—consider asking a therapist or counselor for help and insight.
If you've tried everything and there doesn't seem to be a way to fix the problem, you may have to learn to accept it. This can be difficult, but try to focus on the positive aspects of your life and remember that every situation is temporary. Don't dwell on what's going wrong—instead, think about what's going right. Find support by talking to friends or family. Seek professional help if you're having trouble coping.
Davidson JE, Sternberg RJ, editors. The Psychology of Problem Solving . Cambridge University Press; 2003. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511615771
Sarathy V. Real world problem-solving . Front Hum Neurosci . 2018;12:261. Published 2018 Jun 26. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2018.00261
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7

7 Steps to Better Problem-Solving Process
Discover the Problem-Solving Process, from identifying issues to implementing optimal solutions. Explore the key steps and benefits to enhance decision-making. Read This blog covers each crucial step—identifying, analysing root causes, brainstorming solutions, evaluating options, and ensuring success through monitoring.

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- Introduction to Management
- Introduction to Managing People
- Senior Management Training

Navigating problems is like solving a complex puzzle. It starts with recognising the issue and ends with implementing a successful solution. The Problem-Solving Process includes key steps: identifying the problem, clarifying it, generating solutions, evaluating options, and executing the best one. Each step builds on the previous, ensuring we tackle the root cause rather than just the symptoms.
The Problem-Solving Process embodies a curiosity, open-mindedness, and resilience mindset, viewing challenges as opportunities for growth and learning. Whether facing minor annoyances or major obstacles, this method equips us with the skills to transform barriers into opportunities and make wise choices. In this blog, we’ll explore this approach in depth.
Table of contents
1) What is a Problem-Solving Process?
2) Steps of the Problem-Solving Process
3) Benefits of the Problem-Solving Process
4) Creating Your Process for Problem-Solving
5) Conclusion
What is a Problem-Solving Process?
The Problem-Solving Process is a crucial analytical skill that helps individuals identify, analyse, and develop effective solutions to various challenges. It serves as a guiding framework, promoting logical and systematic approaches to address complex issues. By examining the root causes of problems and assessing potential options, individuals can make informed decisions and optimise outcomes.
Emphasising critical thinking and creativity, the Problem-Solving Process enhances adaptability and resilience in the face of adversity. Whether dealing with personal dilemmas or professional challenges, mastering this process empowers individuals to navigate uncertainties and achieve success.

Steps of Problem-Solving Process
The Problem-Solving Process is a systematic approach to identifying, analysing, and resolving issues efficiently. Each step is designed to break down complex problems into manageable tasks, leading to effective solutions.
Step 1: Identify the Problem
Initiate the Problem-Solving process by visualising the ideal scenario. Define the standard against which the current situation will be measured. Ask critical questions like, "If things were going perfectly, what would that look like?"
Further, determine the acceptable variation from the norm, considering factors like engineering precision or behavioural flexibility. Assess how much deviation is tolerable. This step sets the stage for a clear understanding of the problem's context and the criteria for an optimal outcome.
Step 2: Analyse the Problem
Understand the problem's urgency by identifying its stage: emergent, mature, or crisis. An emergent problem allows time for corrective action without immediate threats. At the same time, a mature problem causes more than minor damage, necessitating quick intervention. A crisis demands immediate correction due to severe repercussions. Thus, evaluating the potential damage guides decision-making and makes sure an appropriate level of urgency is assigned to the problem.
Step 3: Describe the Problem
Craft a concise problem statement in a clear yet short manner. This concise articulation serves as a focal point for the Problem-Solving effort. Further, statement should be distributed to the team for consensus, ensuring everyone involved agrees on the root cause.
The critical question to ask here is, "Is your premise correct?" Validating the accuracy of the premise ensures a shared comprehension of the problem.
Step 4: Look for Root Causes
This step involves a thorough investigation to uncover the underlying issues and come up with targeted solutions. Delve into the root causes of the problem by asking a series of questions: who, what, when, why, how, and where. You can use the 5Why method or Fishbone Diagram to explore the factors that led to a departure from the set standards. Also, assess the possibility of solving the problem permanently while aligning with effective leadership principles.
Step 5: Develop Alternate Solutions
This step emphasises the importance of exploring a range of possibilities before committing to a specific course of action. So, generate a list of diverse solutions beyond the initial perspective. Apply the One-third Plus One Rule for consensus-building, involving key stakeholders in the Decision-making Process. Further, rank solutions based on their efficiency, cost, and long-term value. Carefully select the most suitable solution, considering available resources and potential impacts.
Step 6: Implement the Solution
Translate the chosen solution into action by creating an implementation plan. Outline responsibilities, timelines, and contingency measures to ensure a smooth execution. Moreover, clearly communicate team roles and track the solution's progress. This step involves strategic planning and coordination to bring the selected solution to completion. Also, anticipate potential deviations from the plan and establish mechanisms for prompt resolution.
Step 7: Measure the Results
Evaluate the solution's effectiveness by measuring and tracking results. Answer critical questions about its success, learning opportunities, and applicability to future challenges. This step involves a systematic assessment of the outcomes against the desired objectives. Insights gained from this evaluation contribute to continuous improvement and the refinement of Problem-Solving skills.
The focus is on deriving meaningful conclusions and utilising them for continuous enhancement.
Increase your productivity and efficiency with our Management Courses – Register now!
Benefits of the Problem-Solving Process
Developing and implementing a Problem-Solving Process brings significant benefits. Listed below are the benefits that develop during this Process:
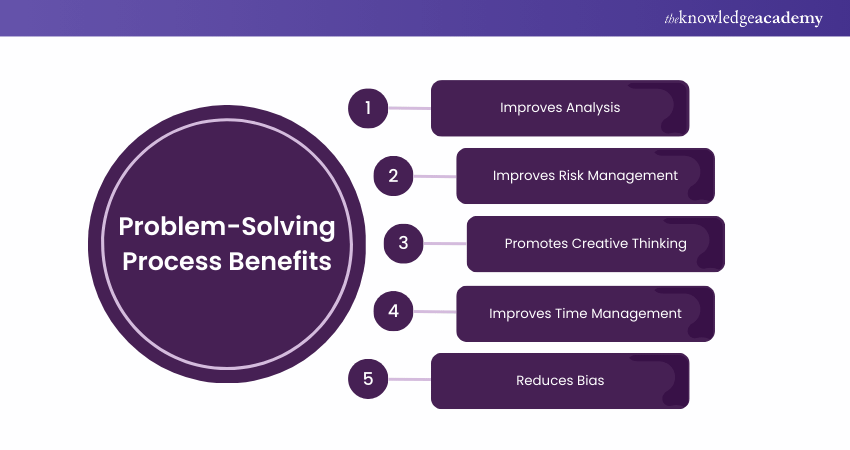

1) Improves Analysis
Individuals develop and refine their analytical skills as they engage in the Problem-Solving journey. This involves systematically examining complex situations, breaking them into manageable components, and comprehensively evaluating each element.
Through analysis, individuals gain a deeper understanding of the underlying factors contributing to the problem, leading to more precise and informed Problem Solving and Decision Making. Moreover, Problem Solving encourages individuals to gather relevant data, conduct research, and consider various perspectives. This can help enhance the accuracy and depth of their analysis.
2) Improves Risk Management
Individuals and teams naturally encounter various challenges and uncertainties as they engage in problem-Solving activities. In response, they learn to identify, assess, and mitigate potential risks associated with different solutions.
This heightened risk management awareness allows for a more comprehensive evaluation of each proposed solution's possible consequences and likelihood of success. By carefully considering and addressing risks, decision-makers can make more informed and calculated choices, minimising potential adverse outcomes.
3) Promotes Creative Thinking
The Problem Solving Process serves as a catalyst for promoting creative thinking and unlocking innovative solutions to complex challenges. Individuals and teams engage in Problem Solving activities and are encouraged to explore various ideas and perspectives.
This fosters divergent thinking, allowing the generation of unconventional and imaginative solutions that may not be initially apparent. By challenging conventional norms and encouraging the exploration of alternative approaches, Problem Solving stimulates the creative faculties of the mind.
4) Improves Time Management
The Problem-Solving Process significantly improves time management by instilling a structured approach to tackling challenges, promoting efficient decision-making, and cultivating a habit of prioritisation and productivity. Individuals and teams can better allocate time and resources as they break down complex problems into manageable steps.
Moreover, the Process encourages swift evaluation of potential solutions, ensuring timely progress. These skills become ingrained, enabling individuals and teams to meet deadlines and optimise productivity. By embracing this process, individuals can effectively manage time in various aspects of life and work.
Reduces Bias
The Problem-Solving Process offers the invaluable benefit of reducing bias in decision-making. As individuals and teams work through problem-Solving activities, they are compelled to approach challenges systematically and objectively. This structured approach encourages considering various perspectives and examining evidence and data without preconceived notions or personal biases.
Learn to strengthen your team with our Team Development Course today!
Potential Risks and How Can They be Mitigated by Problem-Solving Process?
Efficient risk management requires a systematic approach to identifying, evaluating, and minimising potential risks in any project or business endeavour. Here’s how the Problem-Solving process can be beneficial:

1) Risk Identification
The first step involves recognising potential risks that may impact the project or organisation. This includes brainstorming, analysing past data, and consulting experts to uncover hidden risks.
2) Risk Assessment
Once identified, each risk is evaluated based on its likelihood and potential impact. This stage involves prioritising risks to address the most significant threats first. Tools like risk matrices can be helpful in this process.
3) Risk Mitigation Strategies
After assessment, strategies are developed to minimise each risk. This might involve implementing safeguards, exploring alternative approaches, or transferring risk through insurance. The goal is to reduce the likelihood or impact of each risk.
4) Contingency Planning
If mitigation strategies fail, contingency plans are created. These plans outline steps to take if a risk materialises, ensuring the organisation can respond quickly and effectively.
5) Monitoring and Review
Continuous monitoring and reviewing of risks ensure that mitigation strategies remain effective and can adapt to emerging threats.
6) Communication
Effective communication throughout the risk management process ensures that all stakeholders are informed and prepared to address potential risks.
Creating Your Process your Process for Problem-Solving
Below are the Problem-Solving steps that can help you create a suitable process:
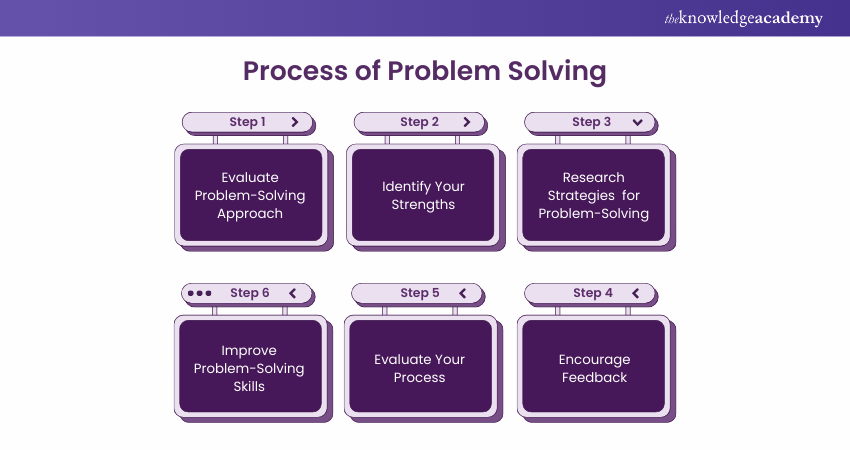
1) Evaluate Problem-Solving Approach approach
To create an effective Process for Problem Solving, it is crucial to evaluate the Problem-Solving approach. Assess the success of previous solutions, identify areas for improvement, and gather feedback from team members. Further, adjust the Process based on insights gained, fostering continuous improvement and enhancing Problem-Solving capabilities.
2) Identify Your Strengths your strengths
When creating a Problem-Solving Process, it's essential to identify your strengths. Recognise the skills and expertise within your team and your talents. Leveraging these strengths will enable you to assign tasks effectively and collaborate efficiently. It will also help capitalise on your team's unique abilities to achieve successful Problem-Solving outcomes.
3) Research Strategies for Problem-Solving
To create an effective Problem-Solving Process, researching feasible strategies is vital. Explore various Problem-Solving Techniques, methodologies, and best practices. Consider their applicability to your specific challenges and team dynamics. A well-informed approach ensures you adopt the most suitable strategies to tackle problems efficiently and achieve desired outcomes.
4) Encourage Feedback
While creating a Problem-Solving Process, it is crucial to encourage feedback. Foster an open and supportive environment for team members to freely share their thoughts and experiences. Valuable insights from diverse perspectives empower continuous improvement, refine Problem-Solving strategies, and enhance overall effectiveness in resolving challenges successfully.
5) Evaluate Your Process
When creating your Problem-Solving Process, testing and revising are essential steps. Implement the strategy in real-life scenarios to evaluate its effectiveness. Seek feedback from team members and superiors to examine strengths and areas for improvement. Make necessary adjustments to refine and optimise the process for better Problem Solving outcomes.
6) Improve Problem-Solving Skills
To create an effective Problem-Solving Process, prioritise improving Problem Solving skills. Encourage continuous learning through workshops, training, and skill-building exercises—practice solving diverse problems to gain experience and confidence. By investing in skill development, individuals and teams can enhance their Problem-Solving capabilities and achieve better outcomes in challenging situations.
Conclusion
Developing a well-defined and adaptive Problem-Solving Process is crucial for navigating the complexities of life and work successfully. By fostering creativity, promoting collaboration, and continuously refining strategies, individuals and teams can approach challenges confidently and with agility, ultimately leading to improved problem resolution and overall success.
Learn to implement Problem-Solving skills with our Problem-Solving Training – Sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Choosing the appropriate problem-solving tool depends on the nature of the issue. Mind mapping helps generate ideas by visually displaying connections between concepts. On the other hand, the Fishbone diagram systematically identifies potential causes, with branches representing different categories of causes.
The 7-Diamond Problem Solving Process is a systematic approach to tackling complex issues. It involves the following seven steps:
a) Define the Problem
b) Gather Data
c) Analyse Data
d) Develop Hypotheses
e) Verify Hypotheses
f) Identify Root Cause
g) Implement Solution
The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue , encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs , videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA .
The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass , a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
The Knowledge Academy offers various Management Courses , including the Problem-Solving Course, Productivity and Time Management and Costing and Pricing Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Problem-Solving .
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics related to Leadership, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Business skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Fri 14th Feb 2025
Fri 16th May 2025
Fri 25th Jul 2025
Fri 29th Aug 2025
Fri 10th Oct 2025
Fri 28th Nov 2025
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Biggest christmas sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- ISO 9001 Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The fifth step of the problem solving process is to implement the solution. Last but not least, one should evaluate and monitor the solution's progress. Responses may vary but should include some or all of the following information: The first step of the problem solving process is to identify and define the problem. The second step, which is to ...
In problem solving, analogies make the problem easier to understand and less complex, helping in coming to a resolution. True or false? The last step of the problem solving process is to choose the best solution.
Apr 18, 2022 · It is important to remember that there are many different problem-solving processes with different steps, and this is just one example. Problem-solving in real-world situations requires a great deal of resourcefulness, flexibility, resilience, and continuous interaction with the environment.
Aug 28, 2023 · Steps of Problem-Solving Process. The Problem-Solving Process is a systematic approach to identifying, analysing, and resolving issues efficiently. Each step is designed to break down complex problems into manageable tasks, leading to effective solutions. Step 1: Identify the Problem
Helpful problem-solving techniques include using flowcharts to identify the expected steps of a process and cause-and-effect diagrams to define and analyze root causes. Generate alternative solutions Postpone the selection of one solution until several problem-solving alternatives have been proposed.
Now I can execute the final step of problem-solving. Step 4: What’s the relationship between the two? I see the connection. I can use all of my problem-solving strategies and methods to solve my particular problem. I know the infinitive for the Spanish word “drink” is “beber”. Last night, I changed it to “bebo” to express a ...