- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- enVision Math
- EngageNY Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy


Go Math Grade 4 Chapter 4 Answer Key Pdf Divide by 1-Digit Numbers
Go Math Grade 4 Chapter 4 Answer Key Pdf: Quick and easy learning is possible with our Go Math Answer Key. We have provided the solutions for all the questions with a brief explanation. The solutions are prepared by the Math Experts. So, we suggest the students and parents to Download Go Math Grade 4 Answer Key Chapter 4 Divide by 1-Digit Numbers pdf.
Divide by 1-Digit Numbers Go Math Grade 4 Chapter 4 Answer Key Pdf
Get the step by step explanations for all the questions. This Go Math Answer Key helps a lot while doing the homework and also while preparing for the exams. All you have to do is to click on the below link and solve the questions. In addition to the exercise and homework problems, we have also provided the answers for the mid-chapter checkpoint and review test.
Chapter 4 Divide by 1-Digit Numbers – Lesson: 1
Common Core – Page No. 201
- Common Core – Lesson Check – Page No. 202
Chapter 4 Divide by 1-Digit Numbers – Lesson: 2
Page No. 205
Page no. 206.
Chapter 4 Divide by 1-Digit Numbers – Lesson: 3
Common Core – Page No. 207
- Common Core -Lesson Check – Page No. 208
Chapter 4 Divide by 1-Digit Numbers – Lesson: 4
Common Core – Page No. 211
Page no. 212.
Chapter 4 Divide by 1-Digit Numbers – Lesson: 5
- Interpret the Remainder – Common Core – Page No. 213
- Common Core – Lesson Check – Page No. 214
Chapter 4 Divide by 1-Digit Numbers – Lesson: 6
Page No. 216
Page no. 217.
Chapter 4 Divide by 1-Digit Numbers – Lesson: 7
Page No. 218
- Divide Tens, Hundreds, and Thousands – Common Core – Page No. 219
- Common Core – Lesson Check – Page No. 220
Chapter 4 Divide by 1-Digit Numbers – Lesson: 8
Page No. 222
Page no. 223, page no. 224.
Chapter 4 Divide by 1-Digit Numbers – Lesson: 9
- Estimate Quotients Using Compatible Numbers – Common Core – Page No. 224
- Common Core – Lesson Check – Page No. 226
Chapter 4 Divide by 1-Digit Numbers – Lesson: 10
- Model the division on the grid – Page No. 229
Page No. 230
Chapter 4 Divide by 1-Digit Numbers – Lesson: 11
- Division and the Distributive Property – Common Core – Page No. 231
- Common Core – Lesson Check – Page No. 232
Mid Chapter Checkpoint
- Mid Chapter Checkpoint – Page No. 233
- Mid Chapter Checkpoint – Page No. 234
Chapter 4 Divide by 1-Digit Numbers – Lesson: 12
- Use repeated subtraction to divide – Page No. 237
- Use repeated subtraction to divide – Page No. 238
Chapter 4 Divide by 1-Digit Numbers – Lesson: 13
- Divide Using Repeated Subtraction – Common Core – Page No. 239
- Common Core – Lesson Check – Page No. 240
Chapter 4 Divide by 1-Digit Numbers – Lesson: 14
Page No. 243
Page no. 244.
Chapter 4 Divide by 1-Digit Numbers – Lesson: 15
- Divide Using Partial Quotients – Common Core – Page No. 245
- Common Core – Lesson Check – Page No. 246
Chapter 4 Divide by 1-Digit Numbers – Lesson: 16
Page No. 249
Page no. 250.
Chapter 4 Divide by 1-Digit Numbers – Lesson: 17
- Model Division with Regrouping – Common Core – Page No. 251
- Common Core – Lesson Check – Page No. 252
Chapter 4 Divide by 1-Digit Numbers – Lesson: 18
Page No. 255
Page no. 256.
Chapter 4 Divide by 1-Digit Numbers – Lesson: 19
- Place the First Digit – Common Core – Page No. 257
- Common Core – Lesson Check – Page No. 258
Chapter 4 Divide by 1-Digit Numbers – Lesson: 20
Page No. 261
Page no. 262.
Chapter 4 Divide by 1-Digit Numbers – Lesson: 21
- Divide by 1-Digit Numbers – Common Core – Page No. 263
- Common Core – Lesson Check – Page No. 264
Chapter 4 Divide by 1-Digit Numbers – Lesson: 22
Page No. 267
Page no. 268.
Chapter 4 Divide by 1-Digit Numbers – Lesson: 23
- Problem Solving Multistep Division Problems – Common Core – Page No. 269
- Common Core – Lesson Check – Page No. 270
Chapter 4 – Review/Test
- Review/Test – Page No. 271
- Review/Test – Page No. 272
- Review/Test – Page No. 273
- Review/Test – Page No. 274
- Review/Test – Page No. 275
- Review/Test – Page No. 276
- Review/Test – Page No. 280
- Review/Test – Page No. 281
- Review/Test – Page No. 282
Estimate Quotients Using Multiples
Find two numbers the quotient is between. Then estimate the quotient.
Question 1. 175 ÷ 6 Think: 6 × 20 = 120 and 6 × 30 = 180. So, 175 ÷ 6 is between 20 and 30. Since 175 is closer to 180 than to 120, the quotient is about 30. between 20 and 30 about 30
Answer: About 30
Explanation: 6 × 20 = 120 and 6 × 30 = 180. 175 is between 120 and 180. 175 ÷ 6 is closest to 20 and 30. So, 175 ÷ 6 is between 20 and 30. So, 175 ÷ 6 will be about 30.
Question 2. 53 ÷ 3 between ______ and about ______
Answer: About 18
Explanation: 17 × 3= 51 and 18 × 3 = 54. 53 is between 51 and 54. 53 ÷ 3 is closest to 17 and 18. So, 53 ÷ 3 is between 17 and 18. So, 53 ÷ 3 will be about 18.
Go Math Grade 4 Lesson 4 Homework Answer Key Question 3. 75 ÷ 4 between ______ and about ______
Answer: About 19
Explanation: 18 × 4= 72 and 19 × 4= 76. 75 is between 72 and 76. 75 ÷ 4 is closest to 18 and 19. So, 75÷ 4 is between 18 and 19. So, 75 ÷ 4 will be about 19.
Question 4. 215 ÷ 9 between ______ and about ______
Answer: About 24
Explanation: 23 × 9= 207 and 24 × 9 = 216. 24 is between 207 and 216. 215 ÷ 9 is closest to 23 and 24. So, 215 ÷ 9 is between 23 and 24. So, 215 ÷ 9 will be about 24.
Question 5. 284 ÷ 5 between ______ and about ______
Answer: About 57
Explanation: 56 × 5 = 280 and 57 × 5 = 285. 284 is between 280 and 285. 284 ÷ 5 is closest to 56 and 57. So, 284 ÷ 5 is between 56 and 57. So, 175 ÷ 6 will be about 57.
Question 6. 191 ÷ 3 between ______ and about ______
Answer: About 64
Explanation: 63 × 3 = 189 and 64 × 3 = 192. 191 is between 189 and 192. 191 ÷ 3 is closest to 63 and 64. So, 191 ÷ 3 is between 63 and 64. So, 175 ÷ 6 will be about 64.
Question 7. 100 ÷ 7 between ______ and about ______
Answer: About 14
Explanation: 14 × 7 = 98 and 15 × 7 = 105. 100 is between 98 and 105. 100 ÷ 7 is closest to 14 and 15. So, 100 ÷ 7 is between 14 and 15. So, 100 ÷ 7 will be about 14.
Question 8. 438 ÷ 7 between ______ and about ______
Answer: About 63
Explanation: 63 × 7 = 441 and 62 × 7 = 434. 438 is between 434 and 441. 438 ÷ 7 is closest to 62 and 63. So, 438 ÷ 7 is between 62 and 63. So, 438 ÷ 7 will be about 63.
Question 9. 103 ÷ 8 between ______ and about ______
Answer: About 13
Explanation: 13 × 8 = 104 and 12 ×8 = 96. 103 is between 96 and 104. 103 ÷ 8 is closest to 12 and 13. So, 103 ÷ 8 is between 12 and 13. So, 103 ÷ 8 will be about 13.
Question 10. 255 ÷ 9 between ______ and about ______
Answer: About 28
Explanation: 28 × 9 = 252 and 29 × 9 = 261. 255 is between 252 and 261. 255 ÷ 9 is closest to 28 and 29. So, 255 ÷ 9 is between 28 and 29. So, 255 ÷ 9 will be about 28.
Problem Solving
Question 11. Joy collected 287 aluminum cans in 6 hours. About how many cans did she collect per hour? about ______ cans
Answer: About 48 cans
Explanation: 47 × 6 = 282 and 48 × 6 = 288. 287 is between 282 and 288. 287 ÷ 6 is closest to 47 and 48. So, 287 ÷ 6 is between 47 and 48. So, 287 ÷6 will be about 48.
Go Math Grade 4 Chapter 4 Pdf Question 12. Paul sold 162 cups of lemonade in 5 hours. About how many cups of lemonade did he sell each hour? about ______ cups
Answer: He about 32 cups of lemonade he sold in each hour
Explanation: 32 × 5 = 160 and 33 × 5 = 165. 162 is between 160 and 165. 162 ÷ 5 is closest to 32 and 33. So, 162 ÷ 5 is between 32 and 33. So, 162 ÷ 5 will be about 32.
Common Core – Page No. 202
Lesson Check
Question 1. Abby did 121 sit-ups in 8 minutes. Which is the best estimate of the number of sit-ups she did in 1 minute? Options: a. about 12 b. about 15 c. about 16 d. about 20
Answer: b. About 15
Explanation: 15 × 8 = 120 and 16 × 8 = 128. 121 is between 120 and 128. 121 ÷ 8 is closest to 120 and 128. So, 121 ÷ 8 is between 15 and 16. So, 121 ÷ 8 will be about 15.
Question 2. The Garibaldi family drove 400 miles in 7 hours. Which is the best estimate of the number of miles they drove in 1 hour? Options: a. about 40 miles b. about 57 miles c. about 60 miles d. about 70 miles
Answer: b. About 57 miles
Explanation: 57 × 7 = 399 and 58 × 7 = 406. 400 is between 399 and 406. 400 ÷ 7 is closest to 57 and 58. So, 400 ÷ 7 is between 57 and 58. So, 400 ÷ 7 will be about 57.
Spiral Review
Question 3. Twelve boys collected 16 aluminium cans each. Fifteen girls collected 14 aluminium cans each. How many more cans did the girls collect than the boys? Options: a. 8 b. 12 c. 14 d. 18
Explanation: Number of aluminium cans boys had= 12× 16=192 Number of aluminium cans girls had = 15× 14=210 Girls collected more cans compared to boys, Number of more cans collected by girls= 210-192=18
Question 4. George bought 30 packs of football cards. There were 14 cards in each pack. How many cards did George buy? Options: a. 170 b. 320 c. 420 d. 520
Answer: c. 420
Explanation: Number of packs of football cards= 30 Number of cards in each pack= 14 Total number of cards George bought=30×14=420
Question 5. Sarah made a necklace using 5 times as many blue beads as white beads. She used a total of 30 beads. How many blue beads did Sarah use? Options: a. 5 b. 6 c. 24 d. 25
Answer: d. 25
Explanation: Let the number of white beads be x while the number of blue beads are 5x. Total number of beads in the necklace=30 beads According to the problem, 5x+x=30 6x=30 x=30/6=5 Therefore the number of blue beads in the necklace are 5x= 5×5=25
Question 6. This year, Ms. Webster flew 145,000 miles on business. Last year, she flew 83,125 miles on business. How many more miles did Ms. Webster fly on business this year? Options: a. 61,125 miles b. 61,875 miles c. 61,985 miles d. 62,125 miles
Answer: b. 61,875 miles
Explanation: Number of miles Ms Webster flew in this year= 145,000 miles Number of miles Ms Webster flew in the last year=83,125 miles Number of more miles travelled by Ms Webster =145,000-83,125=61,875
Use counters to find the quotient and remainder.
Question 1. 10 ÷ 3 _____ R ______
Answer: Quotient: 3 Remainder: 1
Explanation: Quotient: A. Use 10 counters to represent the 10 dominoes. Then draw 3 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 3 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of groups of counters formed = quotient of 10 ÷ 3 D. Number of circles equally filled are 3, therefore, the quotient is 3
Remainder: The number of counters left over is the remainder. The number of counters leftover= 1
For 10 ÷ 3, the quotient is 3 and the remainder is 1, or 3 r1.
Question 2. 28 ÷ 5 _____ R ______
Answer: Quotient: 5 Remainder: 3
Explanation:
Quotient: A. Use 28 counters to represent the 28 dominoes. Then draw 5 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 5 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of groups of counters formed = quotient of 28÷ 5
Remainder: The number of counters left over is the remainder. The number of counters leftover= 3
For 28 ÷ 5, the quotient is 5 and the remainder is 3, or 5 r3.
Question 3. 15 ÷ 6 _____ R ______
Answer: Quotient:2 Remainder:3
Quotient: A. Use 15 counters to represent the 15 dominoes. Then draw 6 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 6 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of circles filled= quotient of 28 ÷ 6
For 28 ÷ 6, the quotient is 2 and the remainder is 3, or 2 r3.
Question 4. 11 ÷ 3 _____ R ______
Answer:Quotient:3 Remainder:2
Quotient: A. Use 11 counters to represent the 3 dominoes. Then draw 3 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 3 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of circles filled = quotient of 11 ÷ 3
Remainder: The number of counters left over is the remainder. The number of counters leftover= 2
For 11 ÷ 3, the quotient is 3 and the remainder is 2, or 3 r2.
Question 5. 29 ÷ 4 _____ R ______
Answer: Quotient:7 Remainder:1
Quotient: A. Use 29 counters to represent the 29 dominoes. Then draw 4 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 4 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of circles filled = quotient of 29 ÷ 4
For 29 ÷ 3, the quotient is 7 and the remainder is 1, or 7 r1.
Lesson 4 Problem Set 4.2 Answer Key Question 6. 34 ÷ 5 _____ R ______
Answer:Quotient: 6 Remainder: 4
Quotient: A. Use 34 counters to represent the 34 dominoes. Then draw 5 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 5 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of circles filled = quotient of 34 ÷ 5
Remainder: The number of counters left over is the remainder. The number of counters leftover= 4
For 34 ÷ 5, the quotient is 6 and the remainder is 4, or 6 r4.
Question 7. 25 ÷ 3 _____ R ______
Answer:Quotient: 8 Remainder: 1
Quotient: A. Use 25 counters to represent the 25 dominoes. Then draw 3 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 3 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of circles filled= quotient of 25 ÷ 3
For 25 ÷ 3, the quotient is 8 and the remainder is 1, or 8 r1.
Question 8. 7)\(\overline { 20 } \) _____ R ______
Answer: Quotient:2 Remainder:6
Quotient: A. Use 20 counters to represent the 20 dominoes. Then draw 7 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 7 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of circles filled= quotient of 7 qw20
Divide. Draw a quick picture to help.
Question 9. 4)\(\overline { 35 } \) _____ R ______

Quotient: A. Use 35 counters to represent the 35 dominoes. Then draw 4 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 4 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of circles filled= quotient of \(\overline { 35 } \)=8
Question 10. 23 ÷ 8 _____ R ______

Quotient: A. Use 23 counters to represent the 23 dominoes. Then draw 8 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 8 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of circles filled= quotient of 23 ÷ 8 = 2
Remainder: The number of counters left over is the remainder. The number of counters leftover= 7
Question 11. Explain how you use a quick picture to find the quotient and remainder. Type below: _________
Answer: Quick pictures can be used to find the quotient and the remainder visually and accurately.
Explanation: Example: 39÷ 5. Use 39 counters. Share the counters equally among 5 groups. The number of counters left over is the remainder. For 39 ÷ 5, the quotient is 7 and the remainder is 2, or 7 r2. When a number cannot be divided evenly, the amount left over is called the remainder.
Question 12. Alyson has 46 beads to make bracelets. Each bracelet has 5 beads. How many more beads does Alyson need so that all the beads she has are used? Explain. _____ more beads
Answer: 4 beads

Question 13. For 13a–13d, choose Yes or No to tell whether the division expression has a remainder. a. 36 ÷ 9 i. yes ii. no
Answer: ii. no

Question 13. b. 23 ÷ 3 i. yes ii. no
Answer: i. yes

Question 13. c. 82 ÷ 9 i. yes ii. no

Question 13. d. 28 ÷ 7 i. yes ii. no

Quotient: A. Use 13 counters to represent the 13 dominoes. Then draw 4 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 4 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of circles filled= quotient of 13 ÷ 4 = 3
Remainder: The number of counters left over is the remainder. The number of counters leftover= 1 Therefore each girl will get 3 marbles.
Question 1. 13 ÷ 4 3 r1
Answer: 3 r1
Quotient: A. Use 13 counters to represent the 13 dominoes. Then draw 4 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 4 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of counters formed in each group = quotient of 13 ÷ 4 D. Number of circles are equally filled with 4 counters, therefore, the quotient is 3
For 13 ÷ 4, the quotient is 3 and the remainder is 1, or 3 r1.
Go Math 4th Grade Lesson 4.3 Answer Key Question 2. 24 ÷ 7 _____ R ______
Answer: 3 r3
Quotient: A. Use 24 counters to represent the 24 dominoes. Then draw 7 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 7 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of counters formed in each group = quotient of 24 ÷ 7 D. Number of circles are equally filled with 3 counters, therefore, the quotient is 3
For 24 ÷ 7, the quotient is 3 and the remainder is 3, or 3 r3.
Question 3. 39 ÷ 5 _____ R ______
Answer: 7 r4
Quotient: A. Use 39 counters to represent the 39dominoes. Then draw 5 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 5 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of counters formed in each group = quotient 39 ÷ 5 D. Number of circles are equally filled with 7 counters, therefore, the quotient is 7
For 39 ÷ 5, the quotient is 7 and the remainder is 4, or 7 r4.
Question 4. 36 ÷ 8 _____ R ______
Answer: 4 r4
Quotient: A. Use 36 counters to represent the 36 dominoes. Then draw 8 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 8 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of counters formed in each group = quotient of 36 ÷ 8 D. Number of circles are equally filled with 4 counters, therefore, the quotient is 4
For 36 ÷ 8, the quotient is 4 and the remainder is 4, or 4 r4.
Question 5. 6)\(\overline { 27 } \) _____ R ______
Answer: 4 r3
Quotient: A. Use 27 counters to represent the 27 dominoes. Then draw 6 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 6 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of counters formed in each group = quotient of 27 ÷6 D. Number of circles are equally filled with 4 counters, therefore, the quotient is 4
For 27 ÷ 6, the quotient is 4 and the remainder is 3, or 4 r3.
Question 6. 25 ÷ 9 _____ R ______
Answer: 2 r7
Quotient: A. Use 25 counters to represent the 25 dominoes. Then draw 9 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 9 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of counters formed in each group = quotient of 25 ÷ 9 D. Number of circles are equally filled with 2 counters, therefore, the quotient is 2
For 25 ÷ 7, the quotient is 2 and the remainder is 7, or 2 r7.
Question 7. 3)\(\overline { 17 } \) _____ R ______
Answer: 5 r2
Quotient: A. Use 17 counters to represent the 17 dominoes. Then draw 3 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 3 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of counters formed in each group = quotient of 17 ÷ 3 D. Number of circles are equally filled with 5 counters, therefore, the quotient is 5
For 17 ÷ 3, the quotient is 5 and the remainder is 2, or 5 r2.
Question 8. 26 ÷ 4 _____ R ______
Answer: 6 r2
Quotient: A. Use 26 counters to represent the 26 dominoes. Then draw 4 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 4 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of counters formed in each group = quotient of 26 ÷ 4 D. Number of circles are equally filled with 6 counters, therefore, the quotient is 6
For 26 ÷ 4, the quotient is 6 and the remainder is 2, or 6 r2.
Question 9. 14 ÷ 3 _____ R ______

Quotient: A. Use 14 counters to represent the 14 dominoes. Then draw 3 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 3 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of circles filled= quotient of 14 ÷ 3 = 4
Question 10. 5)\(\overline { 29 } \) _____ R ______

Quotient: A. Use 29 counters to represent the 29 dominoes. Then draw 5 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 5 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of circles filled= quotient of 29 ÷ 5 = 5

Answer: quotient:6 remainder2
Quotient: A. Use 20 counters to represent the 20 dominoes. Then draw 3 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 3 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of counters formed in each group = quotient of 20 ÷ 3 D. Number of circles are equally filled with 6 counters, therefore, the quotient is 6
For 20 ÷ 3, the quotient is 6 and the remainder is 2, or 6 r2.

Answer: 4 r5
Quotient: A. Use 21 counters to represent the 21 dominoes. Then draw 4 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 4 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of counters formed in each group = quotient of 21 ÷ 4 D. Number of circles are equally filled with 4 counters, therefore, the quotient is 4
Remainder: The number of counters left over is the remainder. The number of counters leftover= 5
For 21 ÷ 4, the quotient is 4 and the remainder is 5, or 4 r5.
Common Core – Page No. 208
Question 1. What is the quotient and remainder for 32 ÷ 6? Options: a. 4 r3 b. 5 r1 c. 5 r2 d. 6 r1
Answer: c. 5 r2
Quotient: A. Use 32 counters to represent the 32 dominoes. Then draw 6 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 5 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of counters formed in each group = quotient of 32 ÷ 6 D. Number of circles are equally filled with 5 counters, therefore, the quotient is 5
For 32 ÷ 6, the quotient is 5 and the remainder is 2, or 5 r2.

Answer: c. 3
Explanation: When a number cannot be divided evenly, the amount left over is called the remainder. The number of counters that are left = remainder = 3
Question 3. Each kit to build a castle contains 235 parts. How many parts are in 4 of the kits? Options: a. 1,020 b. 940 c. 920 d. 840
Answer: b. 940

Question 4. In 2010, the population of Alaska was about 710,200. What is this number written in word form? Options: a. seven hundred ten thousand, two b. seven hundred twelve thousand c. seventy-one thousand, two d. seven hundred ten thousand, two hundred
Answer: d. seven hundred ten thousand, two hundred
Explanation: The ones and tens place of the number are zeroes, so the next place which is hundreds is considered and the value is 7 so, it can be written as seven hundred and in the thousands period it can be written as seven hundred ten thousand.
Question 5. At the theater, one section of seats has 8 rows with 12 seats in each row. In the center of the first 3 rows are 4 broken seats that cannot be used. How many seats can be used in the section? Options: a. 84 b. 88 c. 92 d. 96
Answer: c. 92
Explanation: Number of rows at the theatre = 8 Number of seats each row= 12 Number of seats broken and that cannot be used to sit= 4 Total number of seats that can be used = 12 x 8-4=96-4=92

Answer: d. 300, 180, 40, 24

Question 1. Olivia baked 53 mini-loaves of banana bread to be sliced for snacks at a craft fair. She will place an equal number of loaves in 6 different locations. How many loaves will be at each location? a. Divide to find the quotient and remainder. □ r □ 6)\(\overline { 53 } \) _____ R ______
Answer: Quotient: 8 Remainder: 5
Quotient: A. Use 53 counters to represent the 53 dominoes. Then draw 6 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 6 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of counters formed in each group = quotient of 53 ÷ 6 D. Number of circles are equally filled with 8 counters, therefore, the quotient is 8

Question 1. b. Decide how to use the quotient and remainder to answer the question. Type below: ____________
Remainder: The number of counters left over is the remainder. The number of counters leftover= 5 Therefore, there will be 8 mini loaves at each location.
Interpret the remainder to solve.
Question 2. What if Olivia wants to put only whole loaves at each location? How many loaves will be at each location? _______ whole loaves
Answer: Since there are 8 mini loaves at each location. Then there will be 4 whole loaves.
Explanation: Olivia baked 53 mini-loaves of banana bread
Go Math Grade 4 Lesson 4.4 Answer Key Question 3. Ed carved 22 small wooden animals to sell at the craft fair. He displays them in rows with 4 animals in a row. How many animals will not be in equal rows? _______ animals
Explanation: Total number of small wooden animals=22 Number of animals in each row=4 Number of rows= 22÷4 =5 The total number of animals in the rows= 5 x 4=20 Number of animals which are not in a row= 22-20=2
Question 4. Myra has a 17-foot roll of crepe paper to make 8 streamers to decorate for a party. How long will each streamer be if she cuts the roll into equal pieces? Type below: ____________
Answer: 2 foot

Question 5. Juan has a piano recital next month. Last week he practiced for 8 hours in the morning and 7 hours in the afternoon. Each practice session is 2 hours long. How many full practice sessions did Juan complete? _______ full practice sessions
Answer: 7 full practice sessions
Explanation: Number of hours he practiced in the morning= 8 hours Each practice session is 2 hours long Number of full practice sessions attended by Juan in the morning= 8÷2=4 Number of hours he practiced in the afternoon= 7 hours Number of full practice sessions attended by Juan in the evening= 7÷2=3
Question 6. A total of 25 students sign up to be hosts on Parent’s Night. Teams of 3 students greet parents. How many students cannot be on a team? Explain. _______ student
Answer: 1 student
Explanation: Total number of students = 25 Number of students in each group = 3 The number of students who cannot be in the group= remainder obtained when 25÷3= 1

Question 7. Teresa is making sock puppets just like the one in the picture. If she has 53 buttons, how many puppets can she make? _______ sock puppets
Answer: 17 sock puppets
Explanation: Total number of buttons Teresa has=53 Number of buttons each puppet needs= 3 Number of sock puppets made= Quotient of 53÷3=17 sock puppets
Question 8. Write a question about Teresa and the sock puppets for which the answer is 3. Explain the answer. Type below: ____________
Answer: How many buttons did Teresa use for one sock puppet?
Explanation: Total number of sock puppets made= 17 Number of buttons used for making 17 sock puppets = 52 then, Number of buttons used for one sock puppet= Quotient of 52÷17= 3 buttons
Question 9. Interpret a Result How many more buttons will Teresa need if she wants to make 18 puppets? Explain. _______ buttons
Answer: 1 button
Explanation: After preparing 17 puppets there was 2 buttons leftover then on the addition of 1 button gives 3 buttons which can be used to prepare another puppet.
Question 10. A total of 56 students signed up to play in a flag football league. If each team has 10 students, how many more students will need to sign up so all of the students can be on a team? _______ students
Answer: 4 students
Explanation: Total number of students in the football league= 56 Number of students in each group= 10 then, Number of groups= Quotient of 56÷10=5 groups Remainder= 6 By the addition of 4 students, the group of 6 gets completed by 10 Therefore, 4 students should be added so that all students can be on a team.
Question 11. A teacher plans for groups of her students to eat lunch at tables. She has 34 students in her class. Each group will have 7 students. How many tables will she need? Explain how to use the quotient and remainder to answer the question. _______ tables
Answer: She needs 3 tables

Quotient: A. Use 34 counters to represent the 34 dominoes. Then draw 7 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 7 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of counters formed in each group = quotient of 34 ÷ 7 D. Number of circles are equally filled with 4 counters, therefore, the quotient is 4
Remainder: The number of counters left over is the remainder. The number of counters leftover= 6 The quotient is used to indicate the number of groups Therefore, there will be 4 tables. While the remainder is used to determine the number of students in the incomplete group.
Common Core – Page No. 213
Interpret the Remainder
Question 1. Hakeem has 100 tomato plants. He wants to plant them in rows of 8. How many full rows will he have? Think: 100 ÷ 8 is 12 with a remainder of 4. The question asks “how many full rows,” so use only the quotient. 12 full rows
Answer: 12 full rows
Explanation: Quotient: A. Use 100 counters to represent the 100 dominoes. Then draw 8 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 8 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of counters formed in each group = quotient of 100 ÷ 8 D. Number of circles are equally filled with 12 counters, therefore, the quotient is 12 Therefore, the tomatoes placed in full rows are 12
Go Math Grade 4 Chapter 4 Review Answer Key Question 2. A teacher has 27 students in her class. She asks the students to form as many groups of 4 as possible. How many students will not be in a group? _______ students
Answer: 3 students will not be the group
Explanation: Total number of students in the class= 27 Number of students who make a group=4 Number of groups that can be made =Quotient of 27÷ 4=6 Number of students who do not come under a group= Remainder of 27÷ 4=3
Question 3. A sporting goods company can ship 6 footballs in each carton. How many cartons are needed to ship 75 footballs? _______ cartons
Answer: 12 full cartons and 0.5 or 1/2 carton to ship all the 75 footballs
Explanation: Total number of footballs that should be shipped= 75 Number of footballs placed in each carton = 6 Number of cartons required=Quotient of 75÷ 6=12

Question 4. A carpenter has a board that is 10 feet long. He wants to make 6 table legs that are all the same length. What is the longest each leg can be? _______ foot
Answer: The length of the longest leg=4 foot-long
Explanation: According to the question, Length of the board the carpenter has= 10 foot long Number of table legs that are to be made = 6 Length of the 6 table legs are equal then, Length of each table leg= Quotient of 10÷6=1 foot Length of the longest table leg= Remainder of 10÷6= 4 foot.
Question 5. Allie wants to arrange her flower garden in 8 equal rows. She buys 60 plants. What is the greatest number of plants she can put in each row? _______ plants
Explanation: Total number of plants Allie bought= 60 Number of rows= 8 Number of plants in each row= Quotient of 60÷8=7
Question 6. Joanna has 70 beads. She uses 8 beads for each bracelet. She makes as many bracelets as possible. How many beads will Joanna have left over? _______ beads
Answer: 6 beads
Explanation: Total number of beads Joanna has= 70 beads Number beads used for each bracelet= 8 beads Number of bracelets made with these beads= Quotient of 70÷8= 7 bracelets then, The number of beads leftover= Remainder of 70÷8= 6 beads
Question 7. A teacher wants to give 3 markers to each of her 25 students. Markers come in packages of 8. How many packages of markers will the teacher need? _______ packages
Answer: 10 packages
Explanation: Total number of students= 25 Number of markers each student got= 3 Total number of markers the teacher needs to distribute= 25 x 3= 75 Number of markers in each package= 8 Number of packages the teacher required= Quotient of 75÷8=9 While the remainder= 3 Therefore the total number packages=10
Common Core – Page No. 214
Question 1. Marcus sorts his 85 baseball cards into stacks of 9 cards each. How many stacks of 9 cards can Marcus make? Options: a. 4 b. 8 c. 9 d. 10
Answer: d. 10
Explanation: Total number of baseball cards=85 Number of cards in each stack=9 Number of stacks sorted= Quotient of 85÷9=9 While the remainder=4 So the total number of stacks required= 10
Question 2. A minivan can hold up to 7 people. How many minivans are needed to take 45 people to a basketball game? Options: a. 3 b. 5 c. 6 d. 7
Answer: d. 7
Explanation: A minivan can hold up to 7 people. Total number of people who want to hire the minivan= 45 people Number of minivans required= Quotient of 45÷7= 6 vans While the remainder is 3. Total number of minivans required to take the people to the baseball game= 7 minivans
Question 3. Mrs. Wilkerson cut some oranges into 20 equal pieces to be shared by 6 friends. How many pieces did each person get and how many pieces were left over? Options: a. 2 pieces with 4 pieces leftover b. 3 pieces with 2 pieces leftover c. 3 pieces with 4 pieces leftover d. 4 pieces with 2 pieces leftover
Answer: b. 3 pieces with 2 pieces leftover
Explanation: Total number of orange pieces= 20 Number of friends= 6 Number of pieces each friend got= Quotient of 20÷6= 3 pieces Number of pieces leftover= Remainder of 20÷6= 2 pieces
Question 4. A school bought 32 new desks. Each desk cost $24. Which is the best estimate of how much the school spent on the new desks? Options: a. $500 b. $750 c. $1,000 d. $1,200
Answer: b. $750

Question 5. Kris has a box of 8 crayons. Sylvia’s box has 6 times as many crayons as Kris’s box. How many crayons are in Sylvia’s box? Options: a. 48 b. 42 c. 36 d. 4
Answer: 48 crayons
Explanation: Number of crayons in Kris box=8 Number of crayons in Sylvia’s box= 6 times as many crayons as Kris’s box= 6 x 8=48
Question 6. Yesterday, 1,743 people visited the fair. Today, there are 576 more people at the fair than yesterday. How many people are at the fair today? Options: a. 1,167 b. 2,219 c. 2,319 d. 2,367
Answer: c. 2,319

Question 1. Divide. 2,800 ÷ 7 What basic fact can you use? ___________ 2,800 = 28 ___________ 28 hundreds ÷ 7 = ___________ 2,800 ÷ 7 = ___________ Type below: ___________
Answer: 400
Explanation: STEP 1 Identify the basic fact. 28 ÷ 7 STEP 2 Use place value. 2,800 = 28 hundreds STEP 3 Divide. 28 hundreds ÷ 4 = 4 hundreds 2,800 ÷ 7 = 400
Go Math Grade 4 Chapter 4 Lesson 6 Homework Answer Key Question 2. Divide. 280 ÷ 7 What basic fact can you use? ___________ 280 = 28 ___________ 28 tens ÷ _____ = 4 ___________ 280 ÷ 7 = _____ Type below: ___________
Explanation: STEP 1 Identify the basic fact. 28 ÷ 7 STEP 2 Use place value. 280 = 28 tens STEP 3 Divide. 28 tens ÷ 4 = 4 tens 280 ÷ 7 = 40
Use basic facts and place value to find the quotient.
Lesson 4.6 Answer Key 4th Grade Question 3. 360 ÷ 6 = ______
Explanation: STEP 1 Identify the basic fact. 36 ÷ 6 STEP 2 Use place value. 360 = 36 tens STEP 3 Divide. 36 tens ÷6 = 6 tens 360 ÷ 6 = 60
Question 4. 2,000 ÷ 5 = ______
Explanation: STEP 1 Identify the basic fact. 20 ÷ 5 STEP 2 Use place value. 2,000 = 20 hundreds STEP 3 Divide. 20 hundreds ÷ 5 = 4 hundreds 2,000 ÷ 5 = 400
Question 5. 4,500 ÷ 9 = ______
Answer: 500
Explanation: STEP 1 Identify the basic fact. 45 ÷ 9 STEP 2 Use place value. 4,500 = 45 hundreds STEP 3 Divide. 45 hundreds ÷ 9 = 5 hundreds 4,500 ÷ 9 = 500
Question 6. 560 ÷ 8 = ______
Explanation: STEP 1 Identify the basic fact. 56 ÷ 8 STEP 2 Use place value. 560 = 56 tens STEP 3 Divide. 56 tens ÷ 8 = 7 tens 560 ÷ 8 = 70
Question 7. 6,400 ÷ 8 = ______
Answer: 800
Explanation: STEP 1 Identify the basic fact. 64 ÷ 8 STEP 2 Use place value. 6,400 =64 hundreds STEP 3 Divide. 64 hundreds ÷ 8 = 8 hundreds 6,400 ÷ 8 = 800
Question 8. 3,500 ÷ 7 = ______
Explanation: STEP 1 Identify the basic fact. 35 ÷ 7 STEP 2 Use place value. 3,500 = 35 hundreds STEP 3 Divide. 35 hundreds ÷ 7 = 5 hundreds 3,500 ÷ 7 = 500
Use Patterns Algebra Find the unknown number.
Question 9. 420 ÷ ______ = 60

Lesson 4.6 Division and the Distributive Property Question 10. ______ ÷ 4 = 30
Answer: 120
Explanation: To find the dividend (the missing number) we must multiply the divisor and the quotient. Therefore the dividend is 30 x 4=120.
Question 11. 810 ÷ ______ = 90

Question 12. Divide 400 ÷ 40. Explain how patterns and place value can help. ______
Explanation: STEP 1 Identify the basic fact. 40 ÷ 4 STEP 2 Use place value. 400 = 40 tens STEP 3 Divide. 40 tens ÷ 4 = 1 tens 400 ÷ 40 = 10
Question 13. Eileen collected 98 empty cans to recycle, and Carl collected 82 cans. They packed an equal number of cans into each of three boxes to take to the recycling center. How many cans were in each box? ______ cans
Answer: 60 cans
Explanation: Total number of cans = 98+82=180 cans Number of boxes= 3 Number of cans in each box= 180 ÷3=60 cans
Question 14. It costs a baker $18 to make a small cake. He sells 8 small cakes for $240. How much more is the selling price of each cake than the cost? $ ______
Answer: $96
Explanation: Cost of each cake= $18 Number of cakes baked= 8 The actual cost of the cakes = $18 x $8=$144 The selling price of the cakes=$240 Amount gained on the cakes= $240-$144=$96

Answer: 100 pennies
Explanation: Total number of pennies= 600 Number of rolls= 6 The number of pennies= Quotient of 600 ÷ 6=100
Question 16. Sela has 6 times as many coins now as she had 4 months ago. If Sela has 240 coins now, how many coins did she have 4 months ago? ______ coins
Answer: 60 coins
Explanation: Let the number of coins four months ago be x coins. According to the question, Number of coins Sela has at present = 4x 4x=240 x= 240 ÷ 4=60 Therefore the number of coins Sela has=60
Question 17. Chip collected 2,090 dimes. Sue collected 1,910 dimes. They divided all their dimes into 8 equal stacks. How many dimes are in each stack? ______ dimes
Explanation: Number of dimes Chip collected= 2,090 Number of dimes Sue collected= 1,910 Total number of dimes= 2,090+1,910= 4100 Number of stacks= 8 Number of dimes in each stack = Quotient of 4100 ÷8=512
Question 18. Communicate Mr. Roberts sees a rare 1937 penny. The cost of the penny is $210. If he saves $3 each week, will Mr. Roberts have enough money to buy the penny in one year? Explain. ______
Answer: No Mr. Roberts cannot buy the penny in one year.
Explanation: Amount saved in each week= $3 Number of weeks in a year= 52 The total amount saved= 52 x 3=$156 Cost of the penny=$210 Therefore Mr. Roberts cannot buy the penny in one year.
Question 19. Mrs. Fletcher bought 5 coins for $32 each. Later, she sold all the coins for $300. How much more did Mrs. Fletcher receive for each coin than she paid? Explain. $ ______
Explanation: Number of coins=5 Cost of each coin = $32 Total cost of the coins= $32 x 5=$160 She sold the coins for $300 Cost of each coin= $300 ÷ 5= $60
Question 20. Which quotients are equal to 20? Mark all that apply. Options: a. 600 ÷ 2 b. 1,200 ÷ 6 c. 180 ÷ 9 d. 140 ÷ 7 e. 500 ÷ 5
Answer: c. 180 ÷ 9 d. 140 ÷ 7
Explanation: Quotient: A. Use 180 counters to represent the 180 dominoes. Then draw 9 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 9 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of counters formed in each group = quotient of 180 ÷ 9 D. Number of circles are equally filled with 20 counters, therefore, the quotient is 20
Quotient: A. Use 140 counters to represent the 140 dominoes. Then draw 7 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 7 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of counters formed in each group = quotient of 140 ÷ 7 D. Number of circles are equally filled with 20 counters, therefore, the quotient is 20
Insect Flight

Question 21. About how many times does a damselfly’s wings beat in 1 minute? ______ times
Answer: 900
Explanation: Total number of wingbeats of Damselfly in 3 minutes= 2,700 Number of wingbeats of Damselfly in 1 minute= 2,700 ÷3=900
Question 22. About how many times do a scorpion fly’s wings beat in 6 minutes? ______ times
Answer: 10,000
Explanation: Total number of wingbeats of scorpionfly in 3 minutes=5,000 Number of parts of time-intervals in 6 minutes = 6÷3=2 Number of wingbeats of scorpionfly in 6 minutes= 5,000 x 2 = 10,000
Question 23. In one minute, about how many more times do a damselfly’s wings beat than a large white butterfly’s wings? ______ more times
Answer: 200
Total number of wingbeats of large white butterfly in 3 minutes= 2,100 Number of wingbeats of large white butterfly in 1 minute= 2,100 ÷3=700
Number of more times the damselfly’s wings beat than a large white butterfly=900-700=200
Lesson 4.7 Divide Using Repeated Subtraction Question 24. What’s the Question? The answer is about 2,300 times. Type below: ___________
Answer: About how many times do an Aeschind dragonfly’s wings beat in 1 minute?
Explanation: Total number of wingbeats of Aeschind dragonfly’s in 3 minutes= 6,900 Number of wingbeats of Aeschind dragonfly’s in 1 minute= 6,900 ÷3=2,300
Common Core – Page No. 219
Divide Tens, Hundreds, and Thousands
Question 1. 3,600 ÷ 4 = 900 Think: 3,600 is 36 hundreds. Use the basic fact 36 ÷ 4 = 9. So, 36 hundreds ÷ 4 = 9 hundreds, or 900.
Explanation: STEP 1 Identify the basic fact. 36 ÷ 4 STEP 2 Use place value. 3,600 = 36 hundreds STEP 3 Divide. 36 hundered ÷ 4 = 9 hundreds 3,600 ÷ 4 = 900
Question 2. 240 ÷ 6 = ______
Explanation: STEP 1 Identify the basic fact. 24 ÷ 6 STEP 2 Use place value. 240 = 24 tens STEP 3 Divide. 24 tens ÷ 6 = 4 tens 240 ÷ 6 = 40
Go Math Chapter 4 Grade 4 Lesson 4.7 Answer Key Question 3. 5,400 ÷ 9 = ______
Answer: 600
Explanation: STEP 1 Identify the basic fact. 54 ÷ 9 STEP 2 Use place value. 5,400 = 54 hundreds STEP 3 Divide. 54 hundreds ÷ 9 = 6 hundreds 5,400 ÷ 9 = 600
Question 4. 300 ÷ 5 = ______
Explanation: STEP 1 Identify the basic fact. 30 ÷ 5 STEP 2 Use place value. 300 = 30 tens STEP 3 Divide. 30 tens ÷ 5 = 60 tens 300 ÷ 5 = 60
Question 5. 4,800 ÷ 6 = ______
Explanation: STEP 1 Identify the basic fact. 48 ÷ 6 STEP 2 Use place value. 4,800 = 48 hundreds STEP 3 Divide. 48 hundreds ÷ 6 = 80 hundreds 4,800 ÷ 6 = 800
Question 6. 420 ÷ 7 = ______
Explanation: STEP 1 Identify the basic fact. 42 ÷ 7 STEP 2 Use place value. 420 = 42 tens STEP 3 Divide. 42 tens ÷ 7 = 60 tens 420 ÷ 7 = 60
Question 7. 150 ÷ 3 = ______
Explanation: STEP 1 Identify the basic fact. 15 ÷ 3 STEP 2 Use place value. 150 = 15 tens STEP 3 Divide. 15 tens ÷ 3 = 5 tens 150 ÷ 3 = 50
Question 8. 6,300 ÷ 7 = ______
Explanation: STEP 1 Identify the basic fact. 63 ÷ 7 STEP 2 Use place value. 6,300 = 63 hundreds STEP 3 Divide. 63 hundreds ÷ 7 = 9 hundreds 6,300 ÷ 7 = 900
Question 9. 1,200 ÷ 4 = ______
Answer: 300
Explanation: STEP 1 Identify the basic fact. 12 ÷ 4 STEP 2 Use place value. 1,200 = 12 hundreds STEP 3 Divide. 12 hundreds ÷ 4 = 3 hundreds 1,200 ÷ 4 = 300
Question 10. 360 ÷ 6 = ______
Explanation: STEP 1 Identify the basic fact. 36 ÷ 6 STEP 2 Use place value. 360 = 36 tens STEP 3 Divide. 36 tens ÷ 6 = 6 tens 360 ÷ 6 = 60
Find the quotient.
Question 11. 28 ÷ 4 = ______ 280 ÷ 4 = ______ 2,800 ÷ 4 = ______
Answer: 7, 70, 700
Explanation: Quotient: A. Use 28 counters to represent the 28 dominoes. Then draw 4 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 4 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of counters formed in each group = quotient of 28 ÷ 4 D. Number of circles are equally filled with 7 counters, therefore, the quotient is 7
STEP 1 Identify the basic fact. 28 ÷ 4 STEP 2 Use place value. 280 = 28 tens STEP 3 Divide. 28 tens ÷ 4 = 7 tens 280 ÷ 4 = 70
STEP 1 Identify the basic fact. 28 ÷ 4 STEP 2 Use place value. 2,800 = 28 hundreds STEP 3 Divide. 28 hundreds ÷ 4 = 7 hundreds 2,800 ÷ 4 = 700
Go Math Grade 4 Lesson 4.7 Answer Key Question 12. 18 ÷ 3 = ______ 180 ÷ 3 = ______ 1,800 ÷ 3 = ______
Answer: 6, 60, 600
Explanation: Quotient: A. Use 18 counters to represent the 18 dominoes. Then draw 3 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 3 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of counters formed in each group = quotient of 18 ÷ 3 D. Number of circles are equally filled with 6 counters, therefore, the quotient is 6
STEP 1 Identify the basic fact. 18 ÷ 3 STEP 2 Use place value. 180 = 18 tens STEP 3 Divide. 18 tens ÷ 3 = 6 tens 180 ÷ 6 = 60
STEP 1 Identify the basic fact. 18 ÷ 3 STEP 2 Use place value. 1,800 = 18 hundreds STEP 3 Divide. 18 hundreds ÷ 3 = 6 hundreds 1,800 ÷ 3 = 600
Question 13. 45 ÷ 9 = ______ 450 ÷ 9 = ______ 4,500 ÷ 9 = ______
Answer: 5, 50, 500
Explanation: Quotient: A. Use 45 counters to represent the 45 dominoes. Then draw 9 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 9 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of counters formed in each group = quotient of 45 ÷ 9 D. Number of circles are equally filled with 5 counters, therefore, the quotient is 5
STEP 1 Identify the basic fact. 45 ÷ 9 STEP 2 Use place value. 450 = 45 tens STEP 3 Divide. 45 tens ÷ 9 = 5 tens 450 ÷ 9 = 50
STEP 1 Identify the basic fact. 45 ÷ 9 STEP 2 Use place value. 4,500 = 45 hundreds STEP 3 Divide. 45 hundreds ÷ 9 = 5 hundreds 4,500 ÷ 9 = 500
Question 14. At an assembly, 180 students sit in 9 equal rows. How many students sit in each row? ______ students
Explanation: Total number of students= 180 Number of rows= 9 Number of students in each row= 180 ÷9=20
Question 15. Hilary can read 560 words in 7 minutes. How many words can Hilary read in 1 minute? ______ words
Explanation: Total number of words Hilary can read in 7 minutes = 560 Number of words Hilary can read in 1 minute= 560 ÷ 7= 80
Question 16. A company produces 7,200 gallons of bottled water each day. The company puts 8 one-gallon bottles in each carton. How many cartons are needed to hold all the one-gallon bottles produced in one day? ______ cartons
Explanation: Total number of gallons bottled in each day= 7,200 Number of gallons bottled in each carton= 8 Number of cartons used= 7,200 ÷ 8= 900
Question 17. An airplane flew 2,400 miles in 4 hours. If the plane flew the same number of miles each hour, how many miles did it fly in 1 hour? ______ miles
Explanation: Total number of miles flew in 4 hours= 2,400 Number of miles flew in 1 hour= 2,400÷4=600
Common Core – Page No. 220
Question 1. A baseball player hits a ball 360 feet to the outfield. It takes the ball 4 seconds to travel this distance. How many feet does the ball travel in 1 second? Options: a. 9 feet b. 40 feet c. 90 feet d. 900 feet
Answer: c. 90 feet
Explanation: The height to which the player hits a ball=360 feet Height to which the ball travels in 1 second= 360÷4= 90 feet
Question 2. Sebastian rides his bike 2,000 meters in 5 minutes. How many meters does he bike in 1 minute? Options: a. 4 meters b. 40 meters c. 50 meters d. 400 meters
Answer: d. 400 meters
Explanation: Total number of meters travelled in 5 minutes= 2,000 Number of meters travelled in 1 minute= 2,000÷5= 400
Question 3. A full container of juice holds 63 ounces. How many 7-ounce servings of juice are in a full container? Options: a. 1 b. 8 c. 9 d. 10
Answer: c. 9
Explanation: A full container of juice holds= 63 ounces Quantity of servings of juice in one glass=7 ounce The number of servings of the juice are = 63÷7=9
Go Math Lesson 4.7 4th Grade Answer Key Question 4. Paolo pays $244 for 5 identical calculators. Which is the best estimate of how much Paolo pays for one calculator? Options: a. $40 b. $50 c. $60 d. $245
Answer: b. $50
Explanation: Amount Paolo pays for the identical calculators = $244 Number of identical calculators=5 The best estimated value of each identical calculator=$244 ÷ 5is approximately $50
Question 5. A football team paid $28 per jersey. They bought 16 jerseys. How much money did the team spend on jerseys? Options: a. $44 b. $196 c. $408 d. $448
Answer: d. $448
Explanation: Cost of each jersey=$28 Number of jerseys= 16 Total cost of the jerseys= $28 x 16= $448
Question 6. Suzanne bought 50 apples at the apple orchard. She bought 4 times as many red apples as green apples. How many more red apples than green apples did Suzanne buy? Options: a. 10 b. 25 c. 30 d. 40
Answer: d. 40
Explanation: Let the number of green apples be x and the number of red apples be 4x 4x + x = 50 x = 50 ÷ 5= 10 Number of red balls = 4x = 4 x 10 = 40
Question 1. Estimate. 1,718 ÷ 4 Think: What number close to 1,718 is easy to divide by 4? ______ is close to 1,718. What basic fact can you use? ______ ÷ 4 ______ is close to 1,718. What basic fact can you use? ______ ÷ 4 Choose 1,600 because __________________________________. 16 ÷ 4 = ______ 1,600 ÷ ______ = ______ 1,718 ÷ 4 is about ______ Type below: _________
Explanation: What number close to 1,718 is easy to divide by 4? 1,600 is close to 1,718. What basic fact can you use? 1,600 ÷ 4 Choose 1,600 because it is close to 1,718 and can easily be divided by 4. 16 ÷ 4 = 4 1,600 ÷ 4 = 400 1,600 ÷ 4 is about 400
Use compatible numbers to estimate the quotient.
Question 2. 455 ÷ 9 ______
Explanation: What number close to 455 is easy to divide by 9? 450 is close to 455. What basic fact can you use? 450 ÷ 9 Choose 450 because it is close to 455 and can easily be divided by 9. 45 ÷ 9 = 5 450 ÷ 9 = 50 455 ÷ 9 is about 50
Question 3. 1,509 ÷ 3 ______
Explanation: What number close to 1,509 is easy to divide by 3? 1,500 is close to 1,509. What basic fact can you use? 1,500 ÷ 3 Choose 1,500 because it is close to 1,509 and can easily be divided by 3. 15 ÷ 3 = 5 1,500 ÷ 3 = 500 1,509 ÷ 3 is about 500
Question 4. 176 ÷ 8 ______
Explanation: What number close to 176 is easy to divide by 8? 160 is close to 176. What basic fact can you use? 160 ÷ 8 Choose 160 because it is close to 176 and can easily be divided by 8. 16 ÷ 8 = 2 160 ÷ 8 = 20 176 ÷ 8 is about 20
Go Math Grade 4 Chapter 4 Answer Key Lesson 4.8 Question 5. 2,795 ÷ 7 ______
Answer: 400
Explanation: What number close to 2,795 is easy to divide by 7? 2,800 is close to 2,795. What basic fact can you use? 2,800 ÷ 7 Choose 2,800 because it is close to 2,795 and can easily be divided by 7. 28 ÷ 7 = 4 2,800 ÷ 7 = 400 2,795 ÷ 7 is about 400
Use compatible numbers to find two estimates that the quotient is between.
Question 6. 5,321 ÷ 6 ______ and ______
Explanation: What number close to 5,321 is easy to divide by 6? 5,400 is close to 5,321. What basic fact can you use? 5,400 ÷ 6 Choose 5,400 because it is close to 5,321 and can easily be divided by 6. 54 ÷ 6 = 9 5,400 ÷ 6 = 900 5,321 ÷ 6 is about 900
Question 7. 1,765 ÷ 6 ______ and ______
Explanation: What number close to 1,765 is easy to divide by 6? 1,800 is close to 1,765. What basic fact can you use? 1,800 ÷ 6 Choose 1,800 because it is close to 1,765 and can easily be divided by 6. 18 ÷ 6 = 3 1,800 ÷ 6 = 300 1,765 ÷ 6 is about 300
Question 8. 1,189 ÷ 3 ______ and ______
Explanation: What number close to 1,189 is easy to divide by 3? 1,200 is close to 1,189. What basic fact can you use? 1,200 ÷ 3 Choose 1,200 because it is close to 1,189 and can easily be divided by 3. 12 ÷ 3 = 4 1,200 ÷ 3 = 400 1,189 ÷ 3 is about 400
Question 9. 2,110 ÷ 4 ______ and ______
Explanation: What number close to 2,110 is easy to divide by 4? 2,000 is close to 2,110. What basic fact can you use? 2,000 ÷ 4 Choose 2,000 because it is close to 2,110 and can easily be divided by 4. 20 ÷ 4 = 5 2,000 ÷ 4 = 500 2,110 ÷ 4 is about 500
Reason Abstractly Algebra Estimate to compare. Write <, >, or =.
Question 10. 613 ÷ 3 ______ 581 ÷ 2
Answer: 613 ÷ 3 < 581 ÷ 2
Explanation: What number close to 613 is easy to divide by 3? 600 is close to 613. What basic fact can you use? 600 ÷ 3 Choose 600 because it is close to 613 and can easily be divided by 3. 6 ÷ 3 = 2 600 ÷ 3 = 200 613 ÷ 3 is about 200
What number close to 581 is easy to divide by 2? 580 is close to 581. What basic fact can you use? 580 ÷ 2 Choose 580 because it is close to 581 and can easily be divided by 2. 58 ÷ 2 = 29 580 ÷ 2 = 290 581 ÷ 2 is about 290
Question 11. 364 ÷ 4 ______ 117 ÷ 6
Answer: 364 ÷ 4 > 117 ÷ 6
Explanation: What number close to 364 is easy to divide by 4? 360 is close to 364. What basic fact can you use? 360 ÷ 4 Choose 360 because it is close to 364 and can easily be divided by 4. 36 ÷ 4 = 9 360 ÷ 4 = 90 364 ÷ 4 is about 90
What number close to 117 is easy to divide by 6? 120 is close to 117. What basic fact can you use? 120 ÷ 6 Choose 120 because it is close to 117 and can easily be divided by 6. 12 ÷ 6 = 2 120 ÷ 6 = 20 117 ÷ 6 is about 20
Question 12. 2,718 ÷ 8 ______ 963 ÷ 2
Answer: 2,718 ÷ 8 < 963 ÷ 2
Explanation: What number close to 2,718 is easy to divide by 8? 2,400 is close to 2,718. What basic fact can you use? 2,400 ÷ 8 Choose 2,400 because it is close to 2,718 and can easily be divided by 8. 24 ÷ 8 = 3 2,400 ÷ 8 = 300 2,718 ÷ 8 is about 300
What number close to 963 is easy to divide by 2? 960 is close to 963. What basic fact can you use? 960 ÷ 2 Choose 960 because it is close to 963 and can easily be divided by 2. 96 ÷ 2 = 48 960 ÷ 2 = 480 963 ÷ 2 is about 480
Question 13. If Cade shoots 275 free throw baskets in 2 hours, about how many can he shoot in 5 hours? about ______ free throw baskets
Answer: 688 free throw baskets
Explanation: Number of free-throw baskets in 2 hours= 275 Number of free-throw baskets in 1 hour = 275÷2=137.5 Number of free-throw baskets in 5 hours= 137.5 x 5= 687.5 =rounding to nearest whole number 688 free throw baskets ( approx)
Question 14. A carpenter has 166 doorknobs in his workshop. Of those doorknobs, 98 are round and the rest are square. If he wants to place 7 square doorknobs in each bin, about how many bins would he need? about ______ bins
Explanation: The total number of doorknobs in a workshop= 166 Number of round doorknobs in a workshop= 98 Number of square doorknobs in a workshop=166-98=68 Number of square doorknobs in each bin= 7 Number of bins= 68÷7= 9.7= rounding to nearest whole number 10 bins (approx)

Question 15. About how many times does a chicken’s heart beat in 1 minute? about ______ times
Answer: 275
Explanation: Number of times the chicken’s heartbeats in 5 minutes= 1,375 Number of times the chicken’s heartbeats in 1 minute= 1,375÷ 5= 275
Question 16. About how many times does a cow’s heart beat in 2 minutes? about ______ times
Answer: 130
Explanation: Number of times the cow’s heartbeats in 5 minutes= 325 Number of times the cow’s heartbeats in 1 minute= 325÷5=65 Number of times the cow’s heartbeats in 2 minutes= 65 x 2=130
Question 17. Use Reasoning About how many times faster does a cow’s heartbeat than a whale’s? about ______ times
Answer: nearly 11 times
Explanation: Number of times the cow’s heartbeats in 5 minutes= 325 Number of times the cow’s heartbeats in 1 minute= 325÷5=65
Number of times the whale’s heartbeats in 5 minutes= 31 Number of times the whale’s heartbeats in 1 minute= 31÷5=6.2= rounding to nearest whole number 6 (approx)
Number of more times the cow’s heartbeats compared to whale’s=65÷6=10.8 times=rounding to a nearest whole number 11(approx)
Question 18. Martha had 154 stamps and her sister had 248 stamps. They combined their collections and put the stamps in an album. If they want to put 8 stamps on each page, about how many pages would they need? about ______ times
Answer: 50.25 pages
Explanation: Number of stamps Martha has= 154 Number of stamps Martha’s sister has= 248 The total number of stamps they have= 154+248=402 Number of stamps on each page= 8 Number of pages= 402÷8= 50.25 pages= 51 (approx)
Question 19. Jamie and his two brothers divided a package of 125 toy cars equally. About how many cars did each of them receive? about ______ times
Answer: 41.67
Explanation: Number of toys Jamie has= 125 toy cars Number of toys Jamie and his two brothers divide= 125÷3= 41.67
Go Math Grade 4 Chapter 4 Test Pdf Question 20. Harold and his brother collected 2,019 cans over a 1-year period. Each boy collected the same number of cans. About how many cans did each boy collect? Explain how you found your answer. about ______ times
Answer: 1,010
Explanation: Number of cans Harold and his brother collected = 2,019 cans Number of cans each boy collected = 2,019÷2= 1,009.5 cans = 1,010 cans(approx)

Answer: Chet can afford the 3-months layaway plan.
Explanation: What number close to $276 is easy to divide by 3? $270 is close to $276. What basic fact can you use? $270 ÷ 3 Choose 270 because it is close to 276 and can easily be divided by 3. 27 ÷ 3 = 9 270 ÷ 3 = 90 $276 ÷ 3 is about 90
Use estimation to solve.
Question 21. Sofia wants to buy a new bike that costs $214. Sofia helps her grandmother with chores each week for $18. Estimate to find which layaway plan Sofia should choose and why. Type below: ___________
Answer: 3 months
Explanation: What number close to $214 is easy to divide by 3? $215 is close to $214. What basic fact can you use? $215 ÷ 3 Choose 215 because it is close to 214 and can easily be divided by 3. 215 ÷ 3 = 71.6=72 (approx) $214 ÷ 3 is about 72
Question 22. Describe a situation when you have used cause and effect to help you solve a math problem. Type below: ___________
Answer: To buy a bike
Explanation: 3-month layaway: $276 ÷ 3 Estimate. $270 ÷ 3 ______ 6-month layaway: $276 ÷ 6 Estimate. $300 ÷ 6 _____ Chet earns $15 each week. Since there are usually 4 weeks in a month, multiply to see which payment he can afford. $15 × 4 = _______ So, Chet can afford the ______ layaway plan.
The above is a profit gaining plan to buy a bike.
Common Core – Page No. 224
Estimate Quotients Using Compatible Numbers
Question 1. 389 ÷ 4 400 ÷ 4 = 100
Answer: 100
Explanation: What number close to 389 is easy to divide by 4? 400 is close to 389. What basic fact can you use? 400 ÷ 4 Choose 400 because it is close to 389 and can easily be divided by 4. 40 ÷ 4 = 10 400 ÷ 4 = 100 389 ÷ 4 is about 100
Question 2. 358 ÷ 3 _____ ÷ 3 = _____
Explanation: What number close to 358 is easy to divide by 3? 360 is close to 358. What basic fact can you use? 360 ÷ 3 Choose 360 because it is close to 358 and can easily be divided by 3. 36 ÷3 = 12 360 ÷ 3 =120 358 ÷ 3 is about 120
Question 3. 784 ÷ 8 _____ ÷ 8 = _____
Explanation: What number close to 784 is easy to divide by 8? 800 is close to 784. What basic fact can you use? 800 ÷ 8 Choose 800 because it is close to 784 and can easily be divided by 8. 80 ÷ 8 = 10 800 ÷ 8 = 100 784 ÷ 8 is about 100
Question 4. 179 ÷ 9 _____ ÷ 9 = _____
Explanation: What number close to 179 is easy to divide by 9? 180 is close to 179. What basic fact can you use? 180 ÷ 9 Choose 180 because it is close to 179 and can easily be divided by 9. 18 ÷ 9 = 2 180 ÷ 9 = 20 179 ÷ 9 is about 20
Question 5. 315 ÷ 8 _____ ÷ 8 = _____
Explanation: What number close to 315 is easy to divide by 8? 320 is close to 315. What basic fact can you use? 320 ÷ 8 Choose 320 because it is close to 315 and can easily be divided by 8. 32 ÷ 8 = 4 320 ÷ 8 =40 315 ÷ 8 is about 40
Question 6. 2,116 ÷ 7 _____ ÷ 7 = _____
Explanation: What number close to 2,116 is easy to divide by 7? 2,100 is close to 2,116. What basic fact can you use? 2,100 ÷ 7 Choose 2,100 because it is close to 2,116 and can easily be divided by 7. 21 ÷ 7= 3 2,100 ÷ 7 = 300 2,116 ÷ 7 is about 300
Grade 4 Chapter 4 Divide By A One Digit Number Question 7. 4,156 ÷ 7 _____ ÷ 7 = _____
Explanation: What number close to 4,156 is easy to divide by 7? 4,200 is close to 4,156. What basic fact can you use? 4,200 ÷7 Choose 4,200 because it is close to 4,156 and can easily be divided by 7. 42 ÷ 7 = 6 4,200 ÷ 7 = 600 4,156 ÷ 7 is about 600
Question 8. 474 ÷ 9 _____ ÷ 9 = _____
Explanation: What number close to 474 is easy to divide by 9? 450 is close to 474. What basic fact can you use? 450 ÷ 9 Choose 450 because it is close to 474 and can easily be divided by 9. 45 ÷ 9 = 5 450 ÷ 9 = 50 474 ÷ 9 is about 50
Question 9. 1,624 ÷ 3 _____ ÷ 3 = _____ _____ ÷ 3 = _____
Answer: The quotient is between 500 and 600
Explanation: What number close to 1,624 is easy to divide by 3? 1,500 is close to 1,624. What basic fact can you use? 1,500 ÷ 3 Choose 1,500 because it is close to 1,624 and can easily be divided by 3. 15 ÷ 3 = 5 1,500 ÷ 3 = 500 1,624 ÷ 3 is about 500
What number close to 1,624 is easy to divide by 3? 1,800 is close to 1,624. What basic fact can you use? 1,800 ÷ 3 Choose 1,800 because it is close to 1,624 and can easily be divided by 3. 18 ÷ 3 = 6 1,800 ÷ 3 = 600 1,624 ÷ 3 is about 600
Question 10. 2,593 ÷ 6 _____ ÷ 6 = _____ _____ ÷ 6 = _____
Answer: The quotient is between 400 and 500
Explanation: What number close to 2,593 is easy to divide by 6? 2,400 is close to 2,593. What basic fact can you use? 2,400 ÷ 6 Choose 2,400 because it is close to 2,593 and can easily be divided by 6. 24 ÷ 6 = 4 2,400 ÷ 6 = 400 2,593 ÷ 6 is about 400
What number close to 2,593 is easy to divide by 6? 3,000 is close to 2,593. What basic fact can you use? 3000 ÷ 6 Choose 3,000 because it is close to 2,593 and can easily be divided by 6. 30 ÷ 6 = 5 3,000 ÷ 6 = 500 2,593 ÷ 6 is about 500
Question 11. 1,045 ÷ 2 _____ ÷ 2 = _____ _____ ÷ 2 = _____
Answer: The quotient is between 520 and 525
Explanation: What number close to 1,045 is easy to divide by 2? 1,040 is close to 1,045. What basic fact can you use? 1,040 ÷ 2 Choose 1,040 because it is close to 1,045 and can easily be divided by 2. 1,04 ÷ 2 = 52 1,040 ÷ 2 = 520 1,045 ÷ 2 is about 520
What number close to 1,045 is easy to divide by 2? 1,050 is close to 1,045. What basic fact can you use? 1,050 ÷ 2 Choose 1,050 because it is close to 1,045 and can easily be divided by 2. 1,050 ÷ 2 = 525 1,045 ÷ 2 is about 525
Go Math Grade 4 Chapter 4 Answer Key Pdf Question 12. 1,754 ÷ 9 _____ ÷ 9 = _____ _____ ÷ 9 = _____
Answer: The quotient is between 195 and 200
Explanation: What number close to 1,754 is easy to divide by 9? 1,755 is close to 1,754. What basic fact can you use? 1,755 ÷ 9 Choose 1,755 because it is close to 1,754 and can easily be divided by 9. 1,755 ÷ 9 = 195 1,754 ÷ 9 is about 195
What number close to 1,754 is easy to divide by 9? 1,800 is close to 1,754. What basic fact can you use? 1,800 ÷ 9 Choose 1,800 because it is close to 1,754 and can easily be divided by 9. 18 ÷ 9 = 2 1,800 ÷ 9 = 200 1,754 ÷ 9 is about 200
Question 13. 2,363 ÷ 8 _____ ÷ 8 = _____ _____ ÷ 8 = _____
Answer: The quotient is between 295 and 300
Explanation: What number close to 2,363 is easy to divide by 8? 2,360 is close to 2,363. What basic fact can you use? 2,360 ÷ 8 Choose 2,360 because it is close to 2,363 and can easily be divided by 8. 2,360 ÷ 8 = 295 2,363 ÷ 8 is about 295
What number close to 2,363 is easy to divide by 8? 2,400 is close to 2,363. What basic fact can you use? 2,400 ÷ 8 Choose 2,400 because it is close to 2,363 and can easily be divided by 8. 24 ÷ 8 = 3 2,400 ÷ 8= 300 2,363 ÷ 8 is about 300
Question 14. 1,649 ÷ 5 _____ ÷ 5 = _____ _____ ÷ 5 = _____
Answer: The quotient is between 329 and 330
Explanation: What number close to 1,649 is easy to divide by 5? 1,645 is close to 1,649. What basic fact can you use? 1,645 ÷ 5 Choose 1,645 because it is close to 1,649 and can easily be divided by 5. 1,645 ÷ 5 = 329 1,649 ÷ 5 is about 329
What number close to 1,650 is easy to divide by 5? 1,650 is close to 1,649. What basic fact can you use? 1,650 ÷ 5 Choose 1,650 because it is close to 1,649 and can easily be divided by 5. 1,650 ÷ 5 = 330 1,649 ÷ 5 is about 330
Question 15. 5,535 ÷ 7 _____ ÷ 7 = _____ _____ ÷ 7 = _____
Answer: The quotient is between 790 and 791
Explanation: What number close to 5,535 is easy to divide by 7? 5,530 is close to 5,535. What basic fact can you use? 5,530 ÷ 7 Choose 5,530 because it is close to 5,535 and can easily be divided by 7. 553 ÷ 7 = 79 5,530 ÷ 7 = 790 5,535 ÷ 7 is about 790
What number close to 5,535 is easy to divide by 7? 5,537 is close to 5,535. What basic fact can you use? 5,537 ÷ 7 Choose 5,537 because it is close to 5,535 and can easily be divided by 7. 553 ÷ 7 = 79 5,537 ÷ 7 = 791 5,535 ÷ 7 is about 791
Question 16. 3,640 ÷ 6 _____ ÷ 6 = _____ _____ ÷ 6 = _____
Answer: The quotient is between 606 and 607
Explanation: What number close to 3,640 is easy to divide by 6? 3,636 is close to 3,640. What basic fact can you use? 3,636 ÷ 6 Choose 3,636 because it is close to 3,640 and can easily be divided by 6. 36 ÷ 6 = 6 3,636 ÷ 6 = 606 3,640 ÷ 6 is about 606
What number close to 3,640 is easy to divide by 6? 3,642 is close to 3,640. What basic fact can you use? 3,642 ÷ 6 Choose 3,642 because it is close to 3,640 and can easily be divided by 6. 3,642 ÷ 6 = 607 3,640 ÷ 6 is about 607
Question 17. A CD store sold 3,467 CDs in 7 days. About the same number of CDs were sold each day. About how many CDs did the store sell each day? about _____ CDs
Answer: 495(approx)
Explanation: Total number of CDs in the store= 3,467 Number of days= 7 Number of CDs sold on one day= 3,467 ÷ 7=495(approx)
Question 18. Marcus has 731 books. He puts about the same number of books on each of 9 shelves in his a bookcase. About how many books are on each shelf? about _____ books
Answer: 81 books(approx)
Explanation: Total number of books Marcus has= 731 Number of shelves= 9 Number of books on each shelf= 731÷9= 81 (approx)
Common Core – Page No. 226
Question 1. Jamal is planting seeds for a garden nursery. He plants 9 seeds in each container. If Jamal has 296 seeds to plant, about how many containers will he use? Options: a. about 20 b. about 30 c. about 200 d. about 300
Answer: b. about 30
Explanation: Total number of seeds Jamal has= 296 Number of seeds placed in each container= 9 Number of containers Jamal used= 296÷9= 32.8=33 (approx) Therefore, the number of containers used is about 30
Question 2. Winona purchased a set of vintage beads. There are 2,140 beads in the set. If she uses the beads to make bracelets that have 7 beads each, about how many bracelets can she make? Options: a. about 30 b. about 140 c. about 300 d. about 14,000
Answer: c. about 300
Explanation: Total number of beads Winona has= 2,140 Number of beads in each bracelet= 7 Number of bracelets made= 2,140÷7=305.7=306(approx) Therefore, the number of bracelets made are about 30
Question 3. A train traveled 360 miles in 6 hours. How many miles per hour did the train travel? Options: a. 60 miles per hour b. 66 miles per hour c. 70 miles per hour d. 600 miles per hour
Answer: a. 60 miles per hour
Explanation: Total number of miles travelled by the train= 360 Time taken by the train to cover 360 miles= 6 hours Number of miles travelled in each hour= 360÷6=60 miles
Go Math Workbook Grade 4 Chapter 4 Multiply With One Digit Numbers Question 4. An orchard has 12 rows of pear trees. Each row has 15 pear trees. How many pear trees are there in the orchard? Options: a. 170 b. 180 c. 185 d. 190
Answer: b. 180
Explanation: Number of rows of pear trees in an orchard= 12 Number of pear trees in each row=15 Total number of pear trees in the orchard= 12 x 15=180
Question 5. Megan rounded 366,458 to 370,000. To which place did Megan round the number? Options: a. hundred thousand b. ten thousand c. thousands d. hundreds
Answer: b. ten thousand
Explanation: The given number is 366,458, the ten thousand place digit has 6 which while rounding off should be changed to the next consecutive number and the digits in the other places should be written as zeroes.
Question 6. Mr. Jessup, an airline pilot, flies 1,350 miles a day. How many miles will he fly in 8 days? Options: a. 1,358 miles b. 8,400 miles c. 10,800 miles d. 13,508 miles
Answer: c. 10,800 miles
Explanation: Number of miles flew by Mr.Jessup in one day= 1,350 miles Number of days=8 Total number of miles flew by Mr.Jessup in 8 days= 1,350 x 8= 10,800 miles
Page No. 229
Model the division on the grid.

Answer: 26 ÷ 2 = (20 ÷ 2) + (6 ÷ 2) = 10 + 3 = 13
Explanation: A. Outline a rectangle on a grid to model 26 ÷ 2. Shade columns of 2 until you have 26 squares. How many groups of 2 can you make? B. Think of 26 as 20 + 6. Break apart the model into two rectangles to show (20 + 6 ) ÷ 2. Label and shade the smaller rectangles. Use two different colours. C. Each rectangle models a division. 26 ÷ 2 = (20÷ 2 ) + (6÷ 2) = 10+ 3 = 13

Answer: 45 ÷ 3 = (15 ÷ 3) + (30 ÷ 3) = 5 + 10 = 15
Explanation: A. Outline a rectangle on a grid to model 45 ÷ 3. Shade columns of 3 until you have 45 squares. How many groups of 3 can you make? _ B. Think of 45 as 15 + 30. Break apart the model into two rectangles to show (15 + 30 ) ÷ 3. Label and shade the smaller rectangles. Use two different colours. C. Each rectangle models a division. 45 ÷ 3 = (15÷ 3 ) + (30÷ 3 ) = 5 + 10 = 15
Question 3. 82 ÷ 2 = (□ ÷ 2) + (□ ÷ 2) = □ + □ = □ ______
Answer: 82 ÷ 2 = (80 ÷ 2) + ( 2÷ 2) = 40 + 1 = 41
Explanation: A. Outline a rectangle on a grid to model 82 ÷ 2. Shade columns of 2 until you have 80 squares. How many groups of 2 can you make? B. Think of 82 as 80 + 2. Break apart the model into two rectangles to show (80 + 2 ) ÷ 2. Label and shade the smaller rectangles. Use two different colors. C. Each rectangle models a division. 82 ÷ 2 = (80 ÷ 2 ) + (2÷ 2) = 40 + 1 = 41
Question 4. 208 ÷ 4 = (□ ÷ 4) + (□ ÷ 4) = □ + □ = □ ______
Answer: 208 ÷ 4 = (200 ÷ 4) + (8 ÷ 4) = 50 + 4 = 54
Explanation: A. Outline another model to show 208 ÷ 4. How many groups of 4 can you make? B. Think of 208 as 200 + 8. Break apart the model, label, and shade to show two divisions. 208 ÷ 4 = (200 ÷ 4 ) + (8 ÷ 4 ) = 50 + 4 = 54
Use base-ten blocks to model the quotient. Then record the quotient.
Question 5. 88 ÷ 4 = ______

Question 6. 36 ÷ 3 = ______

Question 7. 186 ÷ 6 = ______

Question 8. Explain how you can model finding quotients using the Distributive Property. Type below: _________
Answer: We can use the Distributive Property to break apart numbers to make them easier to divide.
Explanation: 50 The Distributive Property of division says that dividing a sum by a number is the same as dividing each addend by the number and then adding the quotients.
Question 9. Justin earned $50 mowing lawns and $34 washing cars. He wants to divide his money into 3 equal accounts. How much will he put in each account? Explain. $ ______
Answer: $28
Explanation: The amount earned by Justin on mowing lawns=$50 The amount earned by Justin on washing cars=$34 Total amount earned=$50 + $34= $84 Number of parts into which he wanted to divide the amount he earned= 3 The amount put in each account= $84 ÷ 3 = $28

Answer: Question: How many candles are there in the gift shop?
Explanation: Count the number of candles in the rows and columns and then multiply them, by this we can find out the total number of candles in the gift shop.
Describe how you could change the problem by changing the number of rows of candles. Then solve the problem. Type below: _________
Answer: There will be no change in the solution by changing the number of rows of candles.
Explanation: By changing the number of rows of candles the number of columns increase but there will be no change in the total number of candles.
Question 11. For 11a–11d, choose Yes or No to indicate if the expression shows a way to break apart the dividend to find the quotient 147 ÷ 7. a. (135 ÷ 7) + (10 ÷ 7) i. yes ii. no
Explanation: Because 137+10 is not equal to 147
Question 11. b. (147 ÷ 3) + (147 ÷ 4) i. yes ii. no
Explanation: Because according to the distributive property we need to divide the dividend into two parts, but not the divisor.
Question 11. c. (140 ÷ 7) + (7 ÷ 7) i. yes ii. no
Explanation: 147 ÷ 7 STEP1 Find the nearest estimates of the number 147 STEP2 We can break the number 147 into 140 + 7 STEP3 We must divide the two parts of the number (dividend) with the divisor. STEP4 (140 ÷ 7) + (7 ÷ 7) STEP5 Add quotients of the above 20 +1= 21
Question 11. d. (70 ÷ 7) + (77 ÷ 7) i. yes ii. no
Explanation: 147 ÷ 7 STEP1 Find the nearest estimates of the number 147 STEP2 We can break the number 147 into 70 + 77 STEP3 We must divide the two parts of the number (dividend) with the divisor. STEP4 (70 ÷ 7) + (77 ÷ 7) STEP5 Add quotients of the above 10 +11= 21
Common Core – Page No. 231
Division and the Distributive Property

Explanation: 54 ÷ 3 STEP1 Find the nearest estimates of the number 54 STEP2 We can break the number 54 into 30 + 24 STEP3 We must divide the two parts of the number (dividend) with the divisor. STEP4 (30 ÷ 3) + (24÷ 3) STEP5 Add quotients of the above 10 +8= 18
Question 2. 81 ÷ 3 = ______
Explanation: 81 ÷ 3 STEP1 Find the nearest estimates of the number 81 STEP2 We can break the number 81 into 21 + 60 STEP3 We must divide the two parts of the number (dividend) with the divisor. STEP4 (60 ÷ 3) + (21 ÷ 3) STEP5 Add quotients of the above 20 +7= 27
Question 3. 232 ÷ 4 = ______
Explanation: 232 ÷ 4 STEP1 Find the nearest estimates of the number 232 STEP2 We can break the number 232 into 200 + 32 STEP3 We must divide the two parts of the number (dividend) with the divisor. STEP4 (200 ÷ 4) + (32 ÷ 4) STEP5 Add quotients of the above 50 +8= 58
Question 4. 305 ÷ 5 = ______
Explanation: 305 ÷ 5 STEP1 Find the nearest estimates of the number 305 STEP2 We can break the number 305 into 300 + 5 STEP3 We must divide the two parts of the number (dividend) with the divisor. STEP4 (300 ÷ 5) + (5 ÷ 5) STEP5 Add quotients of the above 60 +1= 61
Place The First Digit Lesson 4.10 Answer Key Question 5. 246 ÷ 6 = ______
Explanation: 246 ÷ 6 STEP1 Find the nearest estimates of the number 246 STEP2 We can break the number 246 into 240 + 6 STEP3 We must divide the two parts of the number (dividend) with the divisor. STEP4 (240 ÷ 6) + (6 ÷ 6) STEP5 Add quotients of the above 40 +1= 41
Question 6. 69 ÷ 3 = ______
Explanation: 69 ÷ 3 STEP1 Find the nearest estimates of the number 69 STEP2 We can break the number 69 into 60 + 9 STEP3 We must divide the two parts of the number (dividend) with the divisor. STEP4 (60 ÷ 3) + (9 ÷ 3) STEP5 Add quotients of the above 20 +3= 23
Question 7. 477 ÷ 9 = ______
Explanation: 477 ÷ 9 STEP1 Find the nearest estimates of the number 477 STEP2 We can break the number 477 into 450 + 27 STEP3 We must divide the two parts of the number (dividend) with the divisor. STEP4 (450 ÷ 9) + (27 ÷ 9) STEP5 Add quotients of the above 50 +3= 53
Question 8. 224 ÷ 7 = ______
Explanation: 224 ÷ 7 STEP1 Find the nearest estimates of the number 224 STEP2 We can break the number 224 into 210 + 14 STEP3 We must divide the two parts of the number (dividend) with the divisor. STEP4 (210 ÷ 7) + (14 ÷ 7) STEP5 Add quotients of the above 30 +2= 32
Question 9. 72 ÷ 4 = ______
Explanation: 72 ÷ 4 STEP1 Find the nearest estimates of the number 72 STEP2 We can break the number 72 into 40 + 32 STEP3 We must divide the two parts of the number (dividend) with the divisor. STEP4 (40 ÷ 4) + (32 ÷ 4) STEP5 Add quotients of the above 10 +8= 18
Question 10. 315 ÷ 3 = ______
Answer: 105
Explanation: 315 ÷ 3 STEP1 Find the nearest estimates of the number 315 STEP2 We can break the number 315 into 300 + 15 STEP3 We must divide the two parts of the number (dividend) with the divisor. STEP4 (300 ÷ 3) + (15 ÷3) STEP5 Add quotients of the above 100 +5= 105
Question 11. Cecily picked 219 apples. She divided the apples equally into 3 baskets. How many apples are in each basket? ______ apples
Answer: 73 apples
Explanation: The total number of apples Cecily picked= 219 apples Number of parts into which she wanted to divide the apples= 3 Number of apples in each part = Quotient of 147 ÷ 7 STEP1 Find the nearest estimates of the number 219 STEP2 We can break the number 219 into 210 + 9 STEP3 We must divide the two parts of the number (dividend) with the divisor. STEP4 (210 ÷ 3) + (9 ÷ 3) STEP5 Add quotients of the above 70 +3= 73
Question 12. Jordan has 260 basketball cards. He divides them into 4 equal groups. How many cards are in each group? ______ cards
Answer: 65 cards
Explanation: The total number of basketball cards Jordan has= 260 basketball cards Number of parts into which he wanted to divide the cards= 4 Number of apples in each part = Quotient of 260 ÷ 4 STEP1 Find the nearest estimates of the number 260 STEP2 We can break the number 260 into 240 + 20 STEP3 We must divide the two parts of the number (dividend) with the divisor. STEP4 (240 ÷ 4) + (20 ÷ 4) STEP5 Add quotients of the above 60 +5= 65
Question 13. The Wilsons drove 324 miles in 6 hours. If they drove the same number of miles each hour, how many miles did they drive in 1 hour? ______ miles
Answer: 54 miles
Explanation: The total number of miles drove by Wilson= 324 miles Number of hours he drove = 6 Number of miles drove in each hour = Quotient of 324 ÷ 6 STEP1 Find the nearest estimates of the number 324 STEP2 We can break the number 324 into 300 + 24 STEP3 We must divide the two parts of the number (dividend) with the divisor. STEP4 (300 ÷ 6) + (24 ÷ 6) STEP5 Add quotients of the above 50 +4= 54
Question 14. Phil has 189 stamps to put into his stamp album. He puts the same number of stamps on each of 9 pages. How many stamps does Phil put on each page? ______ stamps
Answer: 21 stamps
Explanation: The total number of stamps Phil has= 189 stamps Number of pages= 9 Number of stamps put on each page = Quotient of 189 ÷ 9 STEP1 Find the nearest estimates of the number 189 STEP2 We can break the number 189 into 180 + 9 STEP3 We must divide the two parts of the number (dividend) with the divisor. STEP4 (180 ÷ 9) + (9 ÷ 9) STEP5 Add quotients of the above 20 +1= 21
Common Core – Page No. 232
Question 1. A landscaping company planted 176 trees in 8 equal rows in the new park. How many trees did the company plant in each row? Options: a. 18 b. 20 c. 22 d. 24
Answer: c. 22
Explanation: The total number of trees in the landscaping= 176 trees Number of rows= 8 Number of trees in each row = Quotient of 176 ÷ 8 STEP1 Find the nearest estimates of the number 176 STEP2 We can break the number 176 into 160 + 16 STEP3 We must divide the two parts of the number (dividend) with the divisor. STEP4 (160 ÷ 8) + (16 ÷ 8) STEP5 Add quotients of the above 20 +2= 22
Question 2. Arnold can do 65 pushups in 5 minutes. How many pushups can he do in 1 minute? Options: a. 11 b. 13 c. 15 d. 17
Answer: b. 13
Explanation: The total number of pushups done by Arnold = 65 Number of minutes spent on pushups= 5 Number of pushups done in each minute = Quotient of 65 ÷ 5 STEP1 Find the nearest estimates of the number 65 STEP2 We can break the number 65 into 60 + 5 STEP3 We must divide the two parts of the number (dividend) with the divisor. STEP4 (60 ÷ 5) + (5 ÷ 5) STEP5 Add quotients of the above 12 +1= 13
Question 3. Last Saturday, there were 1,486 people at the Cineplex. There were about the same number of people in each of the 6 theaters. Which is the best estimate of the number of people in each theater? Options: a. between 20 and 30 b. between 80 and 90 c. between 100 and 200 d. between 200 and 300
Answer: d. between 200 and 300
Explanation: Total number of people at the Cineplex= 1,486 people Number of theatres = 6 Number of people at each theatre= estimate of the number of people 1,486 ÷ 6
What number close to 1,486 is easy to divide by 6? 1,488 is close to 1,486. What basic fact can you use? 1,488 ÷ 6 Choose 1,488 because it is close to 1,486 and can easily be divided by 6. 1,488 ÷ 6 = 248 1,486 ÷ 6 is about 248
What number close to 1,486 is easy to divide by 6? 1,482 is close to 1,486. What basic fact can you use? 1,482 ÷ 6 Choose 1,482 because it is close to 1,486 and can easily be divided by 6. 1,482 ÷ 6 = 247 1,486 ÷ 6 is about 247
Question 4. Nancy walked 50 minutes each day for 4 days last week. Gillian walked 35 minutes each day for 6 days last week. Which statement is true? Options: a. Gillian walked 10 minutes more than Nancy. b. Gillian walked 20 minutes more than Nancy. c. Nancy walked 10 minutes more than Gillian. d. Nancy walked 15 minutes more than Gillian.
Answer: d. Nancy walked 15 minutes more than Gillian.
Explanation: Time walked by Nancy= 50 minutes Time walked by Gillian= 35 minutes Nancy walked more time compared to Gillian 50-35=15 minutes Therefore, Nancy walked 15 minutes more than Gillian.
Question 5. Three boys share 28 toy cars equally. Which best describes how the cars are shared? Options: a. Each gets 3 cars with 1 left over. b. Each gets 8 cars with 2 left over. c. Each gets 9 cars with 1 left over. d. Each gets 10 cars with 2 left over.
Answer: c. Each gets 9 cars with 1 left over.
Explanation: Total number of toys three boys have= 28 Number of toys each boy got= 28 ÷3=9.33 Therefore we can say that each gets 9 cars with 1 leftover.
Question 6. An airplane flies at a speed of 474 miles per hour. How many miles does the plane fly in 5 hours? Options: a. 2,070 miles b. 2,140 miles c. 2,370 miles d. 2,730 miles
Answer: c. 2,370 miles
Explanation: Number of miles flew by aeroplane in one hour= 474 Number of hours the aeroplane flew= 5 hours Total number of miles flew in 5 hours= 474 x 5= 2,370 miles
Page No. 233

Question 1. A number that is the product of a number and a counting number is called a _____________. ___________
Answer: Multiple
Explanation: 3 x 4 = 12 In which 4 is a multiple and also 4 is a counting number
Question 2. Numbers that are easy to compute mentally are called _____________. ___________
Answer: Compatible numbers
Explanation: Compatible numbers are pairs of numbers that are easy to add, subtract, multiply, or divide mentally. When using estimation to approximate a calculation, replace actual numbers with compatible numbers.
Question 3. When a number cannot be divided evenly, the amount left over is called the _____________. ___________
Answer: Remainder
Explanation: When we divide 10 with 3 there will be 1 remaining, which is called remainder.
Question 4. 26 ÷ 3 _____ R _____
Answer: Quotient: 8 Remainder: 2

Quotient: A. Use 26 counters to represent the 26 dominoes. Then draw 3 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 8 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of circles filled= quotient of 26 ÷ 3 = 8
Question 5. 19 ÷ 4 _____ R _____
Answer: Quotient: 4 Remainder: 3

Quotient: A. Use 19 counters to represent the 19 dominoes. Then draw 4 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 4 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of circles filled= quotient of 19 ÷ 4 = 4
Question 6. 810 ÷ 9 = _____
Explanation: STEP 1 Identify the basic fact. 81 ÷ 9 STEP 2 Use place value. 810 = 81 tens STEP 3 Divide. 81 tens ÷ 9 = 9 tens 810 ÷ 9 = 90
Question 7. 210 ÷ 7 = _____
Explanation: STEP 1 Identify the basic fact. 21 ÷ 7 STEP 2 Use place value. 210 = 21 tens STEP 3 Divide. 21 tens ÷ 7 = 3 tens 210 ÷ 7 = 30
Question 8. 3,000 ÷ 6 = _____
Explanation: STEP 1 Identify the basic fact. 30 ÷ 6 STEP 2 Use place value. 3,000 = 30 hundreds STEP 3 Divide. 30 hundreds ÷ 6 = 5 hundreds 3,000 ÷ 6 = 500
Question 9. 635 ÷ 9 about _____
Explanation: What number close to 635 is easy to divide by 9? 630 is close to 635. What basic fact can you use? 630 ÷ 9 Choose 630 because it is close to 635 and can easily be divided by 9. 63 ÷ 9 = 7 630 ÷ 9 = 70 635 ÷ 9 is about 70
Question 10. 412 ÷ 5 about _____
Explanation: What number close to 412 is easy to divide by 5? 410 is close to 412. What basic fact can you use? 410 ÷ 5 Choose 410 because it is close to 412 and can easily be divided by 5. 410 ÷ 5 = 82 412 ÷ 5 is about 82
Question 11. 490 ÷ 8 about _____
Explanation: What number close to 490 is easy to divide by 8? 480 is close to 490. What basic fact can you use? 480 ÷ 8 Choose 480 because it is close to 490 and can easily be divided by 8. 48 ÷ 8 = 6 480 ÷ 8 = 60 490 ÷ 8 is about 60
Use grid paper or base-ten blocks to model the quotient. Then record the quotient.
Question 12. 63 ÷ 3 = _____

Question 13. 85 ÷ 5 = _____

Question 14. 168 ÷ 8 = _____

Page No. 234
Question 15. Ana has 296 coins in her coin collection. She put the same number of coins in each of 7 jars. About how many coins are in each jar? about _____ coins
Explanation: The total number of coins Ana has= 296 coins Number of Jars= 7 Number of coins in each Jar= 296 ÷ 7 = 42 coins
Question 16. Which two estimates is the quotient 345 ÷ 8 between? _____ and _____
Answer: The quotient is between 42 and 43
What number close to 345 is easy to divide by 8? 336 is close to 1,624. What basic fact can you use? 336 ÷ 8 Choose 336 because it is close to 345 and can easily be divided by 8. 336 ÷ 8 = 42 345 ÷ 8 is about 42
What number close to 345 is easy to divide by 8? 344 is close to 345. What basic fact can you use? 344 ÷ 8 Choose 344 because it is close to 345 and can easily be divided by 8. 344 ÷ 8 = 43 345 ÷ 8 is about 43
Go Math Grade 4 Chapter 4 Mid Chapter Checkpoint Answer Key Question 17. A total of 8,644 people went to the football game. Of those people, 5,100 sat on the home side and the rest sat on the visitor’s side. If the people sitting on the visitor’s side filled 8 equal-sized sections, how many people sat in each of the sections? about _____ people
Answer: 443
Explanation: Total number of people in the football game= 8,644 Number of people who sat on the homeside= 5,100 Number of people who sat on the visitor’s side= 3,544 Number of equal-sized sections= 8 Number of people who sat in each of the sections= 3,544 ÷ 8= 443
Question 18. There are 4 students on a team for a relay race. How many teams can be made from 27 students? _____ teams
Explanation: The total number of students= 27 Number of students in each team= 4 Number of teams = 27 ÷ 4= 6.75 = 7 (approx)
Question 19. Eight teams of high school students helped clean up trash in the community. Afterwards, they shared 23 pizzas equally. How many pizzas did each team get? _____ \(\frac{ □ }{ □ }\)
Explanation: Total number of pizzas= 23 Number of teams= 8 Number of pizzas each team got= 23 ÷ 8=2.8=3(approx)
Page No. 237
Use repeated subtraction to divide.
Question 1. 84 ÷ 7 _____
Explanation: A. Begin with 84 counters. Subtract 7 counters. B. Subtract 7 counters from 84 and repeat the processes until the remainder cannot be subtracted from the divisor. C. Record the number of counters left and the number of times you subtracted. D. The number of times you subtracted is the quotient is 12.
Question 2. 60 ÷ 4 _____
Explanation: A. Begin with 60 counters. Subtract 4 counters. B. Subtract 4 counters from 60 and repeat the processes until the remainder cannot be subtracted from the divisor. C. Record the number of counters left and the number of times you subtracted. D. The number of times you subtracted is the quotient is 15.
Question 3. 91 ÷ 8 _____ R _____
Answer: 11.3=11(approx)
Explanation: A. Begin with 91 counters. Subtract 8 counters. B. Subtract 8 counters from 91 and repeat the processes until the remainder cannot be subtracted from the divisor. C. Record the number of counters left and the number of times you subtracted. D. The number of times you subtracted is the quotient is 11
Draw a number line to divide.
Question 4. 65 ÷ 5 = _____
Explanation: A. Begin with 65 counters. Subtract 5 counters. B. Subtract 5 counters from 65 and repeat the processes until the remainder cannot be subtracted from the divisor. C. Record the number of counters left and the number of times you subtracted. D. The number of times you subtracted is the quotient is 13

Answer: 11 (approx)
Explanation: How many equal groups of 3 did you subtract? So, 32 ÷ 3 = 10.8=11(approx).
Question 6. John has $40 to spend at the yard sale. He buys 6 books for $2 each. He would like to spend the rest of his money on model cars for his collection. If the cars cost $7 each, how many can he buy? Explain. _____ cars
Answer: 4 cars
Explanation: Total amount John spent at the yard sale= $40 Number of books= 6 Cost of each book= $2 Cost of 6 books= 6 x $2 = $12 Amount left after John bought 6 books= $40 – $12 = $28 Cost of each car= $7 Number of cars bought = $28 ÷ $7 = $4
Page No. 238

Explanation: A. Begin with 108 counters. Subtract 9 counters. B. Subtract 9 counters from 108 and repeat the processes until the remainder cannot be subtracted from the divisor. C. Record the number of counters left and the number of times you subtracted. D. The number of times you subtracted is the quotient is 12.
Question 7. b. How can you use repeated subtraction to solve the problem? Type below: __________
Answer: Repeated subtraction is a method to solve and find the quotient.
Explanation: Example: A. Begin with 65 counters. Subtract 5 counters. B. Subtract 5 counters from 65 and repeat the processes until the remainder cannot be subtracted from the divisor. C. Record the number of counters left and the number of times you subtracted. D. The number of times you subtracted is the quotient is 13
Question 7. c. Tell why you might use multiples of the divisor to solve the problem. Type below: __________
Answer: The multiple which divides 108 is 12
Explanation: The number 108 has multiples which divide 108 evenly, 1 x 108 =108 2 x 54 =108 3 x 36 =108 4 x 27 =108 6 x 18 =108 9 x 12 =108 12 x 9 =108 18 x 6 =108 27 x 4 =108 36 x 3 =108 54 x 2 =108 108 x 1 =108 Multiples which divide 108 are 1,2,3,4,5,6,9,12,18,27,36,54,108.
Question 7. d. Show steps to solve the problem. Type below: __________
Answer: 108 ÷ 9 =12
Explanation: A. Begin with 108 counters. Subtract 9 counters. B. Subtract 9 counters from 108 and repeat the processes until the remainder cannot be subtracted from the divisor. C. Record the number of counters left and the number of times you subtracted. D. The number of times you subtracted is the quotient is 12
Question 7. e. Complete the sentences. There are _______ equal parts of the playground, each _______ feet long. So, _______ climbers can fit along the length of the playground. Type below: __________
Answer: There are ___108____ equal parts of the playground, each __09_____ feet long. So, __12_____ climbers can fit along the length of the playground.
Explanation: A new playground will be 108 feet long. Builders need to allow 9 feet of space for each piece of climbing equipment. Number of climbers that can fit along the length of the playground= 108 ÷ 9 =12

Answer: 240 ÷ 80 expression resembles the second model while 240 ÷ 60 expression resembles the first model.
Explanation: 240 ÷ 80 A. Draw a number line with 80 as each interval. B. Draw up to 240 and count the intervals, it gives the quotient. C. The quotient is 3 240 ÷ 60 A. Draw a number line with 60 as each interval. B. Draw up to 240 and count the intervals, it gives the quotient. C. The quotient is 4
Common Core – Page No. 239
Divide Using Repeated Subtraction Use repeated subtraction to divide.
Question 1. 42 ÷ 3 = 14 3)\(\overline { 42 } \) -30 ← 10 × 3 | 10 ——- 12 -12 ← 4 × 3 | +4 ——- ———– 0 14
Explanation: A. Begin with 42 counters. Subtract 3 counters. B. Subtract 3 counters from 42 and repeat the processes until the remainder cannot be subtracted from the divisor. C. Record the number of counters left and the number of times you subtracted. D. The number of times you subtracted is the quotient is 14
Question 2. 72 ÷ 4 = _____
Explanation: A. Begin with 72 counters. Subtract 4 counters. B. Subtract 4 counters from 72 and repeat the processes until the remainder cannot be subtracted from the divisor. C. Record the number of counters left and the number of times you subtracted. D. The number of times you subtracted is the quotient is 18
Question 3. 93 ÷ 3 = _____
Explanation: A. Begin with 93 counters. Subtract 3 counters. B. Subtract 3 counters from 93 and repeat the processes until the remainder cannot be subtracted from the divisor. C. Record the number of counters left and the number of times you subtracted. D. The number of times you subtracted is the quotient is 31
Question 4. 35 ÷ 4 = _____ r _____
Answer: 8r3
Quotient: A. Use 35 counters to represent the 35 dominoes. Then draw 4 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 4 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of counters formed in each group = quotient of 35 ÷ 4 D. Number of circles are equally filled with 4 counters, therefore, the quotient is 8
For 35 ÷ 4, the quotient is 8 and the remainder is 3, or 8 r3.
Question 5. 93 ÷ 10 = _____ r _____
Answer: 9r3
Quotient: A. Use 93 counters to represent the 93 dominoes. Then draw 10 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 10 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of counters formed in each group = quotient of 93 ÷ 10 D. Number of circles are equally filled with 10 counters, therefore, the quotient is 9
For 93 ÷ 10, the quotient is 9 and the remainder is 3, or 9 r3.
Question 6. 86 ÷ 9 = _____ r _____
Answer: 9r5
Quotient: A. Use 86 counters to represent the 86 dominoes. Then draw 9 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 9 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of counters formed in each group = quotient of 86 ÷ 9 D. Number of circles are equally filled with 9 counters, therefore, the quotient is 9
For 86 ÷ 9, the quotient is 9 and the remainder is 5, or 9 r5.
Question 7. 70 ÷ 5 = _____
Explanation: A. Draw a number line with 5 as each interval. B. Draw up to 70 and count the intervals, it gives the quotient. C. The quotient is 14
Question 8. Gretchen has 48 small shells. She uses 2 shells to make one pair of earrings. How many pairs of earrings can she make? _____ pairs
Answer: 24 pairs
Explanation: Total number of small shells= 48 Number of shells used to make one pair of earrings = 2 Number of pair of earrings made = 48 ÷ 2 =24
Question 9. James wants to purchase a telescope for $54. If he saves $3 per week, in how many weeks will he have saved enough to purchase the telescope? _____ weeks
Answer: $18
Explanation: Cost of the telescope=$54 Amount saved each week = $3 Number of weeks he has to save the money to purchase the telescope = $54 ÷ $3 = $18
Common Core – Page No. 240
Question 1. Randall collects postcards that his friends send him when they travel. He can put 6 cards on one scrapbook page. How many pages does Randall need to fit 42 postcards? Options: a. 3 b. 4 c. 6 d. 7
Explanation: Total number of postcards Randall has = 42 postcards Number of postcards on one scrapbook page = 6 cards Number of pages needed to fit the postcards = 42 ÷ 6=7
Question 2. Ari stocks shelves at a grocery store. He puts 35 cans of juice on each shelf. The shelf has 4 equal rows and another row with only 3 cans. How many cans are in each of the equal rows? Options: a. 6 b. 7 c. 8 d. 9
Answer: c. 8
Explanation: Total number of cans of juice on each shelf = 35 Number of rows = 4 Number of cans on the other shelf = 3 Number of cans placed on the first shelf = 35 – 3 = 32 Number of juice cans in the first row = 32 ÷ 4 = 8 cans
Question 3. Fiona sorted her CDs into separate bins. She placed 4 CDs in each bin. If she has 160 CDs, how many bins did she fill? Options: a. 4 b. 16 c. 40 d. 156
Answer: c. 40
Explanation: Total number of CD’s in Fiona has = 160 CD’s Number of CD’s placed in each bin = 4 Number of bins required to place the CD’s = 160 ÷ 4 = 40
Question 4. Eamon is arranging 39 books on 3 shelves. If he puts the same number of books on each shelf, how many books will there be on each shelf? Options: a. 11 b. 12 c. 13 d. 14
Answer: c. 13
Explanation: Total number of books Eamon has = 39 books Number of shelves = 3 Number of books in each shelf = 39 ÷ 3 = 13
Question 5. A newborn boa constrictor measures 18 inches long. An adult boa constrictor measures 9 times the length of the newborn plus 2 inches. How long is the adult? Options: a. 142 inches b. 162 inches c. 164 inches d. 172 inches
Answer: c. 164 inches
Explanation: Length of newborn boa constrictor = 18 inches Length of an adult boa constrictor = 9 x Length of newborn boa constrictor = 9 x 18 = 162 Total length of an adult boa constrictor = 162 + 2 = 164 inches
Question 6. Madison has 6 rolls of coins. Each roll has 20 coins. How many coins does Madison have in all? Options: a. 110 b. 120 c. 125 d. 130
Answer: b. 120
Explanation: Number of rolls of coins = 6 Number of coins in each roll = 20 Total number of coins Madison has = 20 x 6 = 120

Answer: 37 yards (approx)
Explanation: STEP 1 Start by subtracting a greater multiple, such as 100 times the divisor. For example, you know that you can make at least 100 ft which is long 33 yards. Continue subtracting until the remaining number is less than the multiple, 3. STEP 2 Subtract smaller multiples, such as 3 times the divisor until the remaining number is less than the divisor. In other words, keep going until you no longer a remainder is left in the place of the remainder. Then add the partial quotients to find the quotient. So, there are 110 ft = 110 ÷ 3 = 36.6 yards = 37 yards (approx).
Divide. Use partial quotients.
Question 2. 3)\(\overline { 225 } \) ____
Explanation: STEP 1 Start by subtracting a greater multiple, such as 50 times the divisor. Continue subtracting until the remaining number is less than the multiple, 3. STEP 2 Subtract smaller multiples, such as 3 times the divisor until the remaining number is less than the divisor. In other words, keep going until you no longer a remainder is left in the place of the remainder. Then add the partial quotients to find the quotient. So, there are 50 x 3 = 150 : 225 – 150 = 75 3 x 25 = 75 : 75 – 75 = 0 Therefore the quotient is 75 ( 50 + 25)
Divide. Use rectangular models to record the partial quotients.
Question 3. 428 ÷ 4 = ____
Answer: 107

Question 4. 7)\(\overline { 224 } \) ____
Explanation: STEP 1 Start by subtracting a greater multiple, such as 30 times the divisor. Continue subtracting until the remaining number is less than the multiple, 7. STEP 2 Subtract smaller multiples, such as 7 times the divisor until the remaining number is less than the divisor. In other words, keep going until you no longer a remainder is left in the place of the remainder. Then add the partial quotients to find the quotient. So, there are 30 x 7 = 210 : 224 – 210 = 14 7 x 2 = 14 : 14 – 14 = 0 Therefore the quotient is 32 ( 30 + 2)
Question 5. 7)\(\overline { 259 } \) ____
Explanation: STEP 1 Start by subtracting a greater multiple, such as 30 times the divisor. Continue subtracting until the remaining number is less than the multiple, 7. STEP 2 Subtract smaller multiples, such as 7 times the divisor until the remaining number is less than the divisor. In other words, keep going until you no longer a remainder is left in the place of the remainder. Then add the partial quotients to find the quotient. So, there are 30 x 7 = 210 : 225 – 210 = 49 7 x 7 = 49 : 49 – 49 = 0 Therefore the quotient is 37 ( 30 + 7)
Question 6. 8)\(\overline { 864 } \) ____
Answer: 108
Explanation: STEP 1 Start by subtracting a greater multiple, such as 100 times the divisor. Continue subtracting until the remaining number is less than the multiple, 8. STEP 2 Subtract smaller multiples, such as 8 times the divisor until the remaining number is less than the divisor. In other words, keep going until you no longer a remainder is left in the place of the remainder. Then add the partial quotients to find the quotient. So, there are 100 x 8 = 800 : 864 – 800 = 64 8 x 8 = 64 : 64 – 64 = 0 Therefore the quotient is 108 ( 100 + 8)
Question 7. 6)\(\overline { 738 } \) ____
Answer: 123
Explanation: STEP 1 Start by subtracting a greater multiple, such as 100 times the divisor. Continue subtracting until the remaining number is less than the multiple, 6. STEP 2 Subtract smaller multiples, such as 6 times the divisor until the remaining number is less than the divisor. In other words, keep going until you no longer a remainder is left in the place of the remainder. Then add the partial quotients to find the quotient. So, there are 100 x 6 = 600 : 738 – 600 = 138 6 x 23 = 138 : 138 – 138 = 0 Therefore the quotient is 123 ( 100 + 23)
Question 8. 328 ÷ 2 = ____
Answer: 164

Question 9. 475 ÷ 5 = ____

Question 10. 219 ÷ 3 = ____

Question 11. 488 ÷ 4 = ____
Answer: 122

Question 12. Use Reasoning What is the least number you can divide by 5 to get a three-digit quotient? Explain how you found your answer. ____
Answer: The quotient can be a three-digit number or a two-digit number.
Explanation: Example:
475 ÷ 5 = ____
Explanation: STEP 1 Start by subtracting a greater multiple, such as 90 times the divisor. Continue subtracting until the remaining number is less than the multiple, 5. STEP 2 Subtract smaller multiples, such as 5 times the divisor until the remaining number is less than the divisor. In other words, keep going until you no longer a remainder is left in the place of the remainder. Then add the partial quotients to find the quotient. So, there are 90 x 5 = 450 : 475 – 450 = 25 5 x 5 = 25 : 25 – 25 = 0 Therefore the quotient is 95 (90 + 5)

Question 13. Rob wants to put 8 baseball cards on each page in an album. How many pages will he fill? ____ pages
Answer: 31 pages
Explanation: Total number of baseball cards = 248 Number of cards in each page = 8 Number of pages required = 248 ÷ 8 = 31 pages
Question 14. Rob filled 5 plastic boxes with hockey cards. There were the same number of cards in each box. How many cards did he put in each box? How many cards were left over? Type below: ___________
Answer: There where 12 hockey cards in each box, number of cards leftover = 4
Explanation: Total number of hockey cards = 64 Number of boxes = 5 Number of cards in each box = 64 ÷ 5 = 12.8 that is exactly 60 cards can be fit in 5 boxes and 12 in each box Number of cards leftover = 64 – 60 = 4
Question 15. Rob filled 3 fewer plastic boxes with football cards than basketball cards. He filled 9 boxes with basketball cards. How many boxes did he fill with football cards? How many football cards were in each box? ____ boxes ____ cards
Answer: 6 boxes and 16 cards in each box
Explanation: Number of basketball cards= 189 Number of boxes in which the basketball cards were kept= 9 boxes Number of football cards= 96 Number of boxes in which the football cards were kept = number of boxes in which the basketball cards were kept – 3 = 9-3=6boxes Number of football cards in each box = 96 ÷ 6 =16 cards
Question 16. Marshall can buy 5 T-shirts for $60. If each shirt costs the same amount, what is the cost of 4 T-shirts? $ ____
Answer: $48
Explanation: Number of T-shirts = 5 Cost of 5 T-shirts = $60 Cost of each T- shirt = $60 ÷ 5 = $12 Cost of 4 T-shirts = 12 x 4 = $48

Explanation: STEP 1 Start by subtracting a greater multiple, such as 80 times the divisor. Continue subtracting until the remaining number is less than the multiple, 5. STEP 2 Subtract smaller multiples, such as 5 times the divisor until the remaining number is less than the divisor. In other words, keep going until you no longer a remainder is left in the place of the remainder. Then add the partial quotients to find the quotient. So, there are 80 x 5 = 400 : 485 – 400 = 85 5 x 17 = 85 : 85 – 85 = 0 Therefore the quotient is 97 ( 80 + 17)
Common Core – Page No. 245
Divide Using Partial Quotients Divide. Use partial quotients.
Question 1. 8)\(\overline { 184 } \) -80 ← 10 × 8 10 ——- 104 -80 ← 10 × 8 + 10 ——- -24 -24 ← 3 × 8 + 3 ——– ——– 0 23
Explanation: STEP 1 Start by subtracting a greater multiple, such as 10 times the divisor. Continue subtracting until the remaining number is less than the multiple, 8. STEP 2 Subtract smaller multiples, such as 10 times the divisor until the remaining number is less than the divisor. In other words, keep going until you no longer a remainder is left in the place of the remainder. Then add the partial quotients to find the quotient. So, there are 10 x 8 = 80 : 184 – 80 = 104 10 x 8 = 80 : 104 – 80 = 24 : 3 x 8 = 24 : 24 – 24 = 0 Therefore the quotient is 23 ( 10 + 10 + 3)
Question 2. 6)\(\overline { 258 } \) _____
Explanation: STEP 1 Start by subtracting a greater multiple, such as 40 times the divisor. Continue subtracting until the remaining number is less than the multiple, 6. STEP 2 Subtract smaller multiples, such as 3 times the divisor until the remaining number is less than the divisor. In other words, keep going until you no longer a remainder is left in the place of the remainder. Then add the partial quotients to find the quotient. So, there are 40 x 6 = 240 : 258 – 240 = 18 3 x 6 = 18 : 18 – 18 = 0 Therefore the quotient is 43 ( 40 + 3)
Question 3. 5)\(\overline { 630 } \) _____
Answer: 126
Explanation: STEP 1 Start by subtracting a greater multiple, such as 100 times the divisor. Continue subtracting until the remaining number is less than the multiple, 5. STEP 2 Subtract smaller multiples, such as 20 times the divisor until the remaining number is less than the divisor. In other words, keep going until you no longer a remainder is left in the place of the remainder. Then add the partial quotients to find the quotient. So, there are 100 x 5 = 500 : 630 – 500 = 130 5 x 20 = 100 : 130 – 100 = 30 : 5 x 6 = 30 : 30 – 30 = 0 Therefore the quotient is 126 ( 100 + 20 + 6)
Question 4. 246 ÷ 3 = _____

Question 5. 126 ÷ 2 = _____

Question 6. 605 ÷ 5 = _____
Answer: 121

Divide. Use either way to record the partial quotients.
Question 7. 492 ÷ 3 = _____
Explanation: STEP 1 Start by subtracting a greater multiple, such as 100 times the divisor. Continue subtracting until the remaining number is less than the multiple, 3. STEP 2 Subtract smaller multiples, such as 50 times the divisor until the remaining number is less than the divisor. In other words, keep going until you no longer a remainder is left in the place of the remainder. Then add the partial quotients to find the quotient. So, there are 100 x 3 = 300 : 492 – 300 = 192 50 x 3 = 150 : 192 – 150 = 42 : 3 x 14 = 42 : 42 – 42 = 0 Therefore the quotient is 164 ( 100 + 50 + 14)
Question 8. 224 ÷ 7 = _____
Explanation: STEP 1 Start by subtracting a greater multiple, such as 30 times the divisor. Continue subtracting until the remaining number is less than the multiple, 7. STEP 2 Subtract smaller multiples, such as 30 times the divisor until the remaining number is less than the divisor. In other words, keep going until you no longer a remainder is left in the place of the remainder. Then add the partial quotients to find the quotient. So, there are 30 x 7 = 210 : 224 – 210 = 14 7 x 2 = 14 : 14 – 14 = 0 Therefore the quotient is 32 ( 30 + 2)
Question 9. 692 ÷ 4 = _____
Answer: 173
Explanation: STEP 1 Start by subtracting a greater multiple, such as 100 times the divisor. Continue subtracting until the remaining number is less than the multiple, 4. STEP 2 Subtract smaller multiples, such as 100 times the divisor until the remaining number is less than the divisor. In other words, keep going until you no longer a remainder is left in the place of the remainder. Then add the partial quotients to find the quotient. So, there are 100 x 4 = 400 : 692 – 400 = 392 4 x 50 = 200 : 392 – 200 = 192 : 4 x 48 = 192 : 192 – 192 = 0 Therefore the quotient is 198 ( 100 + 50 + 48)
Question 10. Allison took 112 photos on vacation. She wants to put them in a photo album that holds 4 photos on each page. How many pages can she fill? _____ pages
Explanation: STEP 1 Start by subtracting a greater multiple, such as 20 times the divisor. Continue subtracting until the remaining number is less than the multiple, 4. STEP 2 Subtract smaller multiples, such as 20 times the divisor until the remaining number is less than the divisor. In other words, keep going until you no longer a remainder is left in the place of the remainder. Then add the partial quotients to find the quotient. So, there are 20 x 4 = 80 : 112 – 80 = 32 4 x 8 = 32 : 32 – 32 = 0 Therefore the quotient is 28 ( 20 + 8)
Question 11. Hector saved $726 in 6 months. He saved the same amount each month. How much did Hector save each month? $ _____
Answer: $121
Explanation: STEP 1 Start by subtracting a greater multiple, such as 100 times the divisor. Continue subtracting until the remaining number is less than the multiple, 6. STEP 2 Subtract smaller multiples, such as 100 times the divisor until the remaining number is less than the divisor. In other words, keep going until you no longer a remainder is left in the place of the remainder. Then add the partial quotients to find the quotient. So, there are 100 x 6 = 600 : 726 – 600 = 126 6 x 20 = 120 : 126 – 120 = 6 : 6 x 1 = 6 : 6 – 6 = 0 Therefore the quotient is 121 ( 100 + 20 +1)
Common Core – Page No. 246
Question 1. Annaka used partial quotients to divide 145 ÷ 5. Which shows a possible sum of partial quotients? Options: a. 50 + 50 + 45 b. 100 + 40 + 5 c. 10 + 10 + 9 d. 10 + 4 + 5
Answer: c. 10 + 10 + 9
Explanation: STEP 1 Start by subtracting a greater multiple, such as 100 times the divisor. Continue subtracting until the remaining number is less than the multiple, 4. STEP 2 Subtract smaller multiples, such as 10 times the divisor until the remaining number is less than the divisor. In other words, keep going until you no longer a remainder is left in the place of the remainder. Then add the partial quotients to find the quotient. So, there are 10 x 5 = 50 : 145 – 50 = 95 5 x 10 = 50 : 95 – 50 = 45 : 5 x 9 = 45 : 45 – 45 = 0 Therefore the quotient is 29 ( 10 + 10 +9)
Question 2. Mel used partial quotients to find the quotient 378 ÷ 3. Which might show the partial quotients that Mel found? Options: a. 100, 10, 10, 9 b. 100, 10, 10, 6 c. 100, 30, 30, 6 d. 300, 70, 8
Answer: b. 100, 10, 10, 6
Explanation: STEP 1 Start by subtracting a greater multiple, such as 100 times the divisor. Continue subtracting until the remaining number is less than the multiple, 3. STEP 2 Subtract smaller multiples, such as 10 times the divisor until the remaining number is less than the divisor. In other words, keep going until you no longer a remainder is left in the place of the remainder. Then add the partial quotients to find the quotient. So, there are 100 x 3 = 300 : 378 – 300 = 78 10 x 3 =30 : 78 – 30 = 48 : 3 x 16 = 48 : 48 – 48 = 0 Therefore the quotient is 126 ( 100 + 10 +10 + 6)
Question 3. What are the partial products of 42 × 5? Options: a. 9 and 7 b. 20 and 10 c. 200 and 7 d. 200 and 10
Answer: d. 200 and 10
Explanation: STEP1 42 x 5 Start by multiplying the digit five with the units digit 2 = 5 x 2 =10 Multiply the digit 5 with 4 in the tens place = 4 x 5 = 20 Since 4 is in the tens place when we multiply 4 and 5 we must place it in the hundreds place by assuming units digit to be zero. Therefore, the partial product of 42 x 5 = 200
Question 4. Mr. Watson buys 4 gallons of paint that cost $34 per gallon. How much does Mr. Watson spend on paint? Options: a. $38 b. $126 c. $136 d. $1,216
Answer: c. $136
Explanation: Cost of each gallon of paint = $34 Number of gallons = 4 The total cost of the gallons = $ 34 x 4 = $136

Answer: d. 896

Question 6. An adult male lion eats about 108 pounds of meat per week. About how much meat does an adult male lion eat in one day? Options: a. about 14 pounds b. about 15 pounds c. about 16 pounds d. about 17 pounds
Answer: b. about 15 pounds
Explanation: Mass of meat an adult lion eats in one week = 108 Number of days in a week = 7 Mass of meat ate by the lion in one day = 108 ÷ 7 = 15.4 pounds = about 15 pounds
Divide. Use base-ten blocks.
Question 1. 48 ÷ 3 _____
Explanation: A. Draw 3 circles to represent the divisor. Then use base-ten blocks to model 48. Show 48 as 4 tens and 8 ones. B. Share the tens equally among the 3 groups. C. If there are any tens left, regroup them as ones. Share the ones equally among the 3 groups. D. There are 1 ten(s) and 6 one(s) in each group. So, the quotient is 16.
Question 2. 84 ÷ 4 _____
Explanation: A. Draw 4 circles to represent the divisor. Then use base-ten blocks to model 84. Show 84 as 8 tens and 4 ones. B. Share the tens equally among the 4 groups. C. If there are any tens left, regroup them as ones. Share the ones equally among the 4 groups. D. There are 2 ten(s) and 1 one(s) in each group. So, the quotient is 21.
Question 3. 72 ÷ 5 _____ R _____
Answer: 14 (approx) with 2 as remainder.
Explanation: A. Draw 5 circles to represent the divisor. Then use base-ten blocks to model 72. Show 72 as 7 tens and 2 ones. B. Share the tens equally among the 5 groups. C. If there are any tens left, regroup them as ones. Share the ones equally among the 5 groups. D. There are 1 ten(s) and 4 one(s) in each group. So, the quotient is 14.

Question 5. Explain why you did not need to regroup in Exercise 2. Type below: ___________
Answer: We did not regroup in exercise two because we used the method of counters in which we placed the counters one after the other in the circles and concluded with number of counters in each group and the number of counters left over.
Explanation: Example: 28 ÷ 3(in the form of exercise 2) A. Use 28 counters to represent the 28 dominoes. Then draw 3 circles to represent the 3 players. B. Share the counters equally among the 3 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Find the number of counters in each group and the number of counters left over. Record your answer. 9 counters in each group and 3 counters are leftover.
Example: 84 ÷ 3
A. Draw 3 circles to represent the divisor. Then use base-ten blocks to model 84. Show 84 as 8 tens and 4 ones. B. Share the tens equally among the 3 groups. C. If there are any tens left, regroup them as ones. Share the ones equally among the 3 groups. D. There are 2 ten(s) and 8 one(s) in each group. So, the quotient is 28.
Question 6. Mindy is preparing fruit boxes for gifts. She divides 36 apples evenly into 6 boxes. Then she divided 54 bananas evenly into the same 6 boxes. How many pieces of fruit are in each of Mindy’s boxes? _____ pieces of fruit
Answer: 6+9=15 pieces of fruits are in each box of Mindy’s
Explanation: Total number of apples = 36 Number of boxes in which the apples were kept = 6 Number of apple pieces in each box = 36 ÷ 6 = 6 Total number of bananas = 54 Number of boxes in which the bananas were kept = 6 Number of banana pieces in each box = 54 ÷ 6 = 9 Total number of fruit pieces in each box = 9 + 6 = 15

Explanation: A. Draw 4 circles to represent the divisor. Then use base-ten blocks to model 56. Show 56 as 5 tens and 6 ones. B. Share the tens equally among the 4 groups. C. If there are any tens left, regroup them as ones. Share the ones equally among the 4 groups. D. There are 1 ten(s) and 4 one(s) in each group. So, the quotient is 14.
Sense or Nonsense?

Answer: Zach’s quick picture is correct while Angela’s is not correct.
Explanation: A. Draw 4 circles to represent the divisor. Then use base-ten blocks to model 68. Show 68 as 6 tens and 8 ones. B. Share the tens equally among the 4 groups. C. If there are any tens left, regroup them as ones. Share the ones equally among the 4 groups. D. There are 1 ten(s) and 7 one(s) in each group. So, the quotient is 17. Hence Zach’s statement and the quick picture are correct.
Question 9. Analyze What did Angela forget to do after she shared the tens equally among the 4 groups? Type below: ___________
Answer: Angela forgot to regroup the leftover tens into ones. Share the ones equally among the 4 groups.
Explanation: Since there are 6 tens and 4 circles only 4 tens can be placed in them while the other 2 tens are leftover which must be converted into 20 ones.
Common Core – Page No. 251
Model Division with Regrouping

Answer: 15 r 3
Explanation: A. Draw 4 circles to represent the divisor. Then use base-ten blocks to model 63. Show 63 as 6 tens and 3 ones. B. Share the tens equally among the 4 groups. C. If there are any tens left, regroup them as ones. Share the ones equally among the 4 groups. D. There are 1 ten(s) and 5 one(s) in each group. So, the quotient is 15. E. After grouping, there are 3 blocks which weren’t grouped. So, the remainder is 3
Question 2. 83 ÷ 3 _____ R _____
Answer: 27 r 2

Divide. Draw quick pictures. Record the steps.
Question 3. 85 ÷ 5 _____

Question 4. 97 ÷ 4 _____ R _____
Answer: 24 r 1

Question 5. Tamara sold 92 cold drinks during her 2-hour shift at a festival food stand. If she sold the same number of drinks each hour, how many cold drinks did she sell each hour? _____ cold drinks
Answer: 46 cold drinks
Explanation: Total number of cold drinks Tamara sold = 92 The time in which she sold the drinks = 2 hours Number of drinks she sold in each hour = 92 ÷ 2 = 46
Question 6. In 3 days Donald earned $42 running errands. He earned the same amount each day. How much did Donald earn from running errands each day? $ _____
Answer: $14
Explanation: Total amount earned by Donald = $42 Number of days = 3 Amount earned on each day = $42 ÷ 3 = $14
Common Core – Page No. 252
Question 1. Gail bought 80 buttons to put on the shirts she makes. She uses 5 buttons for each shirt. How many shirts can Gail make with the buttons she bought? Options: a. 14 b. 16 c. 17 d. 18
Answer: b. 16
Explanation: Total number of buttons = 80 Number of buttons used for each shirt = 5 Number of shirts she can make = 80 ÷ 5 =16
Question 2. Marty counted how many breaths he took in 3 minutes. In that time, he took 51 breaths. He took the same number of breaths each minute. How many breaths did Marty take in one minute? Options: a. 15 b. 16 c. 17 d. 19
Answer: c. 17
Explanation: Total number of breaths Marty counted = 51 Time in which the breath was counted = 3 minutes Number of breaths in one minute = 51 ÷ 3 = 17
Question 3. Kate is solving brain teasers. She solved 6 brain teasers in 72 minutes. How long did she spend on each brain teaser? Options: a. 12 minutes b. 14 minutes c. 18 minutes d. 22 minutes
Answer: a. 12 minutes
Explanation: Number of brain teasers solved = 6 Number of minutes spent on brain teasers = 72 minutes Number of minutes spent on each problem = 72 ÷ 6 =12 minutes
Question 4. Jenny works at a package delivery store. She puts mailing stickers on packages. Each package needs 5 stickers. How many stickers will Jenny use if she is mailing 105 packages? Options: a. 725 b. 625 c. 525 d. 21
Answer: c. 525
Explanation: Number of packages = 105 Number of stickers on each package = 5 Total number of stickers on the packages = 105 x 5 = 525
Question 5. The Puzzle Company packs standardsized puzzles into boxes that hold 8 puzzles. How many boxes would it take to pack up 192 standard-sized puzzles? Options: a. 12 b. 16 c. 22 d. 24
Answer: d. 24
Explanation: Total number of puzzles = 192 Number of puzzles in each box = 8 Number of boxes used = 192 ÷ 8 = 24 boxes
Question 6. Mt. Whitney in California is 14,494 feet tall. Mt. McKinley in Alaska is 5,826 feet taller than Mt. Whitney. How tall is Mt. McKinley? Options: a. 21,310 feet b. 20,320 feet c. 20,230 feet d. 19,310 feet
Answer: b. 20,320 feet
Explanation: Height of Mt. Whitney in California = 14,494 feet Height of Mt. McKinley in Alaska is 5,826 feet taller than Mt. Whitney. Therefore the height of Mt. McKinley in Alaska = 14,494 feet + 5,826 feet = 20,320 feet

Answer: 113
Explanation: STEP 1 Use place value to place the first digit. Look at the hundreds in 452. 400 hundred can be shared among 4 groups without regrouping. Now there is 1 ten to share among 4 groups. The first digit of the quotient will be in the hundreds place. STEP 2 Divide the tens. Divide. 45 ÷ 4 Multiply. 4 × 11 = 44 Subtract. 45 − 44 = 1 tens STEP 3 Divide the ones. Regroup 1 ten as 10 ones. Now there are 12 ones to share among 4 groups. Divide. 12 ones ÷ 4 Multiply. 4×3 ones Subtract. 12 ones − 12 ones = 0
So, the quotient is 113
Question 2. 4)\(\overline { 166 } \) ______ R ______
Explanation: STEP 1 Use place value to place the first digit. Look at the hundreds in 166. 1 hundred cannot be shared among 4 groups without regrouping. Now there is 1 ten to share among 4 groups. The first digit of the quotient will be in the tens place. STEP 2 Divide the tens. Divide. 166 ÷ 4 Multiply. 4 × 40 = 160 Subtract. 166 − 160 = 6 STEP 3 Divide the ones. Now there are 6 ones to share among 4 groups. Divide. 6 ones ÷ 4 Multiply. 4×1 ones Subtract. 6 ones − 4 ones = 2
So, the quotient is 41 and remainder is 2
Question 3. 5)\(\overline { 775 } \) ______
Answer: 155
Explanation: STEP 1 Use place value to place the first digit. Look at the hundreds in 775. 700 hundred can be shared among 5 groups without regrouping. Now there is 70 ten to share among 5 groups. The first digit of the quotient will be in the hundreds place. STEP 2 Divide the tens. Divide. 700 ÷ 5 Multiply. 5 × 140 = 700 Subtract. 700 − 700 = 0 STEP 3 Divide the ones. Now there are 70 tens to share among 5 groups. Divide. 70 tens ÷ 5 Multiply. 5×14 Subtract. 75 − 70 tens = 5 ones Multiply 5 x 1 = 5 Subtract 5 ÷ 5 = 0
So, the quotient is 155 (140 + 14 + 1)
Question 4. 4)\(\overline { 284 } \) ______
Explanation: STEP 1 Use place value to place the first digit. Look at the hundreds in 284. 200 hundred can be shared among 4 groups without regrouping. Now there are 20 tens to share among 4 groups. The first digit of the quotient will be in the tens place. STEP 2 Divide the tens. Divide. 200 ÷ 4 Multiply. 4 × 50 = 200 Subtract. 20 − 20 = 0 tens STEP 3 Divide the ones. Now there are 80 tens to share among 4 groups. Divide. 80 tens ÷ 4 Multiply. 4×20 = 80 Subtract. 80 tens − 80 tens = 0 ones There are 4 ones Multiply 4 x 1 = 4 Subtract 4-4 =0
So, the quotient is 71 (50+20+1)
Question 5. 5)\(\overline { 394 } \) ______ R ______
Explanation: STEP 1 Use place value to place the first digit. Look at the hundreds in 394. 300 hundred can be shared among 5 groups without regrouping. Now there is 30 ten to share among 5 groups. The first digit of the quotient will be in the tens place. STEP 2 Divide the tens. Divide. 300 ÷ 5 Multiply. 5 × 60 = 300 Subtract. 300 − 300 = 0 tens STEP 3 Divide the tens. Now there are 9 tens to share among 5 groups. Divide. 9 tens ÷ 5 Multiply. 5×18 tens Subtract. 90 tens − 90 tens = 0 ones There are 4 ones 4 is the remainder. So, the quotient is 78(60+18)
Question 6. 3)\(\overline { 465 } \) ______
Explanation: STEP 1 Use place value to place the first digit. Look at the hundreds in 465. 400 hundred can be shared among 3 groups without regrouping. Now there are 40 tens to share among 3 groups. The first digit of the quotient will be in the hundreds place. STEP 2 Divide the tens. Divide. 400 ÷ 3 Multiply. 3 × 130 = 390 Subtract. 400 − 390 = 1 tens STEP 3 Divide the tens. Now there are 7 tens and 5 ones to share among 3 groups. Divide. 75 ÷ 3 Multiply. 3 × 25 = 75 Subtract. 75 tens − 75 tens = 0
So, the quotient is 155 ( 130+ 25)
Question 7. 8)\(\overline { 272 } \) ______
Explanation: STEP 1 Use place value to place the first digit. Look at the hundreds in 272. 200 hundred can be shared among 8 groups without regrouping. Now there is 27 tens and 2 ones to share among 8 groups. The first digit of the quotient will be in the tens place. STEP 2 Divide the tens. Divide. 270 ÷ 8 Multiply. 8 × 30 = 240 Subtract. 270 − 240 = 3 tens STEP 3 Divide the ones. Regroup 3 tens as 30 ones. Now there are 30 + 2 = 32 ones to share among 8 groups. Divide. 32 ones ÷ 8 Multiply. 8×4 ones Subtract. 32 ones − 32 ones = 0
So, the quotient is 34 (30 + 4)
Practice: Copy and Solve Divide.
Question 8. 516 ÷ 2 = ______
Answer: 258
Explanation: STEP 1 Use place value to place the first digit. Look at the hundreds in 516. 500 hundred can be shared among 2 groups without regrouping. Now there is 50 tens and 16 ones to share among 2 groups. The first digit of the quotient will be in the hundreds place. STEP 2 Divide the tens. Divide. 500 ÷ 2 Multiply. 2 × 250 = 500 Subtract. 516 − 500 = 16 ones STEP 3 Divide the ones. Now there are 16 ones to share among 2 groups. Divide. 16 ones ÷ 2 Multiply. 2×8 ones Subtract. 16 ones − 16 ones = 0
So, the quotient is 258 (250 + 8)
Question 9. 516 ÷ 3 = ______
Answer: 172
Explanation: STEP 1 Use place value to place the first digit. Look at the hundreds in 516. 500 hundred can be shared among 3 groups without regrouping. Now there is 50 tens and 16 ones to share among 3 groups. The first digit of the quotient will be in the hundreds place. STEP 2 Divide the tens. Divide. 500 ÷ 3 Multiply. 3 × 160 = 480 Subtract. 516 − 480 = 36 ones STEP 3 Divide the ones. Now there are 36 ones to share among 3 groups. Divide. 36 ones ÷ 3 Multiply. 3×12 ones Subtract. 36 ones − 36 ones = 0
So, the quotient is 172 (160 + 12)
Question 10. 516 ÷ 4 = ______
Answer: 129
Explanation: STEP 1 Use place value to place the first digit. Look at the hundreds in 516. 500 hundred can be shared among 4 groups without regrouping. Now there is 50 tens and 16 ones to share among 4 groups. The first digit of the quotient will be in the hundreds place. STEP 2 Divide the tens. Divide. 500 ÷ 4 Multiply. 4 × 125 = 500 Subtract. 516 − 500 = 16 ones STEP 3 Divide the ones. Now there are 16 ones to share among 4 groups. Divide. 16 ones ÷ 4 Multiply. 4×4 ones Subtract. 16 ones − 16 ones = 0
So, the quotient is 129 (125 + 4)
Question 11. 516 ÷ 5 = ______ R ______
Answer: 103 R 1
Explanation: STEP 1 Use place value to place the first digit. Look at the hundreds in 516. 500 hundred can be shared among 5 groups without regrouping. Now there is 50 tens and 16 ones to share among 5 groups. The first digit of the quotient will be in the hundreds place. STEP 2 Divide the tens. Divide. 500 ÷ 5 Multiply. 5 × 100 = 500 Subtract. 516 − 500 = 16 ones STEP 3 Divide the ones. Now there are 16 ones to share among 5 groups. Divide. 16 ones ÷ 5 Multiply. 5×3 ones Subtract. 16 ones − 15 ones = 1 one
So, the quotient is 103 (100 + 3) and the remainder is 1
Question 12. Look back at your answers to Exercises 8–11. What happens to the quotient when the divisor increases? Explain. The quotient ______
Answer: The quotient gets decreased when we increase the divisor.
516 ÷ 4 = ______
516 ÷ 5 = ______ R ______
Question 13. Reggie has 192 pictures of animals. He wants to keep half and then divide the rest equally among three friends. How many pictures will each friend get? ______ pictures
Explanation: Total number of animal pictures = 192 Number of animal pictures he kept with him = 192 ÷ 2 = 96 Number of pictures each of his friends got = 96 ÷ 3 = 32 pictures
Question 14. There are 146 students, 5 teachers, and 8 chaperones going to the theater. To reserve their seats, they need to reserve entire rows. Each row has 8 seats. How many rows must they reserve? ______ rows
Answer: 20 rows
Explanation: Total people who went to the theatre = 146 + 5 + 8 = 159 Number of seats in each row = 8 Number of rows which must be reserved for the students = 159 ÷ 8 =19.8 = 20 (approx)

Answer: How many full pages will she have in her album? We can find number of pictures in blue pages? We can find number of pictures in green pages? We can find number of pictures in red pages?
Question 15. b. How will you use division to find the number of full pages? Type below: _________
Answer: Since the total number of pictures and the number of colour pages are given we can divide the total number of pictures are the number of pages to find the number of full pages.
Explanation: Total number of pictures =234 Number of pictures per page = 4 + 6+ 8 = 18 Number of full pages = 234 ÷ 18 =13
Question 15. c. Show the steps you will use to solve the problem. Type below: _________
Question 15. d. Complete the following sentences. Nan has _______ pictures. She wants to put the pictures in an album with pages that each hold _______ pictures. She will have an album with _______ full pages and _______ pictures on another page. Type below: _________
Answer: 234 pictures, 18 pictures, 13 full pages, 0 pictures on another page
Explanation: Total number of pictures =234 Number of pictures per page = 4 + 6+ 8 = 18 Number of full pages = 234 ÷ 18 =13 full pages
Since the remainder is 0 the number of pictures on another page = 0
Question 16. Mr. Parsons bought 293 apples to make pies for his shop. Six apples are needed for each pie. If Mr. Parsons makes the greatest number of apple pies possible, how many apples will be left? _____ pies _____ apples left over.
Answer: 48 pies and 5 apples are leftover
Explanation: Total number of apples= 293 Number of apples that make a pie = 6 Number of pies = Quotient of 293 ÷ 6 = 48 Number of apples leftover = 5

Answer: tens
Explanation: Total number of stickers = 320 Number of classes = 4 Number of stickers in each class = Quotient of 320 ÷ 4 = 80 The first digit of quotient is in the tens place.
Common Core – Page No. 257
Place the First Digit
Question 1. 62 ——- 3)\(\overline { 186 } \) -18 ——- 06 -6 ——- 0
Explanation: STEP 1 Use place value to place the first digit. Look at the hundreds in 186. 180 hundred can be shared among 3 groups without regrouping. Now there is 18 tens and 6 ones to share among 3 groups. The first digit of the quotient will be in the tens place. STEP 2 Divide the tens. Divide. 180 ÷ 3 Multiply. 3 × 60 = 180 Subtract. 186 − 180 = 6 ones STEP 3 Divide the ones. Now there are 6 ones to share among 3 groups. Divide. 6 ones ÷ 3 Multiply. 2×3 ones Subtract. 6 ones − 2 ones =0 one
So, the quotient is 62 (60 + 2) and the remainder is 0
Question 2. 4)\(\overline { 298 } \) _____ R _____
Explanation: STEP 1 Use place value to place the first digit. Look at the hundreds in 298. 280 hundred can be shared among 4 groups without regrouping. Now there is 28 tens and 18 ones to share among 4 groups. The first digit of the quotient will be in the hundreds place. STEP 2 Divide the tens. Divide. 280 ÷ 4 Multiply. 4 × 70 = 280 Subtract. 280 − 280 = 0 ones STEP 3 Divide the ones. Now there are 18 ones to share among 4 groups. Divide. 18 ones ÷ 4 Multiply. 4×4 ones Subtract. 18 ones − 16 ones = 2 ones
So, the quotient is 74 (70 + 4) and the remainder is 2
Question 3. 3)\(\overline { 461 } \) _____ R _____
Answer: 153
Explanation: STEP 1 Use place value to place the first digit. Look at the hundreds in 461. 450 hundred can be shared among 3 groups without regrouping. Now there is 45 tens and 11 ones to share among 3 groups. The first digit of the quotient will be in the hundreds place. STEP 2 Divide the tens. Divide. 450 ÷ 3 Multiply. 3 × 150 = 450 Subtract. 450 − 450 = 0 ones STEP 3 Divide the ones. Now there are 11 ones to share among 3 groups. Divide. 11 ones ÷ 3 Multiply. 3×3 ones Subtract. 11 ones − 9 ones = 2 ones
So, the quotient is 153 (150 + 3) and the remainder is 2
Question 4. 9)\(\overline { 315 } \) _____ R _____
Explanation: STEP 1 Use place value to place the first digit. Look at the hundreds in 315. 310 hundred can be shared among 9 groups without regrouping. Now there is 31 tens and 5 ones to share among 9 groups. The first digit of the quotient will be in the hundreds place. STEP 2 Divide the tens. Divide.310 ÷ 9 Multiply. 9 × 30 = 270 Subtract. 310 − 270 = 40 ones STEP 3 Divide the ones. Now there are 40 + 5 = 45 ones to share among 9 groups. Divide. 45 ones ÷ 9 Multiply. 5×9 ones Subtract. 45 ones − 45 ones = 0 ones
So, the quotient is 35 (30 + 5) and the remainder is 0
Question 5. 2)\(\overline { 766 } \) _____ R _____
Answer: 383
Explanation: STEP 1 Use place value to place the first digit. Look at the hundreds in 766. 760 hundred can be shared among 2 groups without regrouping. Now there is 76 tens and 6 ones to share among 2 groups. The first digit of the quotient will be in the hundreds place. STEP 2 Divide the tens. Divide. 760 ÷ 2 Multiply. 2 × 380 = 760 Subtract. 760 − 760 = 0 ones STEP 3 Divide the ones. Now there are 6 ones to share among 2 groups. Divide. 6 ones ÷ 2 Multiply. 2×3 ones Subtract. 6 ones − 6 ones = 0 ones
So, the quotient is 383 (380 + 3) and the remainder is 0
Question 6. 4)\(\overline { 604 } \) _____ R _____
Answer: 151
Explanation: STEP 1 Use place value to place the first digit. Look at the hundreds in 604. 600 hundred can be shared among 4 groups without regrouping. Now there is 60 tens and 4 ones to share among 4 groups. The first digit of the quotient will be in the hundreds place. STEP 2 Divide the tens. Divide. 600 ÷ 4 Multiply. 4 × 150 = 600 Subtract. 600 − 600 = 0 ones STEP 3 Divide the ones. Now there are 4 ones to share among 4 groups. Divide. 4 ones ÷ 4 Multiply. 4×1 ones Subtract. 4 ones − 4 ones = 0 ones
So, the quotient is 151 (150 + 1) and the remainder is 0
Question 7. 6)\(\overline { 796 } \) _____ R _____
Answer: 132
Explanation: STEP 1 Use place value to place the first digit. Look at the hundreds in 796. 790 hundred can be shared among 6 groups without regrouping. Now there is 79 tens and 6 ones to share among 6 groups. The first digit of the quotient will be in the hundreds place. STEP 2 Divide the tens. Divide. 790 ÷ 6 Multiply. 6 × 131 = 786 Subtract. 790 − 786 = 4 ones STEP 3 Divide the ones. Now there are 4 + 6 = 10 ones to share among 6 groups. Divide. 10 ones ÷ 6 Multiply. 6×1 ones Subtract. 10 ones − 6 ones = 4 ones
So, the quotient is 132 (131 + 1) and the remainder is 4
Question 8. 5)\(\overline { 449 } \) _____ R _____
Explanation: STEP 1 Use place value to place the first digit. Look at the hundreds in 449. 440 hundred can be shared among 5 groups without regrouping. Now there is 44 tens and 9 ones to share among 5 groups. The first digit of the quotient will be in the hundreds place. STEP 2 Divide the tens. Divide. 440 ÷ 5 Multiply. 5 × 88 = 440 Subtract. 440 − 440 = 0 ones STEP 3 Divide the ones. Now there are 9 ones to share among 5 groups. Divide. 9 ones ÷ 5 Multiply. 5×1 ones Subtract. 9 ones − 5 ones = 4 ones
So, the quotient is 89 (88 + 1) and the remainder is 4
Question 9. 6)\(\overline { 756 } \) _____ R _____
Explanation: STEP 1 Use place value to place the first digit. Look at the hundreds in 756. 750 hundred can be shared among 6 groups without regrouping. Now there is 75 tens and 6 ones to share among 6 groups. The first digit of the quotient will be in the hundreds place. STEP 2 Divide the tens. Divide. 750 ÷ 6 Multiply. 6 × 125 = 750 Subtract. 750 − 750 = 0 ones STEP 3 Divide the ones. Now there are 6 ones to share among 6 groups. Divide. 6 ones ÷ 6 Multiply. 6×1 ones Subtract. 6 ones − 6 ones = 0 ones
So, the quotient is 126 (125 + 1) and the remainder is 0
Question 10. 7)\(\overline { 521 } \) _____ R _____
Explanation: STEP 1 Use place value to place the first digit. Look at the hundreds in 521. 520 hundred can be shared among 7 groups without regrouping. Now there is 52 tens and 1 one to share among 7 groups. The first digit of the quotient will be in the hundreds place. STEP 2 Divide the tens. Divide. 520 ÷ 7 Multiply. 7 × 74 = 518 Subtract. 520 − 518 = 2 ones STEP 3 Divide the ones. Now there are 2 + 1 = 3 ones to share among 7 groups. Divide. 3 ones ÷ 7 (not possible)
So, the quotient is 74 and the remainder is 3
Question 11. 5)\(\overline { 675 } \) _____ R _____
Answer: 135
Explanation: STEP 1 Use place value to place the first digit. Look at the hundreds in 675. 670 hundred can be shared among 5 groups without regrouping. Now there is 67 tens and 5 ones to share among 5 groups. The first digit of the quotient will be in the hundreds place. STEP 2 Divide the tens. Divide. 670 ÷ 5 Multiply. 5 × 134 = 670 Subtract. 670 − 670 = 0 ones STEP 3 Divide the ones. Now there are 5 ones to share among 5 groups. Divide. 5 ones ÷ 5 Multiply. 5×1 ones Subtract. 5 ones − 5 ones = 0 ones
So, the quotient is 135 (134 + 1) and the remainder is 0
Question 12. 8)\(\overline { 933 } \) _____ R _____
Answer: 116
Explanation: STEP 1 Use place value to place the first digit. Look at the hundreds in 933. 930 hundred can be shared among 8 groups without regrouping. Now there is 93 tens and 3 ones to share among 8 groups. The first digit of the quotient will be in the hundreds place. STEP 2 Divide the tens. Divide. 930 ÷ 8 Multiply. 8 × 116 = 928 Subtract. 930 − 928 = 2 ones STEP 3 Divide the ones. Now there are 2 + 3 = 5 ones to share among 8 groups. Divide. 5 ones ÷ 8 (not possible)
So, the quotient is 116 (100 + 3) and the remainder is 5
Question 13. There are 132 projects in the science fair. If 8 projects can fit in a row, how many full rows of projects can be made? How many projects are in the row that is not full? _____ full rows _____ projects in the non-full row
Answer: 16 full rows and 4 projects in the non-full row
Explanation: Total number of projects = 132 Number of projects placed in full row = 8 Number of rows having full projects =Quotient of 132 ÷ 8 = 16 Number of projects in the non-full row = Remainder of 132 ÷ 8 = 4
Question 14. There are 798 calories in six 10-ounce bottles of apple juice. How many calories are there in one 10-ounce bottle of apple juice? _____ R _____ calories in one 10-ounce bottles of juice
Answer: 133 calories
Explanation: Number of calories in 6 bottles of apple juice = 798 Number of calories in each bottle = 798 ÷6 = 133 calories
Common Core – Page No. 258
Question 1. To divide 572 ÷ 4, Stanley estimated to place the first digit of the quotient. In which place is the first digit of the quotient? Options: a. ones b. tens c. hundreds d. thousands
Answer: c. hundreds
Explanation: The quotient of 572÷ 4 is 143 STEP 1 Use place value to place the first digit. Look at the hundreds in 572. 560 hundred can be shared among 4 groups without regrouping. Now there is 1 ten to share among 4 groups. The first digit of the quotient will be in the hundreds place.
Question 2. Onetta biked 325 miles in 5 days. If she biked the same number of miles each day, how far did she bike each day? Options: a. 1,625 miles b. 320 miles c. 65 miles d. 61 miles
Answer: c. 65 miles
Explanation: Total number of miles biked = 325 miles Number of days biked = 5 Number of miles biked on each day = Quotient of 325 ÷ 5 = 65
Question 3. Mort makes beaded necklaces that he sells for $32 each. About how much will Mort make if he sells 36 necklaces at the local art fair? Options: a. $120 b. $900 c. $1,200 d. $1,600
Answer: c. $1,200
Explanation: Cost of each beaded necklace = $32 Number of necklaces = 36 The total cost of the necklaces = $32 x 36 = $1,200 (approx)
Question 4. Which is the best estimate of 54 × 68? Options: a. 4,200 b. 3,500 c. 3,000 d. 350
Answer: b. 3,500

Question 5. Ms. Eisner pays $888 for 6 nights in a hotel. How much does Ms. Eisner pay per night? Options: a. $5,328 b. $882 c. $148 d. $114
Answer: c. $148
Explanation: Total pays of Ms Eisner in a hotel = $888 Number of nights = 6 Amount Ms Eisner pay per night = $888 ÷ 6 = $148

Answer: d. 54 ÷ 3
Explanation: Number of counters in each model = 18 Number of models = 3 Total number of counters = 18 x 3 = 54 Therefore the model displays = 54 ÷ 3

Answer: 213

Divide and check.
Question 2. 2)\(\overline { 394 } \) _____
Answer: 197

Question 3. 2)\(\overline { 803 } \) _____ R _____
Answer: 401 R 1

Question 4. 3)\(\overline { 3,448 } \) _____ R _____
Answer: 1149 R 1

Question 5. 2)\(\overline { 816 } \) _____
Answer: 408

Question 6. 4)\(\overline { 709 } \) _____ R _____
Answer: 177 R 1

Question 7. 3)\(\overline { 267 } \) _____

Question 8. The flower shop received a shipment of 248 pink roses and 256 red roses. The shop owner uses 6 roses to make one arrangement. How many arrangements can the shop owner make if he uses all the roses? _____ arrangement
Answer: 84 arrangements
Explanation: Number of pink roses = 248 Number of red roses = 256 Total number of roses = 504 Number of roses in each arrangement = 6 Number of arrangements = 504 ÷ 6 = 84

Question 9. Four teachers bought 10 origami books and 100 packs of origami paper for their classrooms. They will share the cost of the items equally. How much should each teacher pay? _____ $
Answer: $210
Explanation: Number of origami books = 10 Cost of each origami book = $24 Total cost of origami books = $24 x 10 = $240 Number of origami papers = 100 Cost of each origami book = $6 Total cost of origami books = $6 x 100 = $600 Total cost of items = $240 + $600 = $840 Number of teachers = 4 Cost earned by each teacher = $840 ÷ 4 = $210
Question 10. Communicate Six students shared equally the cost of 18 of one of the items in the chart. Each student paid $24. What item did they buy? Explain how you found your answer. __________
Answer: The students bought origami kit.
Explanation: Number of students = 6 Number of items they bought = 18 Amount each student paid = $24 The total amount paid = $24 x 6 =$144 The item they bought can be found by knowing the cost of the item: Cost of the item= The total amount paid ÷ Number of items = 144 ÷ 18 = $8 Therefore the item is origami kit.
Question 11. Ms Alvarez has $1,482 to spend on origami paper. How many packs can she buy? _____ packs
Answer: 247
Explanation: Cost of origami paper = $6 Amount Ms Alvarez was supposed to spend on origami paper = $1,482 Number of packs bought = $1,482 ÷ $6 = 247
Question 12. Evan made origami cranes with red, blue, and yellow paper. The number of cranes in each color is the same. If there are 342 cranes, how many of them are blue or yellow? _____ blue, or yellow
Answer: 114
Explanation: Evan made origami cranes with red, blue, and yellow paper. The number of cranes in each colour is the same. Total number of cranes = 342 Number of cranes of each colour = 342 ÷ 3 = 114 Therefore there are 114 cranes of blue and yellow.
Question 13. On Monday 336 fourth graders went on a field trip to a local park. The teachers divided the students into 8 groups. Use a basic fact. Estimate the number of students in each group. Show your work. _____ about
Explanation: Total number who went to the field trip = 336 Number of groups into which they were divided = 8 groups Number of students in each group = 336 ÷ 8 = 42 students
Common Core – Page No. 263
Divide by 1-Digit Numbers
Question 1. 318 2)\(\overline { 636 } \) 318 -6 × 2 —— ——- 03 636 -2 —— 16 -16 ——- 0
Answer: 318

Question 2. 4)\(\overline { 631 } \) _____ R _____

Question 3. 8)\(\overline { 906 } \) _____ R _____

Question 4. 6)\(\overline { 6,739 } \) _____ R _____

Question 5. 4)\(\overline { 2,328 } \) _____ R _____

Question 6. 5)\(\overline { 7,549 } \) _____ R _____

Question 7. The Briggs rented a car for 5 weeks. What was the cost of their rental car per week? $ _____
Answer: $197
Explanation: Cost of the car of Briggs = $985 Number of weeks = 5 Cost of rent per week = $985 ÷ 5 =$ 197
Question 8. The Lees rented a car for 4 weeks. The Santos rented a car for 2 weeks. Whose weekly rental cost was lower? Explain. The rental cost of _____
Answer: Weekly rental cost was lower for Lees compared to Santos
Explanation: Cost of the car of Lees = $632 Number of weeks = 4 Cost of rent per week = $632 ÷ 4 =$ 158
Cost of the car of Santos = $328 Number of weeks = 2 Cost of rent per week = $328 ÷ 2 =$ 164 Therefore weekly rental cost was lower for Lees compared to Santos.
Common Core – Page No. 264
Question 1. Which expression can be used to check the quotient 646 ÷ 3? Options: a. (251 × 3) + 1 b. (215 × 3) + 2 c. (215 × 3) + 1 d. 646 × 3
Answer: c. (215 × 3) + 1
Explanation: Multiply 215 x 3 = 645 Then add 1 to 645 Then the dividend is 645 + 1 = 646
Question 2. There are 8 volunteers at the telethon. The goal for the evening is to raise $952. If each volunteer raises the same amount, what is the minimum amount each needs to raise to meet the goal? Options: a. $7,616 b. $944 c. $119 d. $106
Answer: a. $7,616

Answer: d. 5 × 17 = 85
Explanation: By counting the number of counters we can give the expression. Number of counters in one row = 17 Number of rows = 5 Therefore the expression = 5 × 17 = 85
Question 4. The computer lab at a high school ordered 26 packages of CDs. There were 50 CDs in each package. How many CDs did the computer lab order? Options: a. 1,330 b. 1,300 c. 1,030 d. 130
Answer: b. 1,300
Explanation: Number of packages = 26 Number of CDs in each pack = 50 Total number of CDs the computer lab ordered = 26 x 50 = 1,300
Question 5. Which of the following division problems has a quotient with the first digit in the hundreds place? Options: a. 892 ÷ 9 b. 644 ÷ 8 c. 429 ÷ 5 d. 306 ÷ 2
Answer: d. 306 ÷ 2
Explanation: Use place value to place the first digit. Look at the hundreds in 306. 300 hundred can be shared among 2 groups without regrouping. Now there is 30 tens and 6 ones to share among 2 groups. The first digit of the quotient will be in the hundreds place.
Question 6. Sharon has 64 ounces of juice. She is going to use the juice to fill as many 6-ounce glasses as possible. She will drink the leftover juice. How much juice will Sharon drink? Options: a. 4 ounces b. 6 ounces c. 10 ounces d. 12 ounces
Answer: a. 4 ounces

Question 1. A firehouse pantry has 52 cans of vegetables and 74 cans of soup. Each shelf holds 9 cans. What is the least number of shelves needed for all the cans? First, draw a bar model for the total number of cans. Next, add to find the total number of cans. Then, draw a bar model to show the number of shelves needed. Finally, divide to find the number of shelves needed. So, _______ shelves are needed to hold all of the cans. _______ shelves

Question 2. What if 18 cans fit on a shelf? What is the least number of shelves needed? Describe how your answer would be different. _______ shelves
Answer: 7 shelves
Explanation: Total number of cans = 126 Number of cans which can fit in one shelf = 18 Number of shelves required to place all the cans = 126 ÷ 18 = 7 shelves
Question 3. Julio’s dad bought 10 dozen potatoes. The potatoes were equally divided into 6 bags. How many potatoes are in each bag? _______ potatoes
Answer: 20 potatoes
Explanation: Total number of potatoes = 10 dozens x 12 = 120 Number of bags = 6 Number of potatoes in each bag = 120 ÷ 6 = 20
Question 4. At the garden shop, each small tree costs $125 and each large tree costs $225. How much will 3 small trees and 1 large tree cost? $ _______
Answer: $600
Explanation: Number of small trees = 3 Cost of each small tree = $125 Total cost of the small trees = $125 x 3 = $375 Number of large trees = 1 Cost of each large tree = $225 Total cost of the plants = $375 + $225 = $600
Question 5. Ms Johnson bought 6 bags of balloons. Each bag has 25 balloons. She fills all the balloons and puts 5 balloons in each bunch. How many bunches can she make? _______ bunches
Explanation: Number of bags = 6 Number of ballons in each bag = 25 Total number of ballons = 25 x 6 = 150 Number of ballons in each bunch = 5 Number of bunches = Total number of ballons ÷ Number of ballons in each bunch = 150 ÷ 5 = 30
Question 6. An adult’s dinner costs $8. A family of 2 adults and 2 children pays $26 for their dinners. How much does a child’s dinner cost? Explain. $ _______
Answer: $10
Explanation: Number of adults = 2 Number of children = 2 Cost of dinner of an adult = $8 The total cost of dinner of the adults = $8 x 2 = $16 Total amount paid = $26 Amount spent on children dinner = $26 – $16 = $10 Cost of dinner for the diner = $10 ÷ 2 = $5
Question 7. Communicate Use the table at the right. Maria bought 80 ounces of apples. She needs 10 apples to make a pie. How many apples will be left over? Explain. _______ apples
Explanation: Given the average weight of the apples = 5 ounces Mass of apples Maria bought = 80 ounces Number of apples = Mass of apples Maria bought ÷ average weight of the apples = 80 ÷ 5 = 16 Number of apples which make a pie = 10 Number of apples leftover = 16 – 10 = 6
Question 8. Taylor has 16 tacks. She buys 2 packages of 36 tacks each. How many garage sale posters can she put up if she uses 4 tacks for each poster? _______ posters
Explanation: Number of packages = 2 Number of posters in each package = 36 Total number of tacks = 36 x 2 = 72 Number of tacks for each poster = 4 Number of garage sale posters = 72 ÷ 4 = 18
Question 9. Ryan bought 8 dozen bandages for the track team first-aid kit. The bandages were divided equally into 4 boxes. How many bandages are in each box? _______ bandages
Explanation: Number of bandages bought for the track team first-aid kit = 8 dozens x 12 = 96 Number of boxes = 4 Number of bandages in each box = 96 ÷ 4 = 24
Common Core – Page No. 269
Problem Solving Multistep Division Problems
Solve. Draw a diagram to help you.

Answer: 45 people can be served.

Question 2. There are 8 pencils in a package. How many packages will be needed for 28 children if each child gets 4 pencils? ________ packages
Answer: 14 packages

Question 3. There are 3 boxes of tangerines. Each box has 93 tangerines. The tangerines will be divided equally among 9 classrooms. How many tangerines will each classroom get? ________ tangerines

Question 4. Misty has 84 photos from her vacation and 48 photos from a class outing. She wants to put all the photos in an album with 4 photos on each page. How many pages does she need? ______ pages

Common Core – Page No. 270
Question 1. Gavin buys 89 blue pansies and 86 yellow pansies. He will plant the flowers in 5 rows with an equal number of plants in each row. How many plants will be in each row? Options: a. 875 b. 175 c. 35 d. 3
Answer: c. 35
Explanation: Number of blue pansies = 89 Number of yellow pansies = 86 Total number of pansies = 89 + 86 = 175 Number of rows = 5 Number of plants in each row = 175 ÷ 5 = 35
Question 2. A pet store receives 7 boxes of cat food. Each box has 48 cans. The store wants to store the cans in equal stacks of 8 cans. How many stacks can be formed? Options: a. 8 b. 42 c. 56 d. 336
Answer: b. 42
Explanation: Number of boxes of cat food = 7 Number of cans in a box = 48 Total number of cans = 48 x 7 = 336 Number of cans in each stack = 8 Number of stacks = 336 ÷ 8 = 42

Answer: d. 364
Explanation: Length = 20 +6 = 26 Breadth = 10 + 4 = 14 Area of the rectangle = 26 x 14 = 364
Question 4. Mr. Hatch bought 4 round-trip airplane tickets for $417 each. He also paid $50 in baggage fees. How much did Mr. Hatch spend? Options: a. $467 b. $1,698 c. $1,718 d. $16,478
Answer: c. $1,718
Explanation: Cost of each ticket of the airplane = $417 Cost baggage fees = $50 Number of trips of the airplane = 5 Cost of the trips = $417 x 5 = $1,668 The total cost of the trip = $1,668 + $50 = $1,718
Question 5. Mae read 976 pages in 8 weeks. She read the same number of pages each week. How many pages did she read each week? Options: a. 109 b. 120 c. 122 d. 984
Answer: c. 122
Explanation: Total number of pages = 976 Number of weeks = 8 Number of pages Mae read in each week = 976 ÷ 8 = 122
Question 6. Yolanda and her 3 brothers shared a box of 156 toy dinosaurs. About how many dinosaurs did each child get? Options: a. 40 b. 50 c. 60 d. 80
Answer: b. 50
Explanation: Total number of toy dinosaurs = 156 Number of brothers = 3 Number of toy dinosaurs each brother got = 156 ÷ 3 = 50
Page No. 271

Answer: B. 50 C. 60 The quotient is between 50 and 60

Answer: The quotient is between 15 and 20.

Answer: 19 ÷ 3 = 6 r 1
Explanation: Count the total number of counters =Dividend = 19 Number of circles = Divisor = 3 After the distribution of the counters, The quotient is 6 because in each circle there are 6 counters The leftover counter is the remainder = 1
For 4a–4d, choose Yes or No to tell whether the division sentence has a remainder.
Question 4. a. 28 ÷ 4 i. yes ii. no

Question 4. b. 35 ÷ 2 i. yes ii. no

Question 4. c. 40 ÷ 9 i. yes ii. no

Question 4. d. 45 ÷ 5 i. yes ii. no

Page No. 272
Question 5. A park guide plans the swan boat rides for 40 people. Each boat can carry 6 people at a time. What is the best way to interpret the remainder in this situation so that everyone gets a ride? Type below: ____________
Answer: 4 people are leftover after the boat takes 6 people at a time for a ride, therefore, these four people go on the ride in the next round.
Explanation: Quotient: A. Use 40 counters to represent the 40 people. Then draw 6 circles to represent the divisor. B. Share the counters equally among the 6 groups by placing them in the circles. C. Number of counters formed in each group = quotient of 40 ÷ 6 D. Number of circles are equally filled with 6 counters, therefore, the quotient is 6 Therefore, the quotient is 6 and the remainder is 4 It means that the boat takes 7 rounds in which 6 are filled with 6 people while 4 people are leftover they take the last ride.
Question 6. Nolan divides his 88 toy cars into boxes. Each box holds 9 cars. How many boxes does Nolan need to store all of his cars? ______ boxes
Explanation: Total number of toys Nolan has = 88 Number of cars placed in each box = 9 Number of boxes = 88 ÷ 9 = 9.7 = 10 (approx) We take approximate value because all the toys must be fit in the box.
A group of 140 tourists are going on a tour. The tour guide rents 15 vans. Each van holds 9 tourists.
Question 7. Part A Write a division problem that can be used to find the number of vans needed to carry the tourists. Then solve. Type below: ____________
Answer: 140 divided by 9 gives the number of vans needed to carry the tourists

Question 7. Part B What does the remainder mean in the context of the problem? Type below: ____________
Answer: The leftover of tourists = Remainder =5
Explanation: The leftover of tourists= Remainder =5 Can be placed in a different van or can be adjusted in the 15 vans.
Question 7. Part C How can you use your answer to determine if the tour guide rented enough vans? Explain. Type below: ____________
Answer: The number of vans would be correct if they were 16 instead of 15
Explanation: Then the answer can be determined as all the 140 tourists have enjoyed their trip to the fullest and traveled comfortably without any hassle and bustle.
Question 8. Solve. 3,200 ÷ 8 = ______

Page No. 273
Question 9. Which quotients are equal to 300? Mark all that apply. Options: a. 1,200 ÷ 4 b. 180 ÷ 9 c. 2,400 ÷ 8 d. 2,100 ÷ 7 e. 90 ÷ 3 f. 3,000 ÷ 3
Answer: a. 1,200 ÷ 4, c. 2,400 ÷ 8, d. 2,100 ÷ 7

Question 10. Margo estimated 188 ÷ 5 to be between 30 and 40. Which basic facts did she use to help her estimate? Mark all that apply. Options: a. 10 ÷ 5 b. 15 ÷ 5 c. 20 ÷ 5 d. 25 ÷ 5
Answer: b. 15 ÷ 5 c. 20 ÷ 5
Explanation: 188 ÷ 5 STEP 1 Identify the basic fact. 15 ÷ 5 STEP 2 Use place value. 150 = 15 tens STEP 3 Divide. 15 tens ÷ 5 = 3 tens 150 ÷ 3 = 30
STEP 1 Identify the basic fact. 20 ÷ 5 STEP 2 Use place value. 200 = 20 tens STEP 3 Divide. 20 tens ÷ 5 = 4 tens 200 ÷ 5 = 40
Therefore we can say that the quotient is between 30 to 40
Question 11. Mathias and his brother divided 2,029 marbles equally. About how many marbles did each of them receive? About _________
Answer: about 1,014 marbles each one recieved
Explanation: Total number of marbles = 2,029 Number of people = 2 Number of marbles each one received = 2,029 ÷ 2 = 1,014
For 12a–12d, choose Yes or No to show how to use the Distributive Property to break apart the dividend to find the quotient 132 ÷ 6.
Question 12. a. (115 ÷ 6) + (17 ÷ 6) i. yes ii. no
Explanation: According to the question, the nearest estimates are 115 and 17 but these are not divisible by 6.
Question 12. b. (100 ÷ 6) + (32 ÷ 6) i. yes ii. no
Explanation: According to the question, the nearest estimates are 100 and 32 but these are not divisible by 6.
Question 12. c. (90 ÷ 6) + (42 ÷ 6) i. yes ii. no
Explanation: STEP1 Find the nearest estimates of the number 132 STEP2 We can break the number 132 into 90 + 42 STEP3 We must divide the two parts of the number (dividend) with the divisor. STEP4 (90 ÷ 6) + (42 ÷ 6) STEP5 Add quotients of the above 15 +7= 22
Question 12 d. (72 ÷ 6) + (60 ÷ 6) i. yes ii. no
Explanation: STEP1 Find the nearest estimates of the number 132 STEP2 We can break the number 132 into 72 + 60 STEP3 We must divide the two parts of the number (dividend) with the divisor. STEP4 (72 ÷ 6) + (60 ÷ 6) STEP5 Add quotients of the above 12 +10= 22

Explanation: Total number of people = 60 Number of people each river raft can hold = 15 Number of rafts needed to give a ride to all the people = 60 ÷ 15 = 4
Page No. 274
A travelling circus brings along everything it needs for a show in big trucks.
Question 14. Part A The circus sets up chairs in rows with 9 seats in each row. How many rows will need to be set up if 513 people are expected to attend the show? ______ rows
Explanation: The total number of people = 513 Number of seats in each row = 9 Number of rows = 513 ÷ 9 = 57
Question 14. Part B Can the rows be divided into a number of equal sections? Explain how you found your answer. Type below: _________
Answer: Yes, the rows can be divided into equal sections. 57 ÷ 3 = 19
Explanation: We can divide 57 using the divisor as 3, then the quotient is 19 and the remainder is 0.
Question 14. Part C Circus horses eat about 250 pounds of horse food per week. About how many pounds of food does a circus horse eat each day? Explain. About ______ pounds
Answer: About 35 pounds

Question 15. Hilda wants to save 825 digital photographs in an online album. Each folder of the album can save 6 photographs. She uses division to find out how may full folders she will have. In what place is the first digit of the quotient? _________
Answer: Hundreds place
Explanation: Use place value to place the first digit. Look at the hundreds in 825. 800 hundred can be shared among 6 groups without regrouping. Now there is 80 tens and 25 ones to share among 6 groups. The first digit of the quotient will be in the hundreds place.
Page No. 275

Answer: 1st picture – 150 ÷ 30 2nd picture – 160 ÷ 40 3rd picture – 150 ÷ 50 4th picture – 160 ÷ 80

Question 17. Popcorn was donated for the school fair by 3 different popcorn vendors. They donated a total of 636 bags of popcorn. Each vendor donated the same number of bags. How many bags of popcorn did each vendor donate? ______ bags

Answer: 212

Page No. 276

Answer: tens place
Explanation: Use place value to place the first digit. Look at the hundreds in 750. 720 hundred can be shared among 9 groups without regrouping. Now there is 72 tens and 30 ones to share among 9 groups. The first digit of the quotient will be in the tens place.
Question 21. Ursula bought 9 dozen rolls of first aid tape for the health office. The rolls were divided equally into 4 boxes. How many rolls are in each box? _____ rolls
Answer: 27 rolls
Explanation: Number of rolls = 9 dozen x 12 = 108 Number of boxes = 4 Number of rolls in each box = Quotient of 108 ÷ 4 = 27 rolls
Question 22. There are 112 seats in the school auditorium. There are 7 seats in each row. There are 70 people seated, filling up full rows of seats. How many rows are empty? _____ empty rows
Answer: 6 rows are empty
Explanation: Total number of seats = 112 Number of seats in each row = 7 Number of rows = 112÷7 = 16
Number of people seated = 70 Number of rows fully occupied by the people = 70 ÷ 7 = 10 Number of empty rows = 16 – 10 = 6

Page No. 280
Answer: 6 x 2 = 12
Explanation: There are a total of 12 counters in the given figure. So, we can see that 6 + 6 = 12 from the above figure. Hence we can write as 6 x 2 = 12

Question 1.
Answer: 4 x 3 = 12
Explanation: The number of columns and rows are 4 and 3 respectively. So we can calculate the multiplication by 4 x 3 = 12
Explanation: The number of columns and rows are 4 and 3 respectively. So we can calculate the multiplication by 4 x 3 = 12.
Use tiles to find all the factors of the product. Record the arrays and write the factors shown.
Question 2. 5: __________ Type below: ________
Question 3. 20: __________ Type below: ________
Question 4. 25: __________ Type below: ________
Page No. 281
Practice: Copy and Solve Use tiles to find all the factors of the product. Record the arrays on grid paper and write the factors shown.
Question 5. 9: ______________ Type below: ________
Question 6. 21: ______________ Type below: ________
Question 7. 17: ______________ Type below: ________
Question 8. 18: ______________ Type below: ________

Question 9. Pablo is using 36 tiles to make a patio. Can he arrange the tiles in another way and show the same factors? Draw a quick picture and explain. Type below: ________
Question 10. How many different rectangular arrays can Pablo make with all 36 tiles, so none of the arrays show the same factors? ________ rectangular arrays
Question 11. If 6 is a factor of a number, what other numbers must be factors of the number? Type below: ________
Question 12. Jean spent $16 on new T-shirts. If each shirt cost the same whole-dollar amount, how many could she have bought? Type below: ________
Page No. 282

Question 13. b. How is finding the number of ways to model a rectangular house related to finding factor pairs? Type below: ________
Question 13. c. Why is finding the factor pairs only the first step in solving the problem? Type below: ________
Question 13. d. Show the steps you used to solve the problem. Type below: ________
Question 13. Complete the sentences. Factor pairs for 18 are ___________________ . There are ______ different ways Carmen can arrange the cubes to model the house. Type below: ________
Question 14. Sarah was organizing vocabulary words using index cards. She arranged 40 index cards in the shape of a rectangle on a poster. For 14a–14e, choose Yes or No to tell whether a possible arrangement of cards is shown. a. 4 rows of 10 cards i. yes ii. no
Question 14. b. 6 rows of 8 cards i. yes ii. no
Question 14. c. 20 rows of 2 cards i. yes ii. no
Question 14. d. 40 rows of 1 card i. yes ii. no
Question 14. e. 35 rows of 5 cards i. yes ii. no
Conclusion:
I think the answers provided in the Go Math Grade 4 Answer Key Chapter 4 Divide by 1-Digit Numbers are beneficial for all the students of 4th grade. Our aim is to help the students to become masters in maths. So, Refer to our HMH Go Math 4th Grade Answer Key Chapter 4 Divide by 1-Digit Numbers and secure good marks in the exams.
Share this:
Leave a comment cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- Engageny Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- enVision Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy
Go Math Grade 4 Answer Key Chapter 6 Fraction Equivalence and Comparison
Gain some basic knowledge about the Fraction Equivalence and Comparison topics by accessing the free Go Math Grade 4 Answer Key Chapter 6 Fraction Equivalence and Comparison. This resource of Go Math Grade 4 Answer Key aid your preparation for the standard tests. All the lessons covered in chapter 6 Fraction Equivalence and Comparison HMH Go Math Grade 4 Solution Key can be more efficient while your practice sessions. So, get the Homework Help needed by referring to the Go Math Grade 4 Answer Key Chapter 6 Fraction Equivalence and Comparison.
Go Math Grade 4 Chapter 6 Fraction Equivalence and Comparison Answer Key
Download Go Math Grade 4 Solution Key Chapter 6 Fraction Equivalence and Comparison and prepare the concepts whenever you wish. Take the help from the given resource and solve the Grade 4 chapter 6 Fraction Equivalence and Comparison regularly to score high. Refer to the detailed Solutions presented here in Go Math Grade 4 Chapter 6 Fraction Equivalence and Comparison Answer Key and review your answers.
Lesson 1: Investigate • Equivalent Fractions
- Equivalent Fractions – Page No. 331
- Equivalent Fractions Lesson Check – Page No. 332
Lesson 2: Generate Equivalent Fractions
- Generate Equivalent Fractions – Page No. 335
- Generate Equivalent Fractions Lesson Check – Page No. 336
- Generate Equivalent Fractions Lesson Check 1 – Page No. 337
- Generate Equivalent Fractions Lesson Check 2 – Page No. 338
Lesson 3: Simplest Form
- Simplest Form – Page No. 341
- Simplest Form Lesson Check – Page No. 342
- Simplest Form Lesson Check 1 – Page No. 343
- Simplest Form Lesson Check 2 – Page No. 344
Lesson 4: Common Denominators
- Common Denominators – Page No. 347
- Common Denominators Lesson Check – Page No. 348
- Common Denominators Lesson Check 1 – Page No. 349
- Common Denominators Lesson Check 2 – Page No. 350
- Common Denominators Lesson Check 3 – Page No. 353
- Common Denominators Lesson Check 4 – Page No. 354
Lesson 5: Problem Solving • Find Equivalent Fractions
- Find Equivalent Fractions – Page No. 355
- Find Equivalent Fractions Lesson Check – Page No. 356
Mid-Chapter Checkpoint
- Mid-Chapter Checkpoint – Page No. 357
- Mid-Chapter Checkpoint Lesson Check – Page No. 358
Lesson 6: Compare Fractions Using Benchmarks
- Compare Fractions Using Benchmarks – Page No. 361
- Compare Fractions Using Benchmarks Lesson Check – Page No. 362
- Compare Fractions Using Benchmarks Lesson Check 1 – Page No. 363
- Compare Fractions Using Benchmarks Lesson Check 2 – Page No. 364
Lesson 7: Compare Fractions
- Compare Fractions – Page No. 367
- Compare Fractions Lesson Check – Page No. 368
- Compare Fractions Lesson Check 1 – Page No. 369
- Compare Fractions Lesson Check 2 – Page No. 370
Lesson 8: Compare and Order Fractions
- Compare and Order Fractions – Page No. 373
- Compare and Order Fractions Lesson Check – Page No. 374
- Compare and Order Fractions Lesson Check 1 – Page No. 375
- Compare and Order Fractions Lesson Check 2- Page No. 376
Review/Test
- Review/Test – Page No. 377
- Review/Test – Page No. 378
- Review/Test – Page No. 379
- Review/Test – Page No. 380
- Review/Test – Page No. 381
- Review/Test – Page No. 382
- Review/Test – Page No. 387
- Review/Test – Page No. 388
Common Core – Equivalent Fractions – Page No. 331
Equivalent Fractions Use the model to write an equivalent fraction.

Answer: \(\frac{4}{6}=\frac{2}{3}\)
Explanation: The first image has 4 parts shaded our of 6 parts. Divide \(\frac{8}{10}\) with 2. You will get \(\frac{2}{3}\). That means 2 parts are shaded out of 3 parts.
Answer: \(\frac{3}{4}\) = \(\frac{6}{8}\)
Explanation: The first image has 3 parts shaded our of 4 parts. Multiply \(\frac{8}{10}\) with 2. You will get \(\frac{6}{8}\). That means 6 parts are shaded out of 8 parts.
Tell whether the fractions are equivalent. Write = or ≠.
Question 3. \(\frac{8}{10}\) _______ \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Answer: \(\frac{8}{10}\) = \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Explanation: Multiply the numerator and denominator of 4 / 5 with 2 8 / 10 = (2 / 2 ) x (4 / 5 ) = 8 / 10 So, 8 / 10 = 4 / 5.
Question 4. \(\frac{1}{2}\) _______ \(\frac{7}{12}\)
Answer: \(\frac{1}{2}\) ≠ \(\frac{7}{12}\)
Explanation: Multiply the numerator and denominator of 1 / 2 with 6 1 / 2 = (6 / 6) x (1 / 2) = (6 / 12) So, 1/2 ≠ 7 / 12
Question 5. \(\frac{3}{4}\) _______ \(\frac{8}{12}\)
Answer: \(\frac{3}{4}\) ≠ \(\frac{8}{12}\)
Explanation: Multiply the numerator and denominator of 3 / 4 with 3 3 / 4 = (3 / 3) x (3 / 4) = (9 / 12) So, 3 / 4 ≠ 8 / 12
Question 6. \(\frac{2}{3}\) _______ \(\frac{4}{6}\)
Answer: \(\frac{2}{3}\) = \(\frac{4}{6}\)
Explanation: Multiply the numerator and denominator of 2 / 3 with 2 2 / 3 = (2 / 2) x ( 2 / 3 ) = 4 / 6 So, 2 / 3 = 4 / 6.
Question 7. \(\frac{5}{8}\) _______ \(\frac{4}{10}\)
Answer: \(\frac{5}{8}\) ≠ \(\frac{4}{10}\)
Explanation: Multiply the numerator and denominator of 5 / 8 with 2 5 / 8 =(2 / 2) x (5 / 8) = (10 / 16) So, 5 / 8 ≠ 4 / 10
Question 8. \(\frac{2}{6}\) _______ \(\frac{4}{12}\)
Answer: \(\frac{2}{6}\) = \(\frac{4}{12}\)
Explanation: Multiply the numerator and denominator of 2 / 6 with 2 2 / 6 = (2 / 2) x (2 / 6) = (4 / 12) So, 2 / 6 = 4 / 12.
Question 9. \(\frac{20}{100}\) _______ \(\frac{1}{5}\)
Answer: \(\frac{20}{100}\) = \(\frac{1}{5}\)
Explanation: Cross Multiply the 20 / 100 with 20 / 20 20 / 100 = (20 / 20) x (20 / 100) = (1 / 5) So, 20 / 100 = 1 / 5.
Question 10. \(\frac{5}{8}\) _______ \(\frac{9}{10}\)
Answer: \(\frac{5}{8}\) ≠ \(\frac{9}{10}\)
Explanation: Multiply the numerator and denominator of 5 / 8 with 2 5 / 8 = (2 / 2) x (5 / 8) = 10 / 16 So, 5 / 8 ≠ 9 / 10
Question 11. Jamal finished \(\frac{5}{6}\) of his homework. Margaret finished \(\frac{3}{4}\) of her homework, and Steve finished \(\frac{10}{12}\) of his homework. Which two students finished the same amount of homework? _______
Answer: Jamal and Steve
Explanation: As per the given data, Jamal finished work = 5 /6 of his homework Margaret finished work = 3 / 4th of her homework Steve finished work = 10 / 12 of his homework Multiply the numerator and denominator of 5/ 6 with 2 Then, (2 / 2) x (5 / 6) = 10 / 12 Then, Jamal and Steve finished the same amount of homework.
Question 12. Sophia’s vegetable garden is divided into 12 equal sections. She plants carrots in 8 of the sections. Write two fractions that are equivalent to the part of Sophia’s garden that is planted with carrots. Type below: ___________
Answer: \(\frac{2}{3}\) and \(\frac{4}{6}\)
Explanation: As per the given data, Sophia’s vegetable garden is divided into 12 equal sections She plants carrots in 8 of the sections out of 12 sections = 8 / 12 By simplifying the 8 / 12, we will get 4 / 6 Again simplify the 4 /6 by dividing method, you will get 2 /3 2 / 3 = (2 / 2) x (2 / 3) = 4 / 6 Then, the equivalent fractions are 2 / 3, 4 /6
Common Core – Equivalent Fractions – Page No. 332
Question 1. A rectangle is divided into 8 equal parts. Two parts are shaded. Which fraction is equivalent to the shaded area of the rectangle? Options: a. \(\frac{1}{4}\) b. \(\frac{1}{3}\) c. \(\frac{2}{6}\) d. \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Answer: a. \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Explanation: As per the given data, A rectangle is divided into 8 equal parts Two parts are shaded Then, the shaded area of rectangle = 2 / 8 By simplifying the 2/ 8, you will get 1/ 4 So, the shaded area of rectangle = 1 / 4
Question 2. Jeff uses 3 fifth-size strips to model \(\frac{3}{5}\). He wants to use tenth-size strips to model an equivalent fraction. How many tenth-size strips will he need? Options: a. 10 b. 6 c. 5 d. 3
Answer: b. 6
Explanation: From the given data, Jeff uses 3 fifth –size strips to model = 3 / 5 size strips If he want to use tenth – size strips to an equivalent fraction = 1 / 10 size strips The number of strips = x (1 / 10) x = 3 / 5 x = 30/5 then, required number of tenth size trips = 6
Question 3. Cassidy places 40 stamps on each of 8 album pages. How many stamps does she place in all? Options: a. 300 b. 320 c. 360 d. 380
Answer: b. 320
Explanation: As per the given data, Cassidy places 40 stamps on each of 8 album pages = 8 x 40 = 320 So, total placed stamps on album pages by Cassidy = 320 stamps
Question 4. Maria and 3 friends have 1,200 soccer cards. If they share the soccer cards equally, how many will each person receive? Options: a. 30 b. 40 c. 300 d. 400
Answer: c. 300
Explanation: As per the given data, Maria and 3 friends have 1200 soccer cards If soccer cards shared equally by four members = 1200/4 = 300 Then, each person received soccer cards = 300
Question 5. Six groups of students sell 162 balloons at the school carnival. There are 3 students in each group. If each student sells the same number of balloons, how many balloons does each student sell? Options: a. 9 b. 18 c. 27 d. 54
Answer: a. 9
Explanation: As per the given, data, Six groups of students sell 162 balloons at the school carnival There are 3 students in each group Then, total number of students in 6 groups = 6 x 3 = 18 If each student sells the same number of balloons = 162 / 18 = 9 Number of balloons sells by each student = 9
Question 6. Four students each made a list of prime numbers. Eric: 5, 7, 17, 23 Maya: 3, 5, 13, 17 Bella: 2, 3, 17, 19 Jordan: 7, 11, 13, 21 Who made an error and included a composite number? Options: a. Eric b. Maya c. Bella d. Jordan
Answer: d. Jordan
Explanation: As per the given data, Four students each made a list of prime numbers. Eric: 5, 7, 17, 23 Maya: 3, 5, 13, 17 Bella: 2, 3, 17, 19 Jordan: 7, 11, 13, 21 21 is not a prime number So, An error made by Jordan
Page No. 335
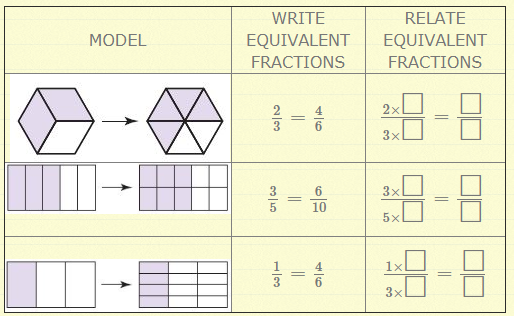
Write two equivalent fractions.
Question 2. \(\frac{4}{5}\) \(\frac{4}{5}\) = \(\frac { 4×□ }{ 5×□ } \) = \(\frac{□}{□}\) \(\frac{4}{5}\) = \(\frac { 4×□ }{ 5×□ } \) = \(\frac{□}{□}\) \(\frac{4}{5}\) = \(\frac{□}{□}\) = \(\frac{□}{□}\) Type below: ___________
Answer: \(\frac{4}{5}\) = \(\frac{8}{10}\) = \(\frac{80}{100}\)
Explanation: Two equivalent fractions of 4/5, (4/5) x (2/2) = 8/10 And (4/5) x (20/20) = 80/100 8/10 = (8/10) (10/10) = (80/100) So, the equivalent fractions of 4/5 = 8/10, 80/100
Question 3. \(\frac{2}{4}\) \(\frac{2}{4}\) = \(\frac { 2×□ }{ 4×□ } \) = \(\frac{□}{□}\) \(\frac{2}{4}\) = \(\frac { 2×□ }{ 4×□ } \) = \(\frac{□}{□}\) \(\frac{2}{4}\) = \(\frac{□}{□}\) = \(\frac{□}{□}\) Type below: ___________
Answer: \(\frac{2}{4}\) = \(\frac{4}{8}\) = \(\frac{8}{16}\)
Explanation: Two equivalent fractions of 2/4, (2/4) x (2/2) = 4/8 And (2/4) x (4/4) = 8/16 4/8 = (4/8) (2/2) = (8/16) So, the equivalent fractions of 2/4 = 4/8, 8/16
Question 4. \(\frac{3}{6}\) \(\frac{3}{6}\) = \(\frac{□}{□}\) = \(\frac{□}{□}\) Type below: ___________
Answer: \(\frac{3}{6}\) = \(\frac{6}{12}\) = \(\frac{12}{24}\)
Explanation: Two equivalent fractions of 3/6, (3/ 6) x (2/2) = 6/12 And (3/6) x (4/ 4) = 12/24 6/12 = (6/12) (2/2) = (12/24) So, the equivalent fractions of 3/6 = 6/12, 12/24
Question 5. \(\frac{3}{10}\) \(\frac{3}{10}\) = \(\frac{□}{□}\) = \(\frac{□}{□}\) Type below: ___________
Answer: \(\frac{3}{10}\) = \(\frac{6}{20}\) = \(\frac{12}{40}\)
Explanation: Two equivalent fractions of 3/10, (3/ 10) x (2/2) = 6/20 And (3/10) x (4/ 4) = 12/40 6/20 = (6/20) (2/2) = (12/40) So, the equivalent fractions of 3/10 = 6/20, 12/40
Question 6. \(\frac{2}{5}\) \(\frac{2}{5}\) = \(\frac{□}{□}\) = \(\frac{□}{□}\) Type below: ___________
Answer: \(\frac{2}{5}\) = \(\frac{4}{10}\) = \(\frac{8}{20}\)
Explanation: Two equivalent fractions of 2/5, (2/ 5) x (2/2) = 4/10 And (2/5) x (4/ 4) = 8/20 4/10 = (4/10) (2/2) = (8/20) So, the equivalent fractions of 2/5 = 4/10, 8/20
Question 7. \(\frac{5}{6}\) ______ \(\frac{10}{18}\)
Answer: \(\frac{5}{6}\) ≠ \(\frac{10}{18}\)
Explanation: Multiply the numerator and denominator of 5/6 with 2 5/6 =(2/2) x (5/6) = (10/12) So, 5/6 ≠ 10/ 18
Question 8. \(\frac{4}{5}\) ______ \(\frac{8}{10}\)
Answer: \(\frac{4}{5}\) = \(\frac{8}{10}\)
Explanation: Multiply the numerator and denominator of 4/5 with 2 4/5 =(2/2) x (4/5) = (8/10) So, 4/5 = 8/10
Question 9. \(\frac{1}{5}\) ______ \(\frac{4}{10}\)
Answer: \(\frac{1}{5}\) ≠ \(\frac{4}{10}\)
Explanation: Multiply the numerator and denominator of 1/5 with 4 1/5 =(4/4) x (1/5) = (4/20) So, 1/5 ≠ 4/10
Question 10. \(\frac{1}{4}\) ______ \(\frac{2}{8}\)
Answer: \(\frac{1}{4}\) = \(\frac{2}{8}\)
Explanation: Multiply the numerator and denominator of 1/4 with 2 1/4 =(2/2) x (1/4) = (2/8) So, 1/4 = 2/8
Page No. 336
Question 11. Kim says the amount of flour in the recipe can be expressed as a fraction. Is she correct? Explain. ______
Answer: As per the given data, Kim says the amount of flour in the recipe can be expressed as a fraction. But in the recipe, 1 tablespoon flour is added. So, Kim says wrong.
Question 12. How could you use a \(\frac{1}{8}\) – cup measuring cup to measure the light corn syrup? Type below: _________
Answer: As per the given data, By using the 1/8 cup measure the 9/12 cup light corn syrup (9/12)/(1/8) = (9 x 8)/12 = (3 x 8)/4 = (3 x 2) = 6 So, required 6 cups of 1/8 to measure the light corn syrup of 9/12.
Question 13. Communicate Explain using words how you know a fraction is equivalent to another fraction. Type below: _________
Answer: If you multiply the numerator and denominator of the first fraction by the same number and the products are the numerator and denominator of the second fraction, then the fractions are equivalent
Question 14. Kyle drank \(\frac{2}{3}\) cup of apple juice. Fill in each box with a number from the list to generate equivalent fractions for \(\frac{2}{3}\). Not all numbers will be used. Type below: _________
Answer: \(\frac{4}{6}\) and \(\frac{12}{18}\)
Explanation: As per the given data, Kyle drank 2/3 cup of apple juice (2/3) x (2/2) = 4/6 (4/6) x (3/3) = 12/18 Equivalent fractions of 2/3 are 4/6 and 12/18
Common Core – Equivalent Fractions – Page No. 337
Write two equivalent fractions for each.
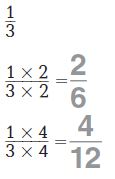
Answer: \(\frac{2}{6}\) and \(\frac{4}{12}\)
Explanation: 1/3 (1/3) x (2/2) = 2/6 (1/3) x (4/4) = 4/12 So, the equivalent fractions of 1/3 are 2/6 and 4/12
Question 2. \(\frac{2}{3}\) Type below: _________
Answer: \(\frac{4}{6}\) and \(\frac{8}{12}\)
Explanation: 2/3 (2/3) x (2/2) = 4/6 (2/3) x (4/4) = 8/12 Then, the equivalent fractions of 2/3 = 4/6 and 8/12
Question 3. \(\frac{1}{2}\) Type below: _________
Answer: \(\frac{2}{4}\) and \(\frac{4}{8}\)
Explanation: 1/2 (1/2) x (2/2) = 2/4 (1/2) x (4/4) = 4/8 Then, the equivalent fractions of 1/2 = 2/4, 4/8
Question 4. \(\frac{4}{5}\) Type below: _________
Answer: \(\frac{8}{10}\) and \(\frac{80}{100}\)
Explanation: 4/5 (4/5) x (2/2) = 8/10 (4/5) x (20/20) = 80/100 Then, the equivalent fractions of 4/5 = 8/10 and 80/100
Tell whether the fractions are equivalent. Write # or ≠.
Question 5. \(\frac{1}{4}\) ______ \(\frac{3}{12}\)
Answer: \(\frac{1}{4}\) = \(\frac{3}{12}\)
Explanation: 1/4 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 1/4 with 3 Then, (1/4) x (3/3) = 3/12 So, 1/4 = 3/12
Question 6. \(\frac{4}{5}\) ______ \(\frac{5}{10}\)
Answer: \(\frac{4}{5}\) ≠ \(\frac{5}{10}\)
Explanation: 4/5 Multiply numerator and denominator of 4/5 with 2 (4/5) x (2/2) = 8/10 Then 4/5 ≠ 5/10
Question 7. \(\frac{3}{8}\) ______ \(\frac{2}{6}\)
Answer: \(\frac{3}{8}\) ≠ \(\frac{2}{6}\)
Explanation: 3/8 ≠ 2/6
Question 8. \(\frac{3}{4}\) ______ \(\frac{6}{8}\)
Explanation: 3/4 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 3/4 with 2 Then, (3/4) x (2/2) = 6/8 So, 3/4 = 6/8
Question 9. \(\frac{5}{6}\) ______ \(\frac{10}{12}\)
Answer: \(\frac{5}{6}\) = \(\frac{10}{12}\)
Explanation: 5/6 Multiply the numerator and denominator with 2 (5/6) x (2/2) = 10/12 So, 5/6 = 10/12
Question 10. \(\frac{6}{12}\) ______ \(\frac{5}{8}\)
Answer: \(\frac{6}{12}\) ≠ \(\frac{5}{8}\)
Explanation: 6/12 ≠ 5/8
Question 11. \(\frac{2}{5}\) ______ \(\frac{4}{10}\)
Answer: \(\frac{2}{5}\) = \(\frac{4}{10}\)
Explanation: 2/5 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 2/5 with 2 (2/5) x (2/2) = 4/10 So, 2/5 = 4/10
Question 12. \(\frac{2}{4}\) ______ \(\frac{3}{12}\)
Answer: \(\frac{2}{4}\) ≠ \(\frac{3}{12}\)
Explanation: 2/4 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 2/4 with 3 (2/4) x (3/3) = 6/12 So, 2/4 ≠ 3/ 12
Question 13. Jan has a 12-ounce milkshake. Four ounces in the milkshake are vanilla, and the rest is chocolate. What are two equivalent fractions that represent the fraction of the milkshake that is vanilla? Type below: _________
Answer: \(\frac{1}{3}\) and \(\frac{2}{6}\)
Explanation: As per the given data, Jan has a 12-ounce milkshake Four ounces in the milkshake are vanilla = 4/12 = 1/3 Then, 8-ounces in milkshake are chocolate = 8/12 = 2/3 4/12 = 1/3 By multiplying 1/3 with 2 (1/3) x (2/2) = 2/6 So, the equivalent fractions of vanilla milkshake are 1/3 and 2/6
Question 14. Kareem lives \(\frac{4}{10}\) of a mile from the mall. Write two equivalent fractions that show what fraction of a mile Kareem lives from the mall. Type below: _________
Answer: \(\frac{2}{5}\) and \(\frac{8}{20}\)
Explanation: As per the given data, Kareem lives 4/10 of a mile from the mall To find the equivalent fractions of 4/10 Simplify the 4/10 = 2/5 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 2/5 with 4 (2/5) x (4/4) = 8/20 Then, the equivalent fraction of a mile Kareem lives from the mall = 2/5 and 8/20
Common Core – Equivalent Fractions – Page No. 338
Question 1. Jessie colored a poster. She colored \(\frac{2}{5}\) of the poster red. Which fraction is equivalent to \(\frac{2}{5}\)? Options: a. \(\frac{4}{10}\) b. \(\frac{7}{10}\) c. \(\frac{4}{5}\) d. \(\frac{2}{2}\)
Answer: a. \(\frac{4}{10}\)
Explanation: As per the given data, Jessie colored a poster She colored 2/5th of the poster red Multiply the numerator and denominator of 2/5 with 2 Then, (2/5) x (2/2) = 4 /10 So, the equivalent fraction of 2/5 is 4/10
Question 2. Marcus makes a punch that is \(\frac{1}{4}\) cranberry juice. Which two fractions are equivalent to \(\frac{1}{4}\)? Options: a. \(\frac{2}{5}, \frac{3}{12}\) b. \(\frac{2}{8}, \frac{4}{12}\) c. \(\frac{3}{4}, \frac{6}{8}\) d. \(\frac{2}{8}, \frac{3}{12}\)
Answer: d. \(\frac{2}{8}, \frac{3}{12}\)
Explanation: As per the given data, Marcus makes a punch that is 1/4th of cranberry juice Multiply the numerator and denominator of 1/4 with 2 Then, (1/4) x (2/2) = 2/8 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 1/4 with 3 Then, (1/4) x (3/3) = 3/12 Equivalent fractions of 1/4 are 2/8 and 3/12
Question 3. An electronics store sells a large flat screen television for $1,699. Last month, the store sold 8 of these television sets. About how much money did the store make on the television sets? Options: a. $160,000 b. $16,000 c. $8,000 d. $1,600
Answer: b. $16,000
Explanation: As per the given data, An electronics store sells a large flat-screen television for $1,699 Last month, the store sold 8 of these television sets = 8 x $1,699 = $13,952. The money is about to $16,000.
Question 4. Matthew has 18 sets of baseball cards. Each set has 12 cards. About how many baseball cards does Matthew have in all? Options: a. 300 b. 200 c. 150 d. 100
Answer: b. 200
Explanation: From the given data, Matthew has 18 sets of basketball cards Each set has 12 cards = 12 x 18 = 216 Total number of basketball cards with Matthew = 216. So, it is near to 200.
Question 5. Diana had 41 stickers. She put them in 7 equal groups. She put as many as possible in each group. She gave the leftover stickers to her sister. How many stickers did Diana give to her sister? Options: a. 3 b. 4 c. 5 d. 6
Answer: d. 6
Explanation: As per the given data, Diana has 41 stickers She put them in 7 equal groups = 41/7 = 5 (remaining 6) She gave the leftover stickers to her sister The number of stickers Diana give to her sister = 6
Question 6. Christopher wrote the number pattern below. The first term is 8. 8, 6, 9, 7, 10, … Which is a rule for the pattern? Options: a. Add 2, add 3. b. Add 6, subtract 3. c. Subtract 6, add 3. d. Subtract 2, add 3
Answer: d. Subtract 2, add 3
Explanation: From the given data, Christopher wrote the number pattern = 8, 6, 9, 7, 10, ….. The first number in the pattern = 8 8 – 2 = 6 + 3 = 9 – 2 = 7 +3 = 10 …. So, the rule for the above pattern is to subtract 2, add 3
Page No. 341
Question 1. Write \(\frac{8}{10}\) in simplest form. \(\frac{8}{10}\) = \(\frac { 8÷□ }{ 10÷□ } \) = \(\frac{□}{□}\) \(\frac{□}{□}\)
Answer: \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Explanation: 8/10 in simplest form Divide the 8/10 with 2 (8/2)/(10/2) = 4/5 So, the simplest form of 8/10 is 4/5
Write the fraction in simplest form.
Question 2. \(\frac{6}{12}\) \(\frac{□}{□}\)
Answer: \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation: 6/12 in simplest form Divide the 6/12 with 6 (6/6)/(12/6) = 1/2 So, the simplest form of 6/12 is 1/2
Question 3. \(\frac{2}{10}\) \(\frac{□}{□}\)
Answer: \(\frac{1}{5}\)
Explanation: 2/10 in simplest form Divide the 2/10 with 2 (2/2)/(10/2) = 1/5 So, the simplest form of 2/10 is 1/5
Question 4. \(\frac{6}{8}\) \(\frac{□}{□}\)
Answer: \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Explanation: 6/8 in simplest form Divide the 6/8 with 2 (6/2)/(8/2) = 3/4 So, the simplest form of 6/8 is 3/4
Question 5. \(\frac{4}{6}\) \(\frac{□}{□}\)
Answer: \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Explanation: 4/6 in simplest form Divide the 4/6 with 2 (4/2)/(6/2) = 2/3 So, the simplest form of 4/6 is 2/3
Question 6. \(\frac{9}{12}\) \(\frac{□}{□}\)
Explanation: 9/12in simplest form Divide the 9/12 with 3 (9/3)/(12/3) = 3/4 So, the simplest form of 9/12 is 3/4
Question 7. \(\frac{4}{8}\) \(\frac{□}{□}\)
Explanation: 4/8in simplest form Divide the 4/8 with 4 (4/4)/(8/4) = 1/2 So, the simplest form of 4/8 is 1/2
Question 8. \(\frac{10}{12}\) \(\frac{□}{□}\)
Answer: \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Explanation: 10/12 in simplest form Divide the 10/12 with 2 (10/2)/(12/2) = 5/6 So, the simplest form of 10/12 is 5/6
Question 9. \(\frac{20}{100}\) \(\frac{□}{□}\)
Explanation: 20 /100 in simplest form Divide the 20/100 with 20 (20/20)/(100/20) = 1/5 So, the simplest form of 20/100 is 1/5
Tell whether the fraction is in simplest form. Write yes or no.
Question 10. \(\frac{2}{8}\) ______
Explanation: 2/8 in simplest form Divide the 2/8 with 2 (2/2)/(8/2) = 1/4 The simplest form of 2/8 is 1/4 So, 2/8 is not the simplest form
Question 11. \(\frac{9}{12}\) ______
Explanation: 9/12 in simplest form Divide the 9/12 with 3 (9/3)/(12/3) = 3/4 The simplest form of 9/12 is 3/4 So, 9/12 is not the simplest form
Question 12. \(\frac{5}{6}\) ______
Answer: Yes
Explanation: 5/6 is not divided by any number Yes, 5/6 is the simplest form
Question 13. \(\frac{4}{10}\) ______
Explanation: 4/10 in simplest form Divide the 4/10 with 2 (4/2)/(10/2) = 2/5 So, 4/10 is not the simplest form
Question 14. There are 18 students in Jacob’s homeroom. Six students bring their lunch to school. The rest eat lunch in the cafeteria. In simplest form, what fraction of students eat lunch in the cafeteria? \(\frac{□}{□}\) of students
Answer: \(\frac{2}{3}\) of students
Explanation: As per the given data, There are 18 students in Jacob’s homeroom 6 students bring their lunch to school = 6/18 = 1/3 The rest eat lunch in the cafeteria = 18 – 6 = 12/18 Divide the numerator and denominator of 12/18 with 6 (12/6) x (18/6) = 2/3 So, 2/3 of students eat lunch in the cafeteria
Page No. 342
Question 15. Identify Relationships What fraction of the states in the southwest region share a border with Mexico? Is this fraction in simplest form? \(\frac{□}{□}\)
Answer: Yes, \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Explanation: As per the given data, Southwest region states = 4 Number of states in the southwest region shares a border with Mexico out of total southwest region states = 3/4 Yes, 3/4 is the simplest form
Question 16. What’s the Question? \(\frac{1}{3}\) of the states in this region are on the Gulf of Mexico. Type below: _________
Answer: In the simplest form, what fraction of the states in the southeast area on the Gulf of Mexico.
Question 17. Pete says that to write \(\frac{4}{6}\) as \(\frac{2}{3}\), you combine pieces, but to write \(\frac{4}{6}\) as \(\frac{8}{12}\), you break apart pieces. Does this make sense? Explain. ______
Answer: As per the given data, Yes, it makes sense, To write 4/6 as 2/3 combine sixth size pieces into equal groups of 2 Then (4/2)/(6/2) = 2/3 To write 4/6 as 8/12, break each sixth piece into 2 pieces Then, 4/6 = (4 x 2)/(6 x 2) = 8/12
Question 18. In Michelle’s homeroom, \(\frac{9}{15}\) of the students ride the bus to school, \(\frac{4}{12}\) get a car ride, and \(\frac{2}{30}\) walk to school. For numbers 18a–18c, select True or False for each statement. a. In simplest form, \(\frac{3}{5}\) of the students ride the bus to school. i. True ii. False
Answer: i. True
Explanation: 9/15 of the students ride the bus to school By dividing the numerator and denominator of 9/15 with 3 (9/3)/(15/3) =3/5 So, 3/5 of the students ride the bus to school True
Question 18. b. In simplest form, \(\frac{1}{4}\) of the students get a car ride to school. i. True ii. False
Answer: ii. False
Explanation: a. 4/12 of the students get a car ride The simplest form of 4/12 = 1/3 So, 1/4 of the students get a car ride to school is a False statement
Question 18. c. In simplest form, \(\frac{1}{15}\) of the students walk to school. i. True ii. False
Explanation: a. 2/30 of the students walk to school By dividing the 2/30 with 2 (2/2)/(30/2) = 1/15 So, 1/15 of the students walk to school is a true statement
Common Core – Simplest Form – Page No. 343
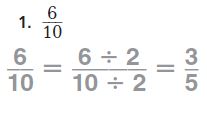
Answer: \(\frac{3}{5}\)
Explanation: To write the 6/10 in a simplest form Divide the numerator and denominator of 6/10 with 2 (6 ÷2)/(10 ÷2) = 3/5 So, the simplest form of 6/10 = 3/5
Question 2. \(\frac{6}{8}\) = \(\frac{□}{□}\)
Explanation: To write the 6/8in a simplest form Divide the numerator and denominator of 6/8 with 2 (6 ÷2)/(8 ÷2) = 3/4 So, the simplest form of 6/8 = 3/4
Question 3. \(\frac{5}{5}\) = \(\frac{□}{□}\)
Answer: \(\frac{1}{1}\) = 1
Explanation: To write the 5/5in a simplest form Divide the numerator and denominator of 5/5 with 5 (5 ÷5)/(5 ÷5) = 1/1 So, the simplest form of 5/5 = 1
Question 4. \(\frac{8}{12}\) = \(\frac{□}{□}\)
Explanation: To write the 8/12in a simplest form Divide the numerator and denominator of 8/12 with 4 (8 ÷4)/(12 ÷4) = 2/3 So, the simplest form of 8/12 = 2/3
Question 5. \(\frac{100}{100}\) = \(\frac{□}{□}\)
Explanation: The simplest form of 100/100 = 1
Question 6. \(\frac{2}{6}\) = \(\frac{□}{□}\)
Answer: \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Explanation: To write the 2/6in a simplest form Divide the numerator and denominator of 2/6 with 2 (2 ÷2)/(6 ÷2) = 1/3 So, the simplest form of 2/6 = 1/3
Question 7. \(\frac{2}{8}\) = \(\frac{□}{□}\)
Answer: \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Explanation: To write the 2/8in a simplest form Divide the numerator and denominator of 2/8 with 2 (2 ÷2)/(8 ÷2) = 1/4 So, the simplest form of 2/8 = 1/4
Question 8. \(\frac{4}{10}\) = \(\frac{□}{□}\)
Answer: \(\frac{2}{5}\)
Explanation: To write the 4/10 in a simplest form Divide the numerator and denominator of 4 /10 with 2 (4 ÷2)/(10 ÷2) = 2/5 So, the simplest form of 4/10 = 2/5
Tell whether the fractions are equivalent. Write = or ≠. (if you dont have ≠on your keybord, copy and paste this one: ≠ )
Question 9. \(\frac{6}{12}\) _______ \(\frac{1}{12}\)
Answer: \(\frac{6}{12}\) ≠ \(\frac{1}{12}\)
Explanation: 6/12 ≠ 1/12
Question 10. \(\frac{3}{4}\) _______ \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Answer: \(\frac{3}{4}\) ≠ \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Explanation: 3/4 ≠ 5/6
Question 11. \(\frac{6}{10}\) _______ \(\frac{3}{5}\)
Answer: \(\frac{6}{10}\) = \(\frac{3}{5}\)
Explanation: 6/10 Divide the numerator and denominator of 6/10 with 2 (6 ÷ 2)/( 10 ÷ 2) = 3/5 So, 6/10 = 3/5
Question 12. \(\frac{3}{12}\) _______ \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Answer: \(\frac{3}{12}\) ≠ \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Explanation: 3/12 ≠ 1/3
Question 13. \(\frac{6}{10}\) _______ \(\frac{60}{100}\)
Answer: \(\frac{6}{10}\) = \(\frac{60}{100}\)
Explanation: 6/10 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 6/10 with 10 (6 x 10)/(10 x 10) = 60/100 So, 6/10 = 60/100
Question 14. \(\frac{11}{12}\) _______ \(\frac{9}{10}\)
Answer: \(\frac{11}{12}\) ≠ \(\frac{9}{10}\)
Explanation: 11/12 ≠ 9/10
Question 15. \(\frac{2}{5}\) _______ \(\frac{8}{20}\)
Answer: \(\frac{2}{5}\) = \(\frac{8}{20}\)
Explanation: 2/5 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 2/5 with 4 (2 x 4)/(5 x 4) = 8/20 So, 2/5 = 8/20
Question 16. \(\frac{4}{8}\) _______ \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Answer: \(\frac{4}{8}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation: 4/8 Divide the numerator and denominator of 4/8 with 4 (4 x 4)/(8 x 4) = 1/2 So, 4/8 = 1/2
Question 17. At Memorial Hospital, 9 of the 12 babies born on Tuesday were boys. In simplest form, what fraction of the babies born on Tuesday were boys? _______
Explanation: As per the given data, At memorial hospital, 9 of the 12 babies born on Tuesday were boys = 9/12 Divide the numerator and denominator of 9/12 with 3 (9 ÷ 3)/(12 ÷ 3) = 3/4 So, in the simplest form 3/4 of the babies born on Tuesday were boys
Question 18. Cristina uses a ruler to measure the length of her math textbook. She says that the book is \(\frac{4}{10}\) meter long. Is her measurement in simplest form? If not, what is the length of the book in simplest form? \(\frac{□}{□}\)
Explanation: As per the given data, Cristiana uses a ruler to measure the length of her math textbook She says that the book is 4/10meter long It is not in simplest form Divide the numerator and denominator of 4/10 with 2 (4÷ 2)/( 10 ÷ 2) = 2/5 The length of the book in the simplest form = 2/5
Common Core – Simplest Form – Page No. 344
Question 1. Six out of the 12 members of the school choir are boys. In simplest form, what fraction of the choir is boys? Options: a. \(\frac{1}{6}\) b. \(\frac{6}{12}\) c. \(\frac{1}{2}\) d. \(\frac{12}{6}\)
Answer: c. \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation: As per the given data, Six out of the 12 members of the school choir are boys = 6/12 To write the simplest form of 6/12, divide the numerator and denominator with 6 Then, (6 ÷ 6)/(12 ÷ 6) = 1/2 In simplest form, 1/2 of the choir is boys
Question 2. Which of the following fractions is in simplest form? Options: a. \(\frac{5}{6}\) b. \(\frac{6}{8}\) c. \(\frac{8}{10}\) d. \(\frac{2}{12}\)
Answer: a. \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Explanation: 5/6 is in the simplest form 6/8 simplest form = 3/4 8/10 simplest form = 4/5 2/12 simplest form = 1/6
Question 3. Each of the 23 students in Ms. Evans’ class raised $45 for the school by selling coupon books. How much money did the class raise in all? Options: a. $207 b. $225 c. $1,025 d. $1,035
Answer: d. $1,035
Explanation: As per the given data, Each of the 23 students in Ms. Evan’s class raised $45 for the school by selling coupon books = 23 x $45 = $1,035
Question 4. Which pair of numbers below have 4 and 6 as common factors? Options: a. 12, 18 b. 20, 24 c. 28, 30 d. 36, 48
Answer: d. 36, 48
Explanation: 36, 48 Here, 36 = 4 x 9 = 2 x 2 x 3 x 3 48 = 6 x 8 = 2 x 3 x 4 x 2
Question 5. Bart uses \(\frac{3}{12}\) cup milk to make muffins. Which fraction is equivalent to \(\frac{3}{12}\)? Options: a. \(\frac{1}{4}\) b. \(\frac{1}{3}\) c. \(\frac{1}{2}\) d. \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Explanation: As per the given data, Bart uses 3/12 cup milk to make muffins Divide the fraction with 3 (3 ÷ 3)/(12 ÷ 3) = 1/4 So, the equivalent fraction for 3/12 = 1/4
Question 6. Ashley bought 4 packages of juice boxes. There are 6 juice boxes in each package. She gave 2 juice boxes to each of 3 friends. How many juice boxes does Ashley have left? Options: a. 24 b. 22 c. 18 d. 12
Answer: c. 18
Explanation: As per the given data, Ashley bought 4 packages of juice boxes There are 6 juice boxes in each package = 6 x 4 = 24 She gave 2 juice boxes to each of 3 friends = 2 x 3 = 6 juice boxes So, 24 – 6 = 18 Total number of juice boxes left with Ashley = 18
Page No. 347
Answer: common denominator: 12
Explanation: List the multiples of 3 = 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, …. List the multiples of 12 = 12, 24, 36, 48, …. So, common denominators of 1/3 and 1/ 12 is 12
Write the pair of fractions as a pair of fractions with a common denominator.
Question 2. \(\frac{1}{2}\) and \(\frac{1}{4}\) Type below: _________
Answer: \(\frac{4}{8}\) and \(\frac{2}{8}\)
Explanation: Common denominator of 1/2 and 1/4 List the multiples of 2 = 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, … List the multiples of 4 = 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, . . . Then, the common denominator of 1/2 and 1/4 is 4 For the Common pair of fractions, multiply the common denominator with fractions That is, (1 x 4) ÷( 2 x 4) and ( 1 x 4 ) ÷ ( 4 x 4) So, the common pair of fractions = 4/8 and 2/8
Question 3. \(\frac{3}{4}\) and \(\frac{5}{8}\) Type below: _________
Answer: \(\frac{6}{8}\) and \(\frac{5}{8}\)
Explanation: Common denominator of 3/4 and 5/8 List the multiples of 4 = 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, . . . List the multiples of 8 = 8, 16, 24, 32, . . . . Then, the common denominator of 3/4 and 5/8 is 8 For the Common pair of fractions, multiply the common denominator with fractions That is, (3 x 8) ÷( 4 x 8) and ( 5 x 8 ) ÷ ( 8 x 8) So, the common pair of fractions = 6/8 and 5/8
Question 4. \(\frac{1}{3}\) and \(\frac{1}{4}\) Type below: _________
Answer: \(\frac{4}{12}\) and \(\frac{3}{12}\)
Explanation: The common denominator of 1/3 and 1/4 List the multiples of 3 = 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, …. List the multiples of 4 = 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, . . . Then, the common denominator of 1 /3 and 1/4 is 12 For the Common pair of fractions, multiply the common denominator with fractions That is, (1 x 12) ÷( 3 x 12) and ( 1 x 12 ) ÷ ( 4 x 12) So, the common pair of fractions = 4/12 and 3/12
Question 5. \(\frac{4}{12}\) and \(\frac{5}{8}\) Type below: _________
Answer: \(\frac{8}{24}\) and \(\frac{15}{24}\)
Explanation: Common denominator of 4/12 and 5/8 List the multiples of 12 = 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, ….. List the multiples of 8 = 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, … Then, the common denominator of 4/12 and 5/8 is 24 For the Common pair of fractions, multiply the common denominator with fractions That is, (4 x 24) ÷( 12 x 24) and ( 5 x 24 ) ÷ ( 8 x 24) So, the common pair of fractions = 8/24 and 15/24
Question 6. \(\frac{1}{4}\) and \(\frac{5}{6}\) Type below: _________
Answer: \(\frac{3}{12}\) and \(\frac{10}{12}\)
Explanation: The common denominator of 1/4 and 5/6 List the multiples of 4 = 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, . . . List the multiples of 6 = 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, …. Then, the common denominator of 1/4 and 5/6 is 12 For the Common pair of fractions, multiply the common denominator with fractions That is, (1 x 12) ÷( 4 x 12) and ( 5 x 12 ) ÷ ( 6 x 12) So, common pair of fractions = 3/12 and 10/12
Question 7. \(\frac{3}{5}\) and \(\frac{4}{10}\) Type below: _________
Answer: \(\frac{6}{10}\) and \(\frac{4}{10}\)
Explanation: Common denominator of 3/5 and 4/10 List the multiples of 5 = 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, ….. List the multiples of 10 = 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 …. Then, the common denominator of 3/5 and 4/10 is 10 For the Common pair of fractions, multiply the common denominator with fractions That is, (3 x 10) ÷( 5 x 10) and ( 4 x 10 ) ÷ ( 10 x 10) So, the common pair of fractions = 6/10 and 4/10
Question 8. \(\frac{3}{4}\) ______ \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Answer: \(\frac{3}{4}\) ≠ \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation: 3/4 ≠ 1/2
Question 9. \(\frac{3}{4}\) ______ \(\frac{6}{8}\)
Explanation: 3/4 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 3/4 with 2 (3 x 2) ÷ ( 4 x 2 ) = 6/8 So, 3/4 = 6/8
Question 10. \(\frac{1}{2}\) ______ \(\frac{4}{8}\)
Answer: \(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{4}{8}\)
Explanation: 1/2 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 1/2 with 4 (1 x 4) ÷ ( 2 x 4 ) = 4/8 So, 1/2 = 4/8
Question 11. \(\frac{6}{8}\) ______ \(\frac{4}{8}\)
Answer: \(\frac{6}{8}\) ≠ \(\frac{4}{8}\)
Explanation: 6/8 ≠ 4/8
Question 12. Jerry has two same-size circles divided into the same number of equal parts. One circle has \(\frac{3}{4}\) of the parts shaded, and the other has \(\frac{2}{3}\) of the parts shaded. His sister says the least number of pieces each circle could be divided into is 7. Is his sister correct? Explain. ______
Answer: As per the given data, Jerry has two same size circles divided into the same number of equal parts One circle has 3/4 of the parts shaded So, non- shaded parts of one circle = 1 – 3/4 = 1/4 Another circle has 2/3 of the parts shaded Non – shaded parts = 1 – 2/3 = 1/3 We can’t draw a conclusion that in how many parts or pieces a circle can be divided So, his sister is incorrect
Page No. 348

Answer: Carrie has a red streamer that is 3/4 yard long The blue streamer that is 5/6 yard long 3/4 ≠ 5/6 She says the streamers are the same length, it doesn’t make any sense.
Question 14. Leah has two same-size rectangles divided into the same number of equal parts. One rectangle has \(\frac{1}{3}\) of the parts shaded, and the other has \(\frac{2}{5}\) of the parts shaded. What is the least number of parts into which both rectangles could be divided? ______ parts
Answer: 15 parts
Explanation: As per the given data, Leah has two same size rectangles divided into the same number of equal parts One rectangle has 1/3 of the parts shaded Other rectangle has 2/5 of the parts shaded 15 parts
Question 15. Julian says a common denominator for \(\frac{3}{4}\) and \(\frac{2}{5}\) is 9. What is Julian’s error? Explain. Type below: ___________
Answer: As per the given data, Julian says a common denominator for 3/4 and 2/5 is 9 To find the common denominator for 3/4 and 2/5 List the multiples of 4 = 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, ….. List the multiples of 5 = 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, …. So, the common denominator for 3/4 and 2/5 is 20 Julian says 9 in place of 20 and it is wrong.
Explanation: As per the given data, Miguel has two same – size rectangles divided into the same number of equal parts. One rectangle has 3/4 of the parts shaded. Another has 5/8 of the parts shaded. The possible parts are 8.
Common Core – Common Denominators – Page No. 349
Answer: \(\frac{8}{12} \text { and } \frac{9}{12}\)
Explanation: 2/3 and 3/4 List the multiples of 3 = 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, … List the multiples of 4 = 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, … Common multiple of 3 and 4 is 12 For the Common pair of fractions, multiply the common denominator with fractions That is, (2 x 12) ÷( 3 x 12) and ( 3 x 12 ) ÷ ( 4 x 12) So, common pair of fractions = 8/12 and 9/12
Question 2. \(\frac{1}{4} \text { and } \frac{2}{3}\) Type below: _________
Answer: \(\frac{3}{12} \text { and } \frac{8}{12}\)
Explanation: 1/4 and 2/3 List the multiples of 4 = 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, … List the multiples of 3 = 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, … Common multiple of 4 and 3 is 12 For the Common pair of fractions, multiply the common denominator with fractions That is, (1 x 12) ÷( 4 x 12) and ( 2 x 12 ) ÷ ( 3 x 12) So, common pair of fractions = 3/12 and 8/12
Question 3. \(\frac{3}{10} \text { and } \frac{1}{2}\) Type below: _________
Answer: \(\frac{3}{10} \text { and } \frac{5}{10}\)
Explanation: 3/10 and 1/2 List the multiples of 10 = 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, …. List the multiples of 2 = 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, …. Common multiple of 10 and 2 is 10 For the Common pair of fractions, multiply the common denominator with fractions That is, (3 x 10) ÷( 10 x 10) and ( 1 x 10 ) ÷ ( 2 x 10) So, common pair of fractions = 3/10 and 5/10
Question 4. \(\frac{3}{5} \text { and } \frac{3}{4}\) Type below: _________
Answer: \(\frac{12}{20} \text { and } \frac{15}{20}\)
Explanation: 3/5 and 3/4 List the multiples of 5 = 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, …. List the multiples of 4 = 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, … Common multiple of 5 and 4 is 20 For the Common pair of fractions, multiply the common denominator with fractions That is, (3 x 20) ÷( 5 x 20) and ( 3 x 20 ) ÷ ( 4 x 20) So, common pair of fractions = 12/20 and 15/20
Question 5. \(\frac{2}{4} \text { and } \frac{7}{8}\) Type below: _________
Answer: \(\frac{4}{8} \text { and } \frac{7}{8}\)
Explanation: 2/4 and 7/8 List the multiples of 4 = 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, … List the multiples of 8 = 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, …. Common multiple of 4 and 8 is 8 For the Common pair of fractions, multiply the common denominator with fractions That is, (2 x 8) ÷( 4 x 8) and ( 7 x 8 ) ÷ ( 8 x 8) So, common pair of fractions = 4/8 and 7/8
Question 6. \(\frac{2}{3} \text { and } \frac{5}{12}\) Type below: _________
Answer: \(\frac{8}{12} \text { and } \frac{5}{12}\)
Explanation: 2/3 and 5/12 List the multiples of 3 = 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, … List the multiples of 12 = 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, … Common multiple of 3 and 12 is 12 For the Common pair of fractions, multiply the common denominator with fractions That is, (2 x 12) ÷( 3 x 12) and ( 5 x 12 ) ÷ ( 12 x 12) So, common pair of fractions = 8/12 and 5/12
Question 7. \(\frac{1}{4} \text { and } \frac{1}{6}\) Type below: _________
Answer: \(\frac{3}{12} \text { and } \frac{2}{12}\)
Explanation: 1/4 and 1/6 List the multiples of 4 = 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, … List the multiples of 6 = 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, … Common multiple of 4 and 6 is 12 For the Common pair of fractions, multiply the common denominator with fractions That is, (1 x 12) ÷( 4 x 12) and ( 1 x 12 ) ÷ ( 6 x 12) So, common pair of fractions = 3/12 and 2/12
Question 8. \(\frac{1}{2}\) ______ \(\frac{2}{5}\)
Answer: \(\frac{1}{2}\) ≠ \(\frac{2}{5}\)
Explanation: Multiply the numerator and denominator of 1/2 with 2 (1 x 2) ÷ (2 x 2) = 2/4 So, 1/2 ≠ 2/5
Question 9. \(\frac{1}{2}\) ______ \(\frac{3}{6}\)
Answer: \(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{3}{6}\)
Explanation: 1/2 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 1/2 with 3 (1 x 3) ÷ (2 x 3) = 3/6 So, 1/2 = 3/6
Question 10. \(\frac{3}{4}\) ______ \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Question 11. \(\frac{6}{10}\) ______ \(\frac{3}{5}\)
Explanation: 6/10 Divide the numerator and denominator of 6/10 with 2 (6 ÷ 2)/(10 ÷2) = 3/5 So, 6/10 = 3/5
Question 12. \(\frac{6}{8}\) ______ \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Answer: \(\frac{6}{8}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Explanation: 6/8 Divide the numerator and denominator of 6/8 with 2 (6 ÷2)/(8 ÷2) = 3/4 So, 6/8 = 3/4
Question 13. \(\frac{3}{4}\) ______ \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Answer: \(\frac{3}{4}\) ≠ \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Explanation: 3/4 ≠ 2/3
Question 14. \(\frac{2}{10}\) ______ \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Answer: \(\frac{2}{10}\) ≠ \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Explanation: 2/10 Divide the numerator and denominator of 2/10 with 2 (2 ÷ 2)/(10 ÷ 2) = 1/5 So, 2/10 ≠ 1/5
Question 15. \(\frac{1}{4}\) ______ \(\frac{3}{12}\)
Explanation: 1/4 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 1/4 with 3 (1 x 3)/(4 x 3) = 3/12 So, 1/4 = 3/12
Question 16. Adam drew two same size rectangles and divided them into the same number of equal parts. He shaded \(\frac{1}{3}\) of one rectangle and \(\frac{1}{4}\) of other rectangle. What is the least number of parts into which both rectangles could be divided? _________
Answer: 12 parts
Explanation: As per the given data, Adam drew two same size rectangles and divided them into the same number of equal parts He shaded 1/3 of one rectangle 1/4 of another rectangle List the multiples of 3 = 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, … List the multiples of 4 = 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, … A common multiple of 3 and 4 is 12 So, the least number of parts which rectangles could be divided = 12 parts
Question 17. Mera painted equal sections of her bedroom wall to make a pattern. She painted \(\frac{2}{5}\) of the wall white and \(\frac{1}{2}\) of the wall lavender. Write an equivalent fraction for each using a common denominator. Type below: _________
Answer: 1/2 are 4/10 and 5/10
Explanation: As per the given data, Mera painted equal sections of her bedroom wall to make a pattern She painted 2/5 of the wall white and 1/2 of the wall lavender List the multiples of 5 = 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, … List the multiples of 2 = 2 ,4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, … The common denominator of 2/5 and 1/2 = 10 Multiply the 2/5 and 1/2 with 10 (2 x 10)/(5 x 10) and (1 x 10)/(2 x 10) 4/10 and 5/10 So, common fractions of 2/5 and 1/2 are 4/10 and 5/10
Common Core – Common Denominators – Page No. 350
Question 1. Which of the following is a common denominator of \(\frac{1}{4}\) and \(\frac{5}{6}\)? Options: a. 8 b. 9 c. 12 d. 15
Answer: c. 12
Explanation: Common denominator of 1/4 and 5/6 List the multiples of 4 = 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, … List the multiples of 6 = 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, …. So, the common denominator of 1/4 and 5/6 is 12
Question 2. Two fractions have a common denominator of 8. Which of the following could be the two fractions? Options: a. \(\frac{1}{2} \text { and } \frac{2}{3}\) b. \(\frac{1}{4} \text { and } \frac{1}{2}\) c. \(\frac{3}{4} \text { and } \frac{1}{6}\) d. \(\frac{1}{2} \text { and } \frac{4}{5}\)
Answer: b. \(\frac{1}{4} \text { and } \frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation: As per the given data, Two fractions have a common denominator of 8 a. 1/2 and 2/3 List the multiples of 2 = 2, 4, 6, 8,10, …. List the multiples of 3 = 3, 6, 9, 12, … There is no common denominator of 8 for 1/2 and 2/3 b. 1/4 and 1 /2 List the multiples of 2 = 2, 4, 6, 8,10, …. List the multiples of 4 = 4, 8, 12, 16, … Here, the common denominator of 1 /4 and 1 /2 is 8 So, the answer is 1/4 and 1/2
Question 3. Which number is 100,000 more than seven hundred two thousand, eighty-three? Options: a. 703,083 b. 712,083 c. 730,083 d. 802,083
Answer: d. 802,083
Explanation: 802,083
Question 4. Aiden baked 8 dozen muffins. How many total muffins did he bake? Options: a. 64 b. 80 c. 96 d. 104
Answer: c. 96
Explanation: As per the given data, Aiden baked 8 dozen muffins 1 dozen = 12 then, 8 dozens = 12 x 8 = 96 So, Aiden baked totally 96 muffins
Question 5. On a bulletin board, the principal, Ms. Gomez, put 115 photos of the fourthgrade students in her school. She put the photos in 5 equal rows. How many photos did she put in each row? Options: a. 21 b. 23 c. 25 d. 32
Answer: b. 23
Explanation: As per the given data, On a bulletin board, the principal, Ms. Gomez, put 115 photos of the fourth-grade students in her school She put the photos in 5 equal rows Then, number of photos in each row = 115/5 = 23 So, Ms. Gomez put photos in each row = 23
Question 6. Judy uses 12 tiles to make a mosaic. Eight of the tiles are blue. What fraction, in simplest form, represents the tiles that are blue? Options: a. \(\frac{2}{3}\) b. \(\frac{2}{5}\) c. \(\frac{3}{4}\) d. \(\frac{12}{18}\)
Answer: a. \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Explanation: As per the given data, Judy uses 12 tiles to make a mosaic Eight of the tiles are blue = 8/12 Divide the numerator and denominator of 8/12 with 4 (8 ÷ 4)/(12 ÷ 4) = 2/3 The simplest form of 8/12 is 2/3
Page No. 353
Answer: Keisha is helping plan a race route for a 10-kilometer charity run.
Question 2. What if distance markers will also be placed at the end of every fourth of the course? Will any of those markers be set up at the same location as another distance marker, a water station, or a viewing area? Explain. Type below: ___________
Answer: It really depends on where you place the other markers.
Question 3. Fifty-six students signed up to volunteer for the race. There were 4 equal groups of students, and each group had a different task. How many students were in each group? _____ students
Answer: 14 students
Explanation: As per the given data, Fifty-six students signed up to volunteer for the race There are four groups of students Number of students in each group = 56/4 = 14 Total number of students in each group = 14
Page No. 354
Question 4. A baker cut a pie in half. He cut each half into 3 equal pieces and each piece into 2 equal slices. He sold 6 slices. What fraction of the pie did the baker sell? \(\frac{□}{□}\)
Explanation: A baker cut a pie in half. He cut each half into 3 equal pieces and each piece into 2 equal slices. He sold 6 slices. So, the remaining part is 1/2 of the pie.
Question 5. Andy cut a tuna sandwich and a chicken sandwich into a total of 15 same-size pieces. He cut the tuna sandwich into 9 more pieces than the chicken sandwich. Andy ate 8 pieces of the tuna sandwich. What fraction of the tuna sandwich did he eat? \(\frac{□}{□}\)
Explanation: Let x be the number of pieces of the chicken sandwich so that x + 9 is the number of pieces of a tuna sandwich. There is a total of 15 same-size pieces. So, we can write as x + (x + 9) = 15 2x + 9 = 15 2x = 6 x = 3. This means that there ate 3 + 9 = 12 pieces of a tuna sandwich. Since Andy ate 8, then this corresponds to a fraction of 8/12 = 2/3.

Answer: 13 throws
Explanation: Take the maximum number to get the minimum throws = 9 X 10 = 90. 6 X 1 = 6; 2 X 2 = 4. Add 90 + 6 + 4 = 100; So, the least number of throws needed to score exactly 100 points = 10 + 1 + 2 = 13.
Explanation: Basically, any fraction obtained by multiplying both the numerator and denominator by the same value would be an equivalent fraction: 2/3 = 2/3 * 4/4 = 8/12 8/12 = 8/12 * 5/5 = 40/60 etc.
Common Core – Find Equivalent Fractions – Page No. 355
Answer: \(\frac{2}{6}\), \(\frac{3}{9}\), \(\frac{4}{12}\)
Explanation: Miranda is braiding her hair. Then she will attach beads to the braid. She wants \(\frac{1}{3}\) of the beads to be red. If the greatest number of beads that will fit on the braid is 12. \(\frac{1}{3}\) X \(\frac{2}{2}\) = \(\frac{2}{6}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) X \(\frac{3}{3}\) = \(\frac{3}{9}\) \(\frac{1}{3}\) X \(\frac{4}{4}\) = \(\frac{4}{12}\)
Question 2. Ms. Groves has trays of paints for students in her art class. Each tray has 5 colors. One of the colors is purple. What fraction of the colors in 20 trays is purple? \(\frac{□}{□}\)
Answer: \(\frac{20}{100}\) or \(\frac{1}{5}\)
Explanation: If you have 20 trays that are 100 colors with 20 being purple. 20/ 100 is 1/5
Question 3. Miguel is making an obstacle course for field day. At the end of every sixth of the course, there is a tire. At the end of every third of the course, there is a cone. At the end of every half of the course, there is a hurdle. At which locations of the course will people need to go through more than one obstacle? Type below: _________
Answer: \(\frac{1}{3}\), \(\frac{1}{2}\), \(\frac{2}{3}\) and final locations
Explanation: We have three fractions with different denominators: sixths, thirds, and halves. The first step is to make all the denominators equal for 1/6, 1/3, 1/2. In this case, we want sixths since LCM(2, 3, 6) = 6 since 1/3 = 2/6, and 1/2 = 3/6. Now we can start solving. 1. There are six tires at the following: 1/6, 2/6, 3/6, 4/6, 5/6, and 6/6. 2. There are three cones at the following (G.C.F.): 2/6 (or 1/3), 4/6 (or 2/3), and 6/6 (or 3/3). 3. There are two hurdles at the following (G.C.F.): 3/6 (or 1/2) and 6/6 (or 2/2). We look for common numbers. 1. On 2/6, there are two obstacles: a tire and a cone. 2. On 3/6, there are two obstacles: a tire and a hurdle. 3. On 4/6, there are two obstacles: a tire and a cone. 4. At 6/6, there are three obstacles: a tire, cone, and a hurdle. 2/6 = 1/3 3/6 = 1/2 4/6 = 2/3 6/6 = 1 The answers are 1/3, 1/2, 2/3, and 1.

Answer: 12 blueberry muffins
Explanation: Preston works in a bakery where he puts muffins in boxes. He makes the following table to remind himself how many blueberry muffins should go in each box. So, he had 2 blueberry muffins out of 6 muffins. 2/6 X 2/2 = 4/12. 4 blueberry muffins out of 12 muffins. 2/6 X 4/4 = 8/24. 8 blueberry muffins out of 24 muffins. 2/6 X 6/6 = 12/36. 12 blueberry muffins out of 36 muffins.
Common Core – Find Equivalent Fractions – Page No. 356
Question 1. A used bookstore will trade 2 of its books for 3 of yours. If Val brings in 18 books to trade, how many books can she get from the store? Options: a. 9 b. 12 c. 18 d. 27
Answer: b. 12
Explanation: A used bookstore will trade 2 of its books for 3 of yours. If Val brings in 18 books to trade 2/3 X 6/6 = 12/18, she get 12 books
Question 2. Every \(\frac{1}{2}\) hour Naomi stretches her neck; every \(\frac{1}{3}\) hour she stretches her legs; and every \(\frac{1}{6}\) hour she stretches her arms. Which parts of her body will Naomi stretch when \(\frac{2}{3}\) of an hour has passed? Options: a. neck and legs b. neck and arms c. legs and arms d. none
Answer: c. legs and arms
Explanation: Summing \(\frac{1}{2}\)‘s only gives integer values giving 1, 2, 3, 4…or integer values +\(\frac{1}{2}\) and 0 + \(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\), 1 \(\frac{1}{2}\), 2 \(\frac{1}{2}\)… So neck is excluded Every \(\frac{1}{3}\): \(\frac{1}{3}\) + \(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{2}{3}\) Legs will be stretched at \(\frac{2}{3}\) hour Every \(\frac{1}{6}\): \(\frac{1}{6}\) + \(\frac{1}{6}\) + \(\frac{1}{6}\) + \(\frac{1}{6}\) = \(\frac{4}{6}\) Divide top and bottom by 2 giving: (4 ÷ 2)/(6 ÷ 2) = \(\frac{2}{3}\) Arms will be stretched at latex]\frac{2}{3}[/latex] hour
Question 3. At the beginning of the year, the Wong family car had been driven 14,539 miles. At the end of the year, their car had been driven 21,844 miles. How many miles did the Wong family drive their car during that year? Options: a. 6,315 miles b. 7,295 miles c. 7,305 miles d. 36,383 miles
Answer: c. 7,305 miles
Explanation: If at the beginning of the year, the Wong family’s car had driven 14539 miles and at the end of the year, it had driven 21844 miles, then subtract 14539 from 21844 to determine the difference between the two values, which will tell you how many miles the Wong family drove their car for during the year. 21844 – 14539 = 7305 miles
Question 4. Widget Company made 3,600 widgets in 4 hours. They made the same number of widgets each hour. How many widgets did the company make in one hour? Options: a. 80 b. 90 c. 800 d. 900
Answer: d. 900
Explanation:
3,600 widgets in 4 hours therefore 3,600 / 4 for one hour = 900 widgets 900 widgets in one hour.
Question 5. Tyler is thinking of a number that is divisible by 2 and by 3. By which of the following numbers must Tyler’s number also be divisible? Options: a. 6 b. 8 c. 9 d. 12
Answer: a. 6
Explanation: The number 6 is divisible by 2 and by 3.
Question 6. Jessica drew a circle divided into 8 equal parts. She shaded 6 of the parts. Which fraction is equivalent to the part of the circle that is shaded? Options: a. \(\frac{2}{3}\) b. \(\frac{3}{4}\) c. \(\frac{10}{16}\) d. \(\frac{12}{18}\)
Answer: b. \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Explanation: Jessica drew a circle divided into 8 equal parts. She shaded 6 of the parts. 6/8 = 3/4
Page No. 357

Question 1. ________ name the same amount. ________
Answer: Equivalent Fractions
Question 2. A _________ is a common multiple of two or more denominators ________
Answer: Common Denominator
Question 3. \(\frac{2}{5}\) Type below: ________
Answer: \(\frac{4}{10}\) and \(\frac{6}{15}\)
Explanation: Two equivalent fractions of 2/5 Multiply the 2/5 with 2 (2 x 2)/(5 x 2) = 4/10 Multiply the 2/5 with 3 (2 x 3)/(5 x 3) = 6/15 So, the equivalent fractions of 2/5 are 4/10 and 6/15
Question 4. \(\frac{1}{3}\) Type below: ________
Answer: \(\frac{2}{6}\) and \(\frac{3}{9}\)
Explanation: Two equivalent fractions of 1/3 Multiply the 1/3 with 2 (1 x 2)/(3 x 2) = 2/6 Multiply the 1/3 with 3 (1 x 3)/(3 x 3) = 3/9 So, the equivalent fractions of 1/3 are 2/6 and 3/9
Question 5. \(\frac{3}{4}\) Type below: ________
Answer: \(\frac{6}{8}\) and \(\frac{9}{12}\)
Explanation: Two equivalent fractions of 3/4 Multiply the 3/4 with 2 (3 x 2)/(4 x 2) = 6/8 Multiply the 3/4 with 3 (3 x 3)/(4 x 3) = 9/12 So, the equivalent fractions of 3/4 are 6/8 and 9/12
Question 6. \(\frac{2}{3}\) ______ \(\frac{4}{12}\)
Answer: \(\frac{2}{3}\) ≠ \(\frac{4}{12}\)
Explanation: 2/ 3 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 2/3 with 2 (2 x 2)/(3 x 2) = 4/6 So, 2/3 ≠ 4/12
Question 7. \(\frac{5}{6}\) ______ \(\frac{10}{12}\)
Answer: \(\frac{5}{6}\) =_ \(\frac{10}{12}\)
Explanation: 5/6 Multiply the 5/6 with 2 (5 x 2)/(6 x 2) = 10/12 So, 5/6 = 10/12
Question 8. \(\frac{1}{4}\) ______ \(\frac{4}{8}\)
Answer: \(\frac{1}{4}\) ≠ \(\frac{4}{8}\)
Explanation: 1/4 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 1/4 with 4 (1 x 4)/(4 x 4) = 4/16 So, 1/4 ≠ 4/8
Question 9. \(\frac{6}{8}\) \(\frac{□}{□}\)
Explanation: 6/8 Divide the numerator and denominator of 6/8 with 2 (6 ÷ 2)/( 8 ÷ 2) = 3/4 The simplest form of 6/8 is 3/4
Question 10. \(\frac{25}{100}\) \(\frac{□}{□}\)
Explanation: 25/100 Divide the numerator and denominator of 25/100 with 25 (25 ÷ 25)/( 100 ÷ 25) = 1/4 The simplest form of 25/100 is 1/4
Question 11. \(\frac{8}{10}\) \(\frac{□}{□}\)
Explanation: 8/10 Divide the numerator and denominator of 8/10 with 2 (8 ÷ 2)/( 10 ÷ 2) = 4/5 The simplest form of 8/10 is 4/5
Question 12. \(\frac{3}{10} \text { and } \frac{2}{5}\) Type below: _________
Answer: \(\frac{3}{10} \text { and } \frac{4}{10}\)
Explanation: 3/ 10 and 2/5 List the multiples of 10 = 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, … List the multiples of 5 = 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, … Common denominator of 3/10 and 2/5 = 10 Multiply the 3/10 and 2/5 with 10 (3 x 10)/(10 x 10) and (2 x 10)/(5 x 10) 3/ 10 and 4/10 Pair of fractions of 3/10 and 2/5 are 3/10 and 4/10
Question 13. \(\frac{1}{3} \text { and } \frac{3}{4}\) Type below: _________
Answer: \(\frac{3}{12} \text { and } \frac{9}{12}\)
Explanation: 1/3 and 3/4 List the multiples of 3 = 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, … List the multiples of 4 = 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, …. The common denominator of 1/3 and 3/4 are 12 Multiply the 1/3 and 3/4 with 12 (1 x 12)/(3 x 12) and (3 x 12)/(4 x 12) 3/ 12 and 9/12. Pair of fractions of 1/3 and 3/4 are 3/12 and 9/12
Page No. 358
Question 14. Sam needs \(\frac{5}{6}\) cup mashed bananas and \(\frac{3}{4}\) cup mashed strawberries for a recipe. He wants to find whether he needs more bananas or more strawberries. How can he write \(\frac{5}{6}\) and \(\frac{3}{4}\) as a pair of fractions with a common denominator? Type below: _________
Answer: \(\frac{10}{12}\) and \(\frac{9}{12}\)
Explanation: Sam needs 5/6 cup mashed bananas and 3/4 cup mashed strawberries for a recipe He wants to find whether he needs more bananas or strawberries List the multiples of 6 = 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 42,….. List the multiples of 4 = 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, …. The common denominator of 6 and 4 is 12 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 5/6 and 3/4 with 12 (5 x 12)/(6 x 12) and (3 x 12)/(4 x 12) 10/12 and 9/12 Pair of fractions with a common denominator for 5/6 and 3/4 are 10/12 and 9/12
Question 15. Karen will divide her garden into equal parts. She will plant corn in \(\frac{8}{12}\) of the garden. What is the fewest number of parts she can divide her garden into? ______ parts
Answer: \(\frac{2}{3}\) parts
Explanation: As per the given data, Keren will divide her garden into equal parts She will plant corn in 8/12 of the garden To get the least number of parts she can divide her garden, simplify the 8/12 Divide the numerator and denominator of 8/12 with 4 (8 ÷ 4)/(12 ÷ 4) = 2/3 So, Karen can divide her garden into 2/3 of parts
Question 16. Olivia is making scarves. Each scarf will have 5 rectangles, and \(\frac{2}{5}\) of the rectangles will be purple. How many purple rectangles does she need for 3 scarves? ______ purple rectangles
Answer: 6 purple rectangles
Explanation: As per the given data, Olivia is making scarves Each scarf will have 5 rectangles and 2/5 of the rectangles will be purple = 5 x 2/5 = 2 That means each scarf will have 2 purple rectangles For 3 scarves = 3 x 2 = 6 So, she needs 6 purple rectangles.
Question 17. Paul needs to buy \(\frac{5}{8}\) pound of peanuts. The scale at the store measures parts of a pound in sixteenths. What measure is equivalent to \(\frac{5}{8}\) pound? \(\frac{□}{□}\) pound of peanuts
Answer: \(\frac{10}{16}\) pound of peanuts
Explanation: As per the given data, Paul needs to buy 5/8 pounds of peanuts The scale at the store measures parts of a pound in sixteenths = 16 x 5/8 = 10 To find Equivalent fraction of 5/8 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 5/8 with 2 (5 x 2)/( 8 x 2) = 10/16 So, the equivalent fraction of 5/8 is 10/16
Page No. 361
Answer: \(\frac{2}{5}\) > \(\frac{1}{8}\)
Explanation: Least common denominator of 5 and 8 = 40 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 2/5 and 1/8 with 40 2/ 5 = (2 x 8)/(5 x 8) = 16/40 1/8 = (1 x 5)/(8 x 5) = 5/40 The denominators are same now So, compare the numerator to find the greater number 16/40 > 5/40 So, 2/5 > 1/8
Compare. Write < or >.
Question 2. \(\frac{1}{2}\) _____ \(\frac{4}{6}\)
Answer: \(\frac{1}{2}\) < \(\frac{4}{6}\)
Explanation: 1/2 and 4/6 Least common denominator of 2 and 6 = 6 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 1/2 and 4/6 with 6 1/ 2 = (1 x 6)/(2 x 6) = 6/12 4/ 6 = (4x 2)/(6 x 2) = 8/12 The denominators are same now So, compare the numerator to find the greater number. 6/12 < 8/12 So, 1/2 < 4/6
Question 3. \(\frac{3}{10}\) _____ \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Answer: \(\frac{3}{10}\) > \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation: 1 / 10 and 1/2 Least common denominator of 10 and 2 = 10 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 3/10 and 1/2 with 10 3/ 10 = (3 x 2)/(10 x 2) = 6/20 1/2 = (1 x 10)/(2 x 10) = 10/20 The denominators are same now So, compare the numerator to find the greater number. 6/20 < 10/20 So, 3/10 > 1/2
Question 4. \(\frac{11}{12}\) _____ \(\frac{4}{8}\)
Answer: \(\frac{11}{12}\) > \(\frac{4}{8}\)
Explanation: 11/12 and 4/8 Least common denominator of 12 and 8 = 24 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 11/12 and 4/8 with 24 11/ 12 = (11 x 8)/(12 x 8) = 88/96 4/8 = (4 x 12)/(8 x 12) = 48/96 The denominators are same now So, compare the numerator to find the greater number 88/96 > 48/96 So, 11/12 > 4/8
Question 5. \(\frac{5}{8}\) _____ \(\frac{2}{5}\)
Answer: \(\frac{5}{8}\) > \(\frac{2}{5}\)
Explanation: 5/ 8 and 2/5 Least common denominator of 5 and 8 = 40 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 5/8 and 2/8 with 40 5/ 8 = (5 x 5)/(8 x 5) = 25/40 2/5 = (2 x 8)/(5 x 8) = 16/40 The denominators are same now So, compare the numerator to find the greater number 25/ 40 > 16/40 So, 5/8 > 2/5
Question 6. \(\frac{8}{10}\) _____ \(\frac{3}{8}\)
Answer: \(\frac{8}{10}\) > \(\frac{3}{8}\)
Explanation: 8/10 and 3/8 Least common denominator of 10 and 8 = 40 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 8/10 and 3/8 with 40 8/ 10 = (8 x 8)/(10 x 8) = 64/80 3/8 = (3 x 10)/(8 x 10) = 30/80 The denominators are same now So, compare the numerator to find the greater number 64/80 > 30/80 So, 8/10 > 3/8
Question 7. \(\frac{1}{3}\) _____ \(\frac{7}{12}\)
Answer: \(\frac{1}{3}\) < \(\frac{7}{12}\)
Explanation: 1/3 and 7/12 Least common denominator of 3 and 12 = 12 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 1/3 and 7/12 with 40. 1/ 3 = (1 x 12)/(3 x 12) = 12/36 7/12 = (7 x 3)/(12 x 3) = 21/36 The denominators are same now So, compare the numerator to find the greater number 12/36 < 21/36 So, 1/3 < 7/12
Question 8. \(\frac{2}{6}\) _____ \(\frac{7}{8}\)
Answer: \(\frac{2}{6}\) < \(\frac{7}{8}\)
Explanation: 2/6 and 7/8 Least common denominator of 6 and 8 = 24 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 2/6 and 7/8 with 40 2/ 6 = (2 x 8)/(6 x 8) = 16/48 7/8 = (7 x 6)/(8 x 6) = 42/48 The denominators are same now So, compare the numerator to find the greater number 16/48<42/48 So, 2/6 < 7/8
Question 9. \(\frac{4}{8}\) _____ \(\frac{2}{10}\)
Answer: \(\frac{4}{8}\) > \(\frac{2}{10}\)
Explanation: 4/8 and 2/10 Least common denominator of 8 and 10 = 40 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 4/8 and 2/10 with 40 4/ 8 = (4 x 10)/(8 x 10) = 40/80 2/10 = (2 x 8)/(10 x 8) = 16/80 The denominators are same now So, compare the numerator to find the greater number 40/80 > 16/80 So, 4/8 > 2/10
Reason Quantitatively Algebra Find a numerator that makes the statement true.
Question 10. \(\frac{2}{4}<\frac { □ }{ 6 } \) □ = _____
Explanation: 2/4 < x/6 Least common denominator of 4 and 6 = 12 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 2/4 < x/6 with 40 2/4 = (2 x 6)/(4 x 6) = 12/24 x/6 = (x x 4)/(6 x 4) = 4 x/24 The denominators are same now So, compare the numerator to find the greater number 12/24 < 4 X 4/24
Question 11. \(\frac{8}{10}>\frac { □ }{ 8 } \) □ = _____
Explanation: 8/10 < x/8 Least common denominator of 10 and 8 = 40 8/10 = (8 x 4)/(10 x 4) = 32/40 x/8 = (x X 5)/(8 x 5) = 5x/40 The denominators are same now So, compare the numerator to find the greater number 8/10 < 5x/40. X will be 1
Question 12. \(\frac{10}{12}>\frac { □ }{ 4 } \) □ = _____
Explanation: 10/12 < x/4 Least common denominator of 12 and 4 = 12 10/12 = (10 x 1)/(12 x 1) = 10/12 x/4 = (x X 3)/(4 x 3) = 3x/12 The denominators are same now So, compare the numerator to find the greater number 10/12 < 3/12. X will be 1.
Question 13. \(\frac{2}{5}<\frac { □ }{ 10 } \) □ = _____
Explanation: 2/5 < x/10 Least common denominator of 5 and 10 = 10 2/5 = (2x 2)/(5 x 2) = 4/10 x/10 = (x X 1)/(10 x 1) = x/10 The denominators are same now So, compare the numerator to find the greater number 2/5 < 5/10. X will be 5.
Question 14. When two fractions are between 0 and \(\frac{1}{2}\), how do you know which fraction is greater? Explain. Type below: _______
Answer: When two fractions are between 0 and \(\frac{1}{2}\). \(\frac{1}{2}\) is greater. As the tenths place of 5 is greater than 0. \(\frac{1}{2}\) is greater.
Question 15. If you know that \(\frac{2}{6}<\frac{1}{2}\) and \(\frac{3}{4}<\frac{1}{2}\), what do you know about \(\frac{2}{6} \text { and } \frac{3}{4}\)? Type below: _______
Explanation: As per the given data, 2/6 < 1/2 and 3/4 < 1/2 Then, 2/6 and 3/4 is The least common denominator of 6 and 4 is 12 (2 x 4)/(6 x 4) and (3 x 6)/(4 x 6) 8/24 and 18/24 Now, the denominators are same, then compare the numerators 8/24 > 18/24 So, 2/6 > 3/4
Question 16. Sandra has ribbons that are \(\frac{3}{4}\) yard, \(\frac{2}{6}\) yard, \(\frac{1}{5}\) yard, and \(\frac{4}{7}\) yard long. She needs to use the ribbon longer than \(\frac{2}{3}\) yard to make a bow. Which length of ribbon could she use for the bow? \(\frac{□}{□}\) yard
Page No. 362
Question 17. Saundra ran \(\frac{7}{12}\) of a mile. Lamar ran \(\frac{3}{4}\) of a mile. Who ran farther? Explain. _______
Answer: As per the given data, Saundra ran 7/12 of a mile Lamar ran 3/4 of a mile The least common denominator of 7/12 and 3/4 is 12 (7x 1)/( 12 x 1) and ( 3 x 3 )/( 4 x 3) 7/12 and 9/12 So, 7/12 < 9/12 So, 7/12 < 3/4 Lamar ran greater distance than Saundra
Question 18. What’s the Question? Selena ran farther than Manny. Type below: _______
Answer: Who ran farther? Selena or Manny
Question 19. Chloe made a small pan of ziti and a small pan of lasagna. She cut the ziti into 8 equal parts and the lasagna into 9 equal parts. Her family ate \(\frac{2}{3}\) of the lasagna. If her family ate more lasagna than ziti, what fraction of the ziti could have been eaten? Type below: _______
Explanation: As per the given data, Chloe made a small pan of ziti and a small pan of lasagna She cut the ziti into 8 equal parts and the lasagna into 9 equal parts Her family ate 2/3 of the lasagna = (2/3) x 9 = 6 parts If her family ate more lasagna than ziti, then that is less than 6 parts So, 1/4 of the ziti = (1/4) x 8 = 2 parts So, 1/4 of ziti eaten by Chloe family
Answer: 2/10 < 4/8 1 / 8 > 2/5 2/10 < 2/5
Explanation: As per the given data, James, Ella, and Ryan biked around eagle lake James biked 2/10 of the distance in an hour Ella biked 4/8 of the distance in an hour Ryan biked 2/5 of the distance in an hour Least common denominator of 2 /10, 4/8, and 2/5 is 40 (2x 4)/(10 x 4), (4 x 5)/(8 x 5), and (2 x 8)/(5 x 8) 8/40, 20/ 40, and 16/ 40 8/40 < 16/40 < 20/40 2/10 < 2/5 < 4/8 So, 2/10 < 4/8 1 / 8 > 2/5 2/10 < 2/5
Common Core – Compare Fractions Using Benchmarks – Page No. 363
Compare. Write < or > .
Answer: \(\frac{1}{8}\) < \(\frac{6}{10}\)
Question 2. \(\frac{4}{12}\) _______ \(\frac{4}{6}\)
Answer: \(\frac{4}{12}\) < \(\frac{4}{6}\)
Explanation: 4/12 and 4/6 4/12 is less than 1/2 4/6 is greater than 1/2 So, 4/12 < 4/6
Question 3. \(\frac{2}{8}\) _______ \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Answer: \(\frac{2}{8}\) < \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation: 2/8 and 1/2 2/8 is less than 1/2 1/2 is equal to 1/2 So, 2/8 < 1/2
Question 4. \(\frac{3}{5}\) _______ \(\frac{3}{3}\)
Answer: \(\frac{3}{5}\) < \(\frac{3}{3}\)
Explanation: 3/5 and 3/3 3/5 is greater than 1/2 3/3 is equal to 1 So, 3/5 < 3/3
Question 5. \(\frac{7}{8}\) _______ \(\frac{5}{10}\)
Answer: \(\frac{7}{8}\) > \(\frac{5}{10}\)
Explanation: 7/8 and 5/10 7/8 is greater than 1/2 5/10 is equal to 1/2 So, 5/10 < 7/8
Question 6. \(\frac{9}{12}\) _______ \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Answer: \(\frac{9}{12}\) > \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Explanation: 9/12 and 1/3 9/ 12 is greater than 1/2 1/3 is less than 1/2 1/3 < 9/12
Question 7. \(\frac{4}{6}\) _______ \(\frac{7}{8}\)
Answer: \(\frac{4}{6}\) < \(\frac{7}{8}\)
Explanation: 4/6 and 7/8 4/6 is greater than 1/2 7/8 is closer to 1 So, 4/6 < 7/8
Question 8. \(\frac{2}{4}\) _______ \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Answer: \(\frac{2}{4}\) < \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Explanation: 2/4 and 2/3 2/4 is equal to 1/2 2/3 is greater than 1/2 So, 2/4 < 2/3
Question 9. \(\frac{3}{5}\) _______ \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Answer: \(\frac{3}{5}\) > \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Explanation: 3/5 and 1/4 3/5 is greater than 1/2 1/4 is less than 1/2 So, 1/4 < 3/5
Question 10. \(\frac{6}{10}\) _______ \(\frac{2}{5}\)
Answer: \(\frac{6}{10}\) > \(\frac{2}{5}\)
Explanation: 6/10 and 2/5 6/10 is greater than 1/2 2/5 is less than 1/2 So, 2/5 < 6/10
Question 11. \(\frac{1}{8}\) _______ \(\frac{2}{10}\)
Answer: \(\frac{1}{8}\) < \(\frac{2}{10}\)
Explanation: 1/8 and 2/10 1/8 is less than 1/2 2/10 is less than 1/2 but greater than 1/8 So, 1/8 < 2/10
Question 12. \(\frac{2}{3}\) _______ \(\frac{5}{12}\)
Answer: \(\frac{2}{3}\) > \(\frac{5}{12}\)
Explanation: 2/3 and 5/12 2/3 is greater than 1/2 5/12 is less than 1/2 So, 5/12 < 2/3
Question 13. \(\frac{4}{5}\) _______ \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Answer: \(\frac{4}{5}\)< \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Explanation: 4/5 and 5/6 4/5 is greater than 1/2 5/6 is greater than 1/2 Common denominator is 30 (4×6)/(5×6) and (5×5)/(6×5) 24/30 and 25/30 24/30 < 25/30 So, 4/5 < 5/6
Question 14. \(\frac{3}{5}\) _______ \(\frac{5}{8}\)
Answer: \(\frac{3}{5}\) < \(\frac{5}{8}\)
Explanation: 3/5 and 5/8 3/5 is greater than 1/2 5/8 is greater than 1/2 Common denominator is 40 (3×8)/(5×8) and (5×5)/(8×5) 24/40 and 25/ 40 24/40 < 25/40 3/5 < 5/8
Question 15. \(\frac{8}{8}\) _______ \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Answer: \(\frac{8}{8}\) > \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Explanation: 8/8 and 3/4 8/8 is equal to 1 3/4 is less than 1 3/4 < 8/8
Question 16. Erika ran \(\frac{3}{8}\) mile. Maria ran \(\frac{3}{4}\) mile. Who ran farther? _________
Answer: Maria
Explanation: As per the data, Erika ran 3/8 mile Maria ran 3/4 mile Multiply the numerator and denominator of 3/4 with 2 (3×2)/(4×2) = 6/8 3/8 < 6/8 So, 3/8 < 3/4 So, Maria ran faster than Erika
Question 17. Carlos finished \(\frac{1}{3}\) of his art project on Monday. Tyler finished \(\frac{1}{2}\) of his art project on Monday. Who finished more of his art project on Monday? _________
Answer: Tyler
Explanation: From the given data, Carlos finished 1/3 of his art project on Monday Tyler finished ½ of his art project on Monday 1/3 is less than 1/2 1/2 is equal to 1/2 So, 1/3 < 1/2 Then, Tyler finished more of his work on Monday
Common Core – Compare Fractions Using Benchmarks – Page No. 364
Answer: a. >
Explanation: 4/6 ? 3/8 By comparing 4/6 with 1/2, 4/6 > 1/2 By comparing 3/8 with 1/2, 3/8 < 1/2 So, 4/6 > 3/8
Question 2. Which of the following fractions is greater than \(\frac{3}{4}\)? Options: a. \(\frac{1}{4}\) b. \(\frac{5}{6}\) c. \(\frac{3}{8}\) d. \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Answer: b. \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Explanation: From the given data, By comparing the 3/4 with 1/2, 3/4 > 1/2 Same as above, compare the options with ½ a. 1/4 < 1/2 b. 5/6 > 1/2 c. 3/8 < 1/2 d. 2/3 > 1/2 5/6 and 2/3 are greater than the 1/2 So, compare the 5/6 with 2/3 Then, 5/6 > 2/3 So, 5/6 > 3/4
Question 3. Abigail is putting tiles on a table top. She needs 48 tiles for each of 8 rows. Each row will have 6 white tiles. The rest of the tiles will be purple. How many purple tiles will she need? Options: a. 432 b. 384 c. 336 d. 48
Answer: c. 336
Explanation: As per the given data Abigail is putting tiles on a table top Number of rows = 8 She needs 48 tiles for each of row = 48×8 = 384 Number of white tiles per row = 6×8 = 48 Rest of the tiles will be purple = 384 – 48 =336 So, the total number of purple color tiles = 336
Question 4. Each school bus going on the field trip holds 36 students and 4 adults. There are 6 filled buses on the field trip. How many people are going on the field trip? Options: a. 216 b. 240 c. 256 d. 360
Answer: b. 240
Explanation: From the given data, Each school bus going on the field trip holds 36 students and 4 adults There are 6 filled buses on the field trip 6 x (36 + 4) = 6 x 40 = 240 So, the total number of people on the field trip = 240
Question 5. Noah wants to display his 72 collector’s flags. He is going to put 6 flags in each row. How many rows of flags will he have in his display? Options: a. 12 b. 15 c. 18 d. 21
Answer: a. 12
Explanation: As mentioned in the data, Noah wants to display his 72 collector’s flag He is going to put 6 flags in each row = 6x = 72 X = 12 So, total 12 number of rows of flags will have in his display
Question 6. Julian wrote this number pattern on the board: 3, 10, 17, 24, 31, 38. Which of the numbers in Julian’s pattern are composite numbers? Options: a. 3, 17, 31 b. 10, 24, 38 c. 10, 17, 38 d. 17, 24, 38
Answer: b. 10, 24, 38
Explanation: As per the given information Julian wrote his number pattern on the board =3, 10, 17, 24, 31, 38 Factors of 3 = 1,3 Factors of 10 = 1,2,5,10 Factors of 17 = 1, 17 Factors of 24 = 1, 2, 3, 4, 6 Factors of 31 = 1, 31 Factors of 38 = 1, 2, 19, 38 So, the composite number is 10, 24, and 38, which numbers have more than 2 factors
Page No. 367
Answer: \(\frac{2}{5}\) > \(\frac{1}{10}\)
Explanation: Compare 2/5 and 1/10 Think: 10 as common denominator Multiply the numerator and denominator of 2/5 with 2 Then, (2×2) ÷ (5×2) = 4/10 Now, compare the 4/10 with 1/10 4/10 > 1/10 So, 2/5 > 1/10
Answer: \(\frac{6}{10}\) < \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Explanation: Compare 6/10 and 3/4 Think: Use 40 as a common denominator So, multiply the denominator and numerator of 3/4 with 10 That is, (3×10) ÷ (4×10) = 30/40 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 6/10 with 4 That is, (6×4) ÷ (10×4) = 24/40 Denominators are same, compare the numerator values of 24/40 and 30/40 So, 24/40 < 30/40 Then, 6/10 < 3/4
Compare. Write <, >, or =.
Question 3. \(\frac{7}{8}\) _____ \(\frac{2}{8}\)
Answer: \(\frac{7}{8}\) > \(\frac{2}{8}\)
Explanation: Compare 7/8 and 2/8 Denominator values are same but numerator values are different Now, compare the numerator values of 7/8 and 2/8 Then, 7/8 > 2/8
Question 4. \(\frac{5}{12}\) _____ \(\frac{3}{6}\)
Answer: \(\frac{5}{12}\) < \(\frac{3}{6}\)
Explanation: Compare 5/12 and 3/6 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 3/6 with 2 (3×2) ÷ (6×2) = 6/12 So, 5/12 < 6/12
Question 5. \(\frac{4}{10}\) _____ \(\frac{4}{6}\)
Answer: \(\frac{4}{10}\) < \(\frac{4}{6}\)
Explanation: Compare 4/10 and 4/6 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 4/6 with 10 (4×10) ÷ (6×10) = 40/60 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 4/10 with 6 (4×6) ÷ (10×6) = 24/60 So, 24/60 < 40/60 Then, 4/10 < 4/6
Question 6. \(\frac{6}{12}\) _____ \(\frac{2}{4}\)
Answer: \(\frac{6}{12}\) = \(\frac{2}{4}\)
Explanation: Compare 6/12 and 2/4 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 2/4 with 3 (2×3) ÷ (4×3) = 6/12 So, 6/12 = 6/12 Then, 6/12 = 2/4
Question 7. \(\frac{1}{3}\) _____ \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Answer: \(\frac{1}{3}\) < \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Explanation: Compare 1/3 and 1/4 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 1/3 with 4 (1×4) ÷ (3×4) = 4/12 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 1/4 with 3 (1×3) ÷ (4×3) = 3/12 So, 4/12 < 3/12 Then, 1/3 < 1/4
Question 8. \(\frac{4}{5}\) _____ \(\frac{8}{10}\)
Explanation: Compare 4/5 and 8/10 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 4/5 with 2 (4×2) ÷ (5×2) = 8/10 So, 8/10 = 8/10 Then, 4/5 = 8/10
Question 9. \(\frac{3}{4}\) _____ \(\frac{2}{6}\)
Answer: \(\frac{3}{4}\) < \(\frac{2}{6}\)
Explanation: Compare 3/4 and 2/6 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 3/4 with 6 (3×6) ÷ (4×6) = 18/24 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 2/6 with 4 (2×4) ÷ (6×4) = 8/24 So, 18/24 < 8/24 Then, 3/4 < 2/6
Question 10. \(\frac{1}{2}\) _____ \(\frac{5}{8}\)
Answer: \(\frac{1}{2}\) < \(\frac{5}{8}\)
Explanation: Compare 1/2 and 5/8 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 1/2 with 4 (1×4) ÷ (2×4) = 4/8 So, 4/8 < 5/8 Then, 1/2 < 5/8
Reason Quantitatively Algebra Find a number that makes the statement true.
Question 11. \(\frac{1}{2}>\frac { □ }{ 3 } \) □ = ______
Explanation: 1/2 > x/3 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 1/2 with 3 (1×3) ÷ (2×3) = 3/6 Multiply the numerator and denominator of x/3 with 2 (Xx2) ÷ (3×2) = 2x/6 3/6 > 2x/6 So, x= 1 Then, 3/6 > 2/6 1/2 > 1/3
Question 12. \(\frac{3}{10}>\frac { □ }{ 5 } \) □ = ______
Explanation: 3/10 > x/5 Multiply the numerator and denominator of x/5 with 2 (Xx2) ÷ (5×2) =2x/10 3/10 > 2x/10 So, x=1 3/10 > 2/10 3/10 > 1/5
Question 13. \(\frac{5}{12}>\frac { □ }{ 3 } \) □ = ______
Explanation: 5/12 > x/3 Multiply numerator and denominator of x/3 with 4 (Xx4) ÷(3×4) = 4x/12 5/12 > 4x/12 So, x = 1 Then, 5/12 > 4/12 5/12 > 1/3
Question 14. \(\frac{2}{3}>\frac { 4 }{ □ } \) □ = ______
Question 15. Students cut a pepperoni pizza into 12 equal slices and ate 5 slices. They cut a veggie pizza into 6 equal slices and ate 4 slices. Use fractions to compare the amounts of each pizza that were eaten. Type below: _________
Answer: \(\frac{5}{12}\) < \(\frac{4}{6}\)
Explanation: As per the given data, Students cut a pepperoni pizza into 12 equal slices and ate 5 slices =5/12 They cut veggie pizza into 6 equal slices and ate 4 slices = 4/6 Compare 5/12 and 4/6 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 4/6 with 2 (4×2) ÷ (6×2) = 8/12 So, 5/12 < 8/12 Then, 5/12 < 4/6
Page No. 368

Answer: I need to find the greatest measure from milk, cottage cheese, or strawberries
Question 16. b. How will you find the answer? Type below: _________
Answer: Equal the denominators of 3/4, 2/6, and 8/12 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 3/4 with 3 (3×3) ÷ (4×3) = 9/12 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 2/6 with 2 (2×2) ÷ (6×2) = 4/12 Compare 4/12 < 8/12 < 9/12 So, 2/6 < 8/12 <3/4
Question 16. c. Show your work. Type below: _________
Answer: 2/6 < 8/12 < 3/4
Question 16. d. Jerry needs more ________ than the other two ingredients. ________
Answer: Jerry needs more strawberries than the other two ingredients
Question 17. Angie, Blake, Carlos, and Daisy went running. Angie ran \(\frac{1}{3}\) mile, Blake ran \(\frac{3}{5}\) mile, Carlos ran \(\frac{7}{10}\) mile, and Daisy ran \(\frac{1}{2}\) mile. Which runner ran the shortest distance? Who ran the greatest distance? The shortest distance: ________ The greatest distance: ________
Answer: The shortest distance: \(\frac{1}{3}\) The greatest distance: \(\frac{7}{10}\)
Explanation: As per the given data, Angie, Blake, Carlos, and Daisy went running Angie ran 1/3 mile, Blake ran 3/5 mile, Carlos ran 7/10 mile, and Daisy ran 1/2 mile Least common denominator of 1/3, 3/5, 7/10, and 1/2 =30 (1x 10)/(3×10), (3×6)/(5×6), (7×3)/(10×3), (1×15)/(2×15) 10/30, 18/30, 21/30, 15/30 10/30 < 15/30 < 18/30 < 21/30 1/3 < 1/2 < 3/5 < 7/10 The shortest distance ran by Angie and that is 1/ 3 The greatest distance ran by Carlos and that is 7/10

Answer: As per the given data, Elaine bought 5/8 pound of potato salad and 4/6 pound of macaroni salad for a picnic Multiply the numerator and denominator of 5/8 with 6 (5×6) / (8×6) = 30/48 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 4/6 with 8 (4×8) / (6×8) = 32/48 30/48 < 32/48 So, 5/8 < 4/6 Elaine bought more macaroni salad than potato salad
Common Core – Compare Fractions – Page No. 369
Compare. Write <, >, or =
Answer: \(\frac{1}{5}\) < \(\frac{2}{10}\)
Question 2. \(\frac{1}{5}\) _____ \(\frac{2}{10}\)
Answer: \(\frac{1}{5}\) = \(\frac{2}{10}\)
Explanation: 1/5 and 2/10 Think: 10 is a common denominator 1/5 = (1×2) / (5×2) = 2/10 2/10 = 2/10 So, 1/5 = 2/10
Question 3. \(\frac{2}{4}\) _____ \(\frac{2}{5}\)
Answer: \(\frac{2}{4}\) > \(\frac{2}{5}\)
Explanation: 2/4 and 2/5 20 is a common denominator 2/4 = (2×5)/(4×5) = 10/20 2/5 = (2×4)/(5×4) = 8/20 10/20 > 8/20 So, 2/4 > 2/5
Question 4. \(\frac{3}{5}\) _____ \(\frac{7}{10}\)
Answer: \(\frac{3}{5}\) < \(\frac{7}{10}\)
Explanation: 3/5 and 7/10 10 is a common denominator 3/5 = (3×2)/(5×2) = 6/10 7/10 6/10 < 7/10 So, 3/5 < 7/10
Question 5. \(\frac{4}{12}\) _____ \(\frac{1}{6}\)
Answer: \(\frac{4}{12}\) > \(\frac{1}{6}\)
Explanation: 4/12 and 1/6 12 is a common denominator 4/12 1/6 = (1×2)/(6×2) = 2/12 4/12 > 2/12 So, 4/12 > 1/6
Question 6. \(\frac{2}{6}\) _____ \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Answer: \(\frac{2}{6}\) = \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Explanation: 2/6 and 1/3 6 is a common denominator 2/6 1/3 = (1×2)/(3×2) = 2/6 So, 2/6 =2/6 So, 2/6 = 1/3
Question 7. \(\frac{1}{3}\) _____ \(\frac{2}{4}\)
Answer: \(\frac{1}{3}\) < \(\frac{2}{4}\)
Explanation: 1/3 and 2/4 12 is a common denominator 1/3 = (1×4)/(3×4) = 4/12 2/4 = (2×3)/(4×3) = 6/12 4/12 < 6/12 So, 1/3 < 2/4
Question 8. \(\frac{2}{5}\) _____ \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Answer: \(\frac{2}{5}\) < \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation: 2/5 and 1/2 10 is a common denominator 2/5 = (2×2)/(5×2) = 4/10 1/2 = (1×5)/(2×5) = 5/10 4/10 < 5/10 So, 2/5 < 1/2
Question 9. \(\frac{4}{8}\) _____ \(\frac{2}{4}\)
Answer: \(\frac{4}{8}\) = \(\frac{2}{4}\)
Explanation: 4/8 and 2/4 8 is a common denominator 4/8 2/4 = (2×2)/(4×2) = 4/8 2/4 = 4/8 So, 4/8 = 2/4
Question 10. \(\frac{7}{12}\) _____ \(\frac{2}{4}\)
Answer: \(\frac{7}{12}\) < \(\frac{2}{4}\)
Explanation: 7/12 and 2/4 12 is a common denominator 7/12 2/4 = (2×3)/(4×3) = 6/12 7/12 < 6/12 So, 7/12 < 2/4
Question 11. \(\frac{1}{8}\) _____ \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Answer: \(\frac{1}{8}\) < \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Explanation: 1/8 and 3/4 8 is a common denominator 1/8 3/4 = (3×2)/(4×2) = 6/8 1/8 < 6/8 So, 1/8 < 3/4
Question 12. A recipe uses \(\frac{2}{3}\) of flour and \(\frac{5}{8}\) cup of blueberries. Is there more flour or more blueberries in the recipe? more _____
Answer: flour
Explanation: From the given data, A recipe uses 2/3 of flour and 5/8 cup of blueberries Common denominator is 24 2/3 = (2×8)/(3×8) = 16/24 5/8 = (5×3)/(8×3) = 15/24 16/24 > 15/24 So, 2/3 > 5/8 So, flour is more in the recipe
Question 13. Peggy completed \(\frac{5}{6}\) of the math homework and Al completed \(\frac{4}{5}\) of the math homework. Did Peggy or Al complete more of the math homework? _________
Answer: Peggy completed more work than Al
Explanation: As per the given data, Peggy completed 5/6 of the math homework A1 completed 4/5 of the math homework 30 is a common denominator 5/6 = (5×5)/(6×5) = 25/30 4/5 = (4×6)/(5×6) =24/30 25/30 > 24/30 So, 5/6 > 4/5 So, Peggy completed more work than Al
Common Core – Compare Fractions – Page No. 370
Question 1. Pedro fills a glass \(\frac{2}{4}\) full with orange juice. Which of the following fractions is greater than \(\frac{2}{4}\)? Options: a. \(\frac{3}{8}\) b. \(\frac{4}{6}\) c. \(\frac{5}{12}\) d. \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Answer: b. \(\frac{4}{6}\)
Explanation: \(\frac{4}{6}\) > \(\frac{2}{4}\)
Question 2. Today Ian wants to run less than \(\frac{7}{12}\) mile. Which of the following distances is less than \(\frac{7}{12}\) mile? Options: a. \(\frac{3}{4}\) mile b. \(\frac{2}{3}\) mile c. \(\frac{5}{6}\) mile d. \(\frac{2}{4}\) mile
Answer: d. \(\frac{2}{4}\) mile
Explanation: \(\frac{2}{4}\) is less than \(\frac{7}{12}\)
Question 3. Ms. Davis traveled 372,645 miles last year on business. What is the value of 6 in 372,645? Options: a. 6 b. 60 c. 600 d. 6,000
Answer: c. 600
Explanation: Ms. Davis traveled 372, 645 miles last year on business The value of 6 in 372,645 is 600
Question 4. One section of an auditorium has 12 rows of seats. Each row has 13 seats. What is the total number of seats in that section? Options: a. 25 b. 144 c. 156 d. 169
Answer: c. 156
Explanation: From the given information One section of an auditorium has 12 rows of seats Each row has 13 seats = 13×12 = 156 seats So, the total number of seats in the auditorium = 156 seats
Question 5. Sam has 12 black-and-white photos and 18 color photos. He wants to put the photos in equal rows so each row has either black-and-white photos only or color photos only. In how many rows can Sam arrange the photos? Options: a. 1, 2, 3, or 6 rows b. 1, 3, 6, or 9 rows c. 1, 2, or 4 rows d. 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, or 9 rows
Answer: a. 1, 2, 3, or 6 rows
Explanation: As per the given information Sam has 12 black and white photos 18 color photos He wants to put the photos in equal rows So each row has either black and white photos only or color photos only H.C.F of 12 and 18 is 6 Rows of 6. 2 rows of black equal 12. 3 rows of white equals 18.
Question 6. The teacher writes \(\frac{10}{12}\) on the board. He asks students to write the fraction in simplest form. Who writes the correct answer? Options: a. JoAnn writes \(\frac{10}{12}\) b. Karen writes \(\frac{5}{12}\) c. Lynn writes \(\frac{6}{5}\) d. Mark writes \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Answer: d. Mark writes \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Explanation: As per the given data, The teacher writes 10/12 on the board He asks students to write the fraction in simplest form For the simplest form of 10/12, divide the 10/12 with 2 (10÷2)/(12÷2) = 5/6 5/6 is the simplest form of 10/12 So, Mark writes the correct answer
Page No. 373
Explanation: 3/10, 11/12, 5/8 3/10 is closer to 0 11/12 is closer to 1 5/8 is closer to 1/2 So, 3/10 < 5/8 < 11/12
Write the fraction with the greatest value.
Question 2. \(\frac{7}{10}, \frac{1}{5}, \frac{9}{10}\) \(\frac{□}{□}\)
Answer: \(\frac{9}{10}\)
Explanation: 7/10, 1/5, and 9/10 7/10 is closer to 1/2 1/5 is closer to 0 9/10 is closer to 1 So, 9/10 > 7/10 > 1/5 Greatest value is 9/10
Question 3. \(\frac{5}{6}, \frac{7}{12}, \frac{7}{10}\) \(\frac{□}{□}\)
Explanation: 7/12 is less than 1/2 7/10 and 5/6 are greater than 1/2 Compare 5/6 and 7/12 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 5/6 with 2 (5×2)/(6×2) = 10/12 > 7/12 So, 5/6 > 7/12 Compare 5/6 and 7/10 Multiply the 5/6 with 10 (5×10)/(6×10) = 50/60 Multiply the 7/10 with 6 (7×6)/(10×6) = 42/60 So, 5/6> 7/10 So, 7/12 <7/10<5/6
Question 4. \(\frac{2}{8}, \frac{1}{8}, \frac{2}{4}, \frac{2}{6}\) \(\frac{□}{□}\)
Answer: \(\frac{2}{4}\)
Explanation: 2/8, 1/8, 2/4, 2/6 Common denominator of 4,6,8 = 24 (2×3)/(8×3), (1×3)/(8×3), (2×6)/(4×6), (2×4)/(6×4) 6/24, 3/24, 12/24, 8/24 Compare the numerator values 12/24 > 8/24 > 6/24 > 3/24 So, 2/4 > 2/6 > 2/8 >1/8
Write the fractions in order from least to greatest.
Question 5. \(\frac{1}{4}, \frac{3}{6}, \frac{1}{8}\) \(\frac{□}{□}\) Type below: ________
Answer: \(\frac{1}{8}, \frac{3}{6}, \frac{1}{4}\)
Explanation: 1/4, 3/6, 1/8 1/ 4 is closer to 1/2 3/6 is equal to 1/2 1/8 is closer to 0 So, 1/8 < 3/6 < 1/4
Question 6. \(\frac{3}{5}, \frac{2}{3}, \frac{3}{10}, \frac{4}{5}\) \(\frac{□}{□}\) Type below: ________
Answer: \(\frac{4}{5}, \frac{3}{10}, \frac{3}{5}, \frac{2}{3}\)
Explanation: 3/5, 2/3, 3/10, 4/5 3/5 is closer to 1/2 2/3 is greater than 1/2 3/10 is less than 1/2 4/5 is closer to 0 So, 4/5 < 3/10 < 3/5 < 2/3
Question 7. \(\frac{3}{4}, \frac{7}{12}, \frac{5}{12}\) \(\frac{□}{□}\) Type below: ________
Answer: \(\frac{5}{12}, \frac{7}{12}, \frac{3}{4}\)
Explanation: 3/4, 7/12, 5/12 3/ 4 is closer to 1 7/12 is greater than 1/2 5/ 12 is closer to 1/2 So, 5/12 < 7/12 < 3/4
Question 8. \(\frac{2}{5}, \frac{1}{3}, \frac{5}{6}\) \(\frac{□}{□}\) Type below: ________
Answer: \(\frac{1}{3}, \frac{2}{5}, \frac{5}{6}\)
Explanation: 2/5, 1/3, 5/6 2/5 is closer to 1/2 1/3 is closer to 0 5/6 is closer to 1 So, 1/3 < 2/5 < 5/6
Question 9. \(\frac{4}{8}, \frac{5}{12}, \frac{1}{6}\) \(\frac{□}{□}\) Type below: ________
Answer: \(\frac{1}{6}, \frac{5}{12}, \frac{4}{8}\)
Explanation: 4/8, 5/12, 1/6 4/8 is equal to1/2 5/12 is closer to 1/2 1/6 is closer to 0 So, 1/6 < 5/12 < 4/ 8
Question 10. \(\frac{7}{100}, \frac{9}{10}, \frac{4}{5}\) \(\frac{□}{□}\) Type below: ________
Answer: \(\frac{7}{100}, \frac{4}{5}, \frac{9}{10}\)
Explanation: 7/100, 9/10, 4/5 7/100 is closer to 0 9/10 is closer to 1 4/5 is greater than 1/2 So, 7/100 < 4/5 < 9/10
Reason Quantitatively Algebra Write a numerator that makes the statement true.
Question 11. \(\frac{1}{2}<\frac { □ }{ 10 } <\frac{4}{5}\) □ = _____
Answer: 6 or 7
Explanation: 1/2 < x/10 < 4/5 Common denominator is 10 (1×5)/(2×5) < x/10 < (4×2)/(5×2) 5/10 < x/10 < 8/10 Then, x = 6 or 7
Question 12. \(\frac{1}{4}<\frac{5}{12}<\frac { □ }{ 6 } \) □ = _____
Explanation: 1/4 < 5/12 < x/6 Common denominator is 24 (1×6)/(4×6) < (5×2)/(12×2) < 4x/(6×4) 6/24 < 10/24 < 4x/24 If x = 6, then 4x = 24 So, 6/24 < 10/24 < 24/24
Question 13. \(\frac { □ }{ 8 } <\frac{3}{4}<\frac{7}{8}\) □ = _____
Answer: 1,2,3,4,5
Explanation: x/8 < 3/4 < 7/8 Common denominator is 8 x/8 < (3×2)/(4×2) < 7/8 x/8 < 6/8 < 7/8 so x = 1,2,3,4,5
Page No. 374

Answer: In which Nancy, Lionel, and Mavis finished the race?
Question 14. b. What information do you need to solve the problem? Type below: _________
Answer: the amount of time it took each runner to finish the race
Question 14. c. What information is not necessary? Type below: _________
Answer: the distance of the race
Question 14. d. How will you solve the problem? Type below: _________
Answer: By using the running race time of Nancy, Lionel, and Mavis
Question 14. e. Show the steps to solve the problem. Type below: _________
Answer: Common denominator of 2/3, 7/12, 3/4 is 12 (2×4)/(3×4), (7/12), (3×3)/(4×3) 8/12, 7/12, 9/12 7/12 < 8/12 < 9/12 7/12 < 2/3 < 3/4 Lionel < Nancy < Mavis
Question 14. f. Complete the sentences. The runner who finished first is _______. The runner who finished second is _______. The runner who finished third is _______. The first: _______ The second: _______ The third: _______
Answer: Lionel finished the race first Nancy finished the race second Mavis finished the race third Lionel Nancy Mavis
Common Core – Compare and Order Fractions – Page No. 375
Answer: \(\frac{2}{12}, \frac{5}{8}, \frac{8}{10}\)
Question 2. \(\frac{1}{5}, \frac{2}{3}, \frac{5}{8}\) Type below: _________
Answer: \(\frac{1}{5}, \frac{5}{8}, \frac{2}{3}\)
Question 3. \(\frac{1}{2}, \frac{2}{5}, \frac{6}{10}\) Type below: _________
Answer: \(\frac{2}{5}, \frac{1}{2}, \frac{6}{10}\)
Question 4. \(\frac{4}{6}, \frac{7}{12}, \frac{5}{10}\) Type below: _________
Answer: \(\frac{5}{10}\) < \(\frac{7}{12}\) < \(\frac{4}{6}\)
Question 5. \(\frac{1}{4}, \frac{3}{6}, \frac{1}{8}\) Type below: _________
Answer: \(\frac{1}{8}\) < \(\frac{1}{4}\) < \(\frac{3}{6}\)
Question 6. \(\frac{1}{8}, \frac{3}{6}, \frac{7}{12}\) Type below: _________
Answer: \(\frac{1}{8}\) < \(\frac{7}{12}\) < \(\frac{3}{6}\)
Question 7. \(\frac{8}{100}, \frac{3}{5}, \frac{7}{10}\) Type below: _________
Answer: \(\frac{8}{100}\) < \(\frac{3}{5}\) < \(\frac{7}{10}\)
Question 8. \(\frac{3}{4}, \frac{7}{8}, \frac{1}{5}\) Type below: _________
Answer: \(\frac{1}{5}\) < \(\frac{3}{4}\) < \(\frac{7}{8}\)
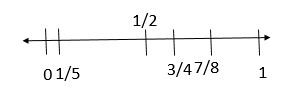
Question 9. Amy’s math notebook weighs \(\frac{1}{2}\) pound, her science notebook weighs \(\frac{7}{8}\) pound, and her history notebook weighs \(\frac{3}{4}\) pound. What are the weights in order from lightest to heaviest? Type below: _________
Answer: \(\frac{1}{2}\) pound, \(\frac{3}{4}\) pound, \(\frac{7}{8}\) pound
Explanation: From the given data, Amy’s math notebook weighs 1/2 pound Science notebook weighs 7/8 pound History notebook weighs 3/4 pound 7/8 is closer to 1 3/4 is greater than 1/2 1/2 < 3/4 < 7/8 So, Amy’s math notebook weight < history notebook weight < science notebook
Question 10. Carl has three picture frames. The thicknesses of the frames are \(\frac{4}{5}\) inch, \(\frac{3}{12}\) inch, and \(\frac{5}{6}\) inch. What are the thicknesses in order from least to greatest? Type below: _________
Answer: \(\frac{3}{12}\) inch, \(\frac{4}{5}\) inch, \(\frac{5}{6}\) inch
Explanation: As per the given data, Carl has three picture frames The thickness of the frames are 4/5 inch, 3/12 inch, 5/6 inch 4/5 is greater than 1/2 3/12 is less than 1/2 5/6 is closer to 1 3/12 < 4/5 < 5/6
Common Core – Compare and Order Fractions – Page No. 376
Question 1. Juan’s three math quizzes this week took him \(\frac{1}{3}\) hour, \(\frac{4}{6}\) hour, and \(\frac{1}{5}\) hour to complete. Which list shows the lengths of time in order from least to greatest? Options: a. \(\frac{1}{3}\) hour, \(\frac{4}{6}\) hour, \(\frac{1}{5}\) hour b. \(\frac{1}{5}\) hour, \(\frac{1}{3}\) hour, \(\frac{4}{6}\) hour c. \(\frac{1}{3}\) hour, \(\frac{1}{5}\) hour, \(\frac{4}{6}\) hour d. \(\frac{4}{6}\) hour, \(\frac{1}{3}\) hour, \(\frac{1}{5}\) hour
Answer: b. \(\frac{1}{5}\) hour, \(\frac{1}{3}\) hour, \(\frac{4}{6}\) hour
Explanation: From the given information Juan’s three math quizzes this week took him 1/3 hour, 4/6 hour, and 1/5 hour Compare 1/3 and 1/2 1/3 is less than 1/2 4/6 is greater than 1/2 1/5 is closer to 0 1/5 < 1/3 < 4/6 So, Juan’s math quizzes times from least to greatest is 1/5, 1/3, 4/6
Question 2. On three days last week, Maria ran \(\frac{3}{4}\) mile, \(\frac{7}{8}\) mile, and \(\frac{3}{5}\) mile. What are the distances in order from least to greatest? Options: a. \(\frac{3}{4}\) mile, \(\frac{7}{8}\) mile, \(\frac{3}{5}\) mile b. \(\frac{3}{5}\) mile, \(\frac{3}{4}\) mile, \(\frac{7}{8}\) mile c. \(\frac{7}{8}\) mile, \(\frac{3}{4}\) mile, \(\frac{3}{5}\) mile d. \(\frac{7}{8}\) mile, \(\frac{3}{5}\) mile, \(\frac{3}{4}\) mile
Answer: b. \(\frac{3}{5}\) mile, \(\frac{3}{4}\) mile, \(\frac{7}{8}\) mile
Explanation: As per the information On three days last week, Maria ran 3/4 mile, 7/8 mile, and 3/5 mile 3/4 is greater than 1/2 7/8 is closer to 1 3/5 is greater than 1/2 Compare 3/5 and 3/4 3/4 is greater than 3/5 So, 3/5 < 3/4 < 7/8 Distance from least to greatest is 3/5, 3/4 , 7/8
Question 3. Santiago collects 435 cents in nickels. How many nickels does he collect? Options: a. 58 b. 78 c. 85 d. 87
Answer: d. 87
Explanation: As per the given data, Santiago collects 435 cents in nickels 1 nickel worth is 5 cents Then, nickels per 435 cents = 435/5 = 87 So, Santiago collects 87 nickels
Question 4. Lisa has three classes that each last 50 minutes. What is the total number of minutes the three classes last? Options: a. 15 minutes b. 150 minutes c. 153 minutes d. 156 minutes
Answer: b. 150 minutes
Explanation: From the given data, Lisa has three classes that each last 50 minutes The total number of minutes the three classes last = 3×50 =150 minutes
Question 5. Some students were asked to write a composite number. Which student did NOT write a composite number? Options: a. Alicia wrote 2. b. Bob wrote 9. c. Arianna wrote 15. d. Daniel wrote 21.
Answer: a. Alicia wrote 2.
Explanation: As per the information Some students were asked to write a composite number a. Alicia wrote 2 Factors of 2 is 1 and 2 b. Bob wrote 9 Factors of 9 is 1, 3, 9 c. Arianna wrote 15 Factors of 15 is 1, 3, 5, 15 d. Daniel wrote 21 Factors of 21 is 1,3,7,21 So, Alicia did not write a composite number
Question 6. Mrs. Carmel serves \(\frac{6}{8}\) of a loaf of bread with dinner. Which fraction is equivalent to \(\frac{6}{8}\)? Options: a. \(\frac{2}{4}\) b. \(\frac{9}{16}\) c. \(\frac{2}{3}\) d. \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Answer: d. \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Explanation: As per the given information Mrs. Carmel serves 6/8 of a loaf of bread with dinner To find the equivalent fraction of 6/8, simplify the 6/8 by dividing with the 2 (6÷2)/(8÷2) = ¾ So, the equivalent fraction of 6/8 is 3/4
Page No. 377
Question 1. For numbers 1a–1d, tell whether the fractions are equivalent by selecting the correct symbol. a. \(\frac{4}{16}\) _____ \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Answer: \(\frac{4}{16}\) = \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Explanation: 4/16 and 1/4 Divide the numerator and denominator of 4/16 with 4 (4÷4)/(16÷4) = 1/4 So, 4/16 = 1/4
Question 1. b. \(\frac{3}{5}\) _____ \(\frac{12}{15}\)
Answer: \(\frac{3}{5}\) ≠ \(\frac{12}{15}\)
Explanation: 3/5 and 12/15 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 3/5 with 3 (3×3)/(5×3) = 9/15 So, 3/5 ≠ 12/15
Question 1. c. \(\frac{5}{6}\) _____ \(\frac{25}{30}\)
Answer: \(\frac{5}{6}\) = \(\frac{25}{30}\)
Explanation: c. 5/6 and 25/30 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 5/6 with 5 (5×5)/(6×5) = 25/30 So, 5/6 = 25/30
Question 1. d. \(\frac{6}{10}\) _____ \(\frac{5}{8}\)
Answer: \(\frac{6}{10}\) ≠ \(\frac{5}{8}\)
Explanation: 6/10 and 5/8 Divide the numerator and denominator of 6/10 with 2 (6÷2)/(10÷2) = 3/5 6/10 ≠5/8
Question 2. Juan’s mother gave him a recipe for trail mix. \(\frac{3}{4}\) cup cereal \(\frac{2}{3}\) cup almonds \(\frac{1}{4}\) cup peanuts \(\frac{1}{2}\) cup raisins Order the ingredients used in the recipe from least to greatest. Type below: _________
Answer: As per the given data, Juan’s mother gave him a recipe for trail mix 3/4 cup cereal and 2/3 cup almonds 1/4 cup peanuts and 1/2 cup raisins 3/4 is closer to 1 2/3 is greater than 1/2 1/4 is less than 1/2 1/2 is equal to 1/2 So, 1/4 < 1/2 <2/3 < 3/4 So, Jaun’s mother gave him a recipe for trail mix in order 1/4 cup of peanuts < 1/2 cup of raisins < 2/3 cup almonds < 3/4 cup of cereals
Answer: From the given data, Taylor cuts 1/5 sheet of construction paper for an arts and crafts project So, the equivalent fractions of 1/5 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 1/5 with 2 (1×2)/(5×2) = 2/10 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 1/5 with 3 (1×3)/(5×3) = 3/15 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 1/5 with 5 (1×5)/(5×5) = 5/25 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 1/5 with 8 (1×8)/(5×8) = 8/40 So, the equivalent fractions of 1/5 are 2/10, 3/15, 5/25, 8/40
Explanation: As per the given data, A mechanic has sockets with the sizes 7/8 inch, 3/16 inch, 1/4 inch, 3/8 inch, 4/8 inch, 11/16 inch 7/8 is greater than 1/2 3/16 is less than 1/2 1/4 is less than 1/2 3/8 is less than 1/2 4/8 is equal to 1/2 11/16 is greater than 1/2
Page No. 378
Explanation: From the given data, Darcy bought 1/2 pound of cheese and 3/4 pound of hamburger for a barbecue 3/4 is greater than 1/2
Question 6. Brad is practicing the piano. He spends \(\frac{1}{4}\) hour practicing scales and \(\frac{1}{3}\) hour practicing the song for his recital. For numbers 6a–6c, select Yes or No to tell whether each of the following is a true statement. a. 12 is a common denominator of \(\frac{1}{4}\) and \(\frac{1}{3}\). i. yes ii. no
Answer: i. yes
Explanation: 12 is a common denominator of 1/3 and 1/4
Question 6. b. The amount of time spent practicing scales can be rewritten as \(\frac{3}{12}\). i. yes ii. no
Explanation: b. The amount of time spent practicing scales can be rewritten as 3/12 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 1/4 with 3 (1×3)/(4×3) = 3/12 Yes, amount of time spent practicing scales can be rewritten as 3/12
Question 6. c. The amount of time spent practicing the song for the recital can be rewritten as \(\frac{6}{12}\). i. yes ii. no
Answer: ii. no
Explanation: c. The amount of time spent practicing the song for the recital can be rewritten as 6/12 The amount of time spent practicing for the song for his recital = 1/3 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 1/3 with 4 (1×4)/(3×4) = 4/12 No, time spent practicing the song for the recital can not be written as 6/12
Question 7. In the school chorus, \(\frac{4}{24}\) of the students are fourth graders. In simplest form, what fraction of the students in the school chorus are fourth graders? \(\frac{□}{□}\)
Answer: \(\frac{1}{6}\)
Explanation: As per the given information, In the school chorus, 4/24 of the students are fourth graders For the simplest form of 4/24 Divide the numerator and denominator of 4/24 with 4 (4÷4)/(24÷4) =1/6 The simplest form of 4/24 is 1/6
Question 8. Which pairs of fractions are equivalent? Mark all that apply. a. \(\frac{8}{12} \text { and } \frac{2}{3}\) b. \(\frac{3}{4} \text { and } \frac{20}{24}\) c. \(\frac{4}{5} \text { and } \frac{12}{16}\) d. \(\frac{7}{10} \text { and } \frac{21}{30}\)
Answer: a. \(\frac{8}{12} \text { and } \frac{2}{3}\)
Explanation: a. 8/12 and 2/3 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 2/3 with 4 (2×4)/(3×4) = 8/12 So, 8/12 = 2/3 b. 3/4 and 20/24 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 3/4 with 6 (3×6)/(4×6) = 18/24 c. 4/5 and 12/16 4/5 ≠ 12/16 d. 7/10 and 21/30 Multiply the numerator and denominator of 7/10 with 3 (7×3)/(10×3) =21/30 So, 7/10 = 21/30
Question 9. Sam worked on his science fair project for \(\frac{1}{4}\) hour on Friday and \(\frac{1}{2}\) hour on Saturday. What are four common denominators for the fractions? Explain your reasoning.
Answer: From the given data, Sam worked on his science fair project for 1/4 hour on Friday and 1/2 hour on Saturday 4,8,12,16 are all common denominators because they all multiples of 2 and 4
Page No. 379
Question 10. Morita works in a florist shop and makes flower arrangements. She puts 10 flowers in each vase, and \(\frac{2}{10}\) of the flowers are daisies. Part A If Morita makes 4 arrangements, how many daisies does she need? Show how you can check your answer. _____ daisies
Answer: 8 daisies
Explanation: If Morita makes 4 arrangements, 4 X 2 = 8.
Question 10. Part B Last weekend, Morita used 10 daisies to make flower arrangements. How many flowers other than daisies did she use to make the arrangements? Explain your reasoning. _____ other flowers
Answer: 40 other flowers
Explanation: If she used 10 daises, she must have made 5 arrangements. In each vase, she put \(\frac{2}{10}\) of the flowers are daisies. So, remaining flowers for each vase = 10 – 2 = 8. If she made 5 arrangements, 8 X 5 = 40 other flowers.
Question 11. In Mary’s homeroom, \(\frac{10}{28}\) of the students have a cat, \(\frac{6}{12}\) have a dog, and \(\frac{2}{14}\) have a pet bird. For numbers 11a–11c, select True or False for each statement. a. In simplest form, \(\frac{5}{14}\) of the students have a cat. i. True ii. False
Explanation: In simplest form 5/14 of the students have a cat From the above, 10/28 of the students have a cat Divide the numerator and denominator of 10/28 with 2 (10÷2)/(28÷2) = 5/14 True
Question 11. b. In simplest form, \(\frac{2}{4}\) of the students have a dog. i. True ii. False
Explanation: In simplest form, 2/4 of the students have a dog From the above, 6/12 of the students have a dog Divide the 6/12 with 3 (6 = 2/4 True
Question 11. c. In simplest form, \(\frac{1}{7}\) of the students have a pet bird. i. True ii. False
Explanation: In the simplest form, 1/7 of the students have a pet bird From the data, 2/14 of the students have a pet bird Divide the numerator and denominator of 2/14 with 2 (2÷2)/(14÷2) = 1/7 True
Page No. 380

Explanation: From the given information Regina, Courtney, and Ellen hiked around Bear Pond Regina hiked 7/10 of the distance in an hour Courtney hiked 3/6 of the distance in an hour Ellen hiked 3 /8 of the distance in an hour Compare 7/10 and 3/6 The common denominator of 7/10 and 3/6 is 30 (7×3)/(10×3) and (3×5)/(6×5) 21/30 and 15/30 So, 21/30 > 15/30 So, 7/10 > 15/30 Compare 3/8 and 3/6 The common denominator of 3/8 and 3/6 is 24 (3×3)/(8×3) and (3×4)/(6×4) 9/24 and 12/24 = 9/24 < 12/24 = 3/8 < 3/6 Compare 7/10 and 3/8 The common denominator of 7/10 and 3/8 is 40 (7×4)/(10×4) and (3×5)/(8×5) 28/40 >15/40 = 7/10 > 3/8
Answer: Ramon use 5/8 cup of buttermilk and 1/2 cup cream cheese By comparing these two ingredients The common denominator of 5/8 and 1/2 are 8 (1×4)/(2×4) =4/8 So, 5/8 > 4/8 So, 5/8 cup buttermilk is > ½ cup cream cheese
Question 13. Part B Ramon says that he needs the same amount of two different ingredients. Is he correct? Support your answer with information from the problem. ______
Answer: Ramon says that he needs the same amount of two ingredients Yes, Ramon uses 3/4 cup parsley and 6/8 cup scallions Multiply the 3/4 with 2 (3×2)/(4×2) = 6/8 So, Ramon uses the same amount that is 3/4 cup for parsley and scallions
Page No. 381
Explanation: As per the information, Sandy is ordering bread rolls for her party She wants 3/5 of the rolls to be whole wheat For an equivalent fraction of 3/5, multiply with 5 (3×5)/(5×5) = 15/25 Again multiply the 15/25 with 4 (15×4)/(25×4) = 60/100
Explanation: 1/4 = 2/8 = 4/16 = 3/12
Page No. 382
Question 17. Part B Is there more than one possible answer to Part A? If so, did you find the least number of parts into which both rectangles could be divided? Explain your reasoning. Type below: _________
Answer: Yes, as long it is a multiple of 12. And yes,12 is the least in order to have 1 rectangle have 3/4 shaded and the other 1/3 shaded.
Question 18. Suki rode her bike \(\frac{4}{5}\) mile. Claire rode her bike \(\frac{1}{3}\) mile. They want to compare how far they each rode their bikes using the benchmark \(\frac{1}{2}\). For numbers 18a–18c, select the correct answers to describe how to solve the problem. a. Compare Suki’s distance to the benchmark: \(\frac{4}{5}\) _____ \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Answer: \(\frac{4}{5}\) ≠ \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation: The fraction \(\frac{4}{5}\) is not equal to \(\frac{1}{2}\).
Question 18. b. Compare Claire’s distance to the benchmark: \(\frac{1}{3}\) _____ \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Answer: \(\frac{1}{3}\) ≠ \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation: The fraction \(\frac{1}{3}\) is not equal to \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 18. c. Suki rode her bike _____ Claire.
Answer: Suki rode her bike faster than Claire.
Page No. 387
Use the model to write an equation.

Answer: \(\frac{3}{5}\) + \(\frac{1}{5}\) = \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Answer: \(\frac{2}{3}\) – \(\frac{1}{3}\) = \(\frac{1}{3}\)
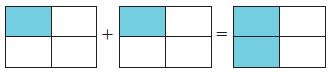
Answer: \(\frac{1}{4}\) + \(\frac{1}{4}\) = \(\frac{2}{4}\)
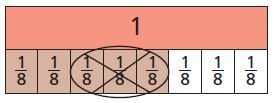
Answer: 1 – \(\frac{5}{8}\) = \(\frac{8}{8}\) – \(\frac{5}{8}\) = \(\frac{3}{8}\)
Use the model to solve the equation.
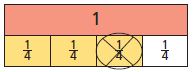
Answer: \(\frac{6}{6}\) = 1
Question 7. Reason Abstractly Sean has \(\frac{1}{5}\) of a cupcake and \(\frac{1}{5}\) of a large cake. a. Are the wholes the same? Explain. ______
Answer: Yes; From the given information, the fraction of the cupcake and large cake are the same.
Question 7. Does the sum \(\frac{1}{5}+\frac{1}{5}=\frac{2}{5}\) make sense in this situation? Explain. ______
Answer: Yes; it makes sense. From the given data, 1 part is out of 5 parts. So, adding two fractions (1 part is out of 5 parts), the complete fraction becomes 2/5.
Question 8. Carrie’s dance class learned \(\frac{1}{5}\) of a new dance on Monday, and \(\frac{2}{5}\) of the dance on Tuesday. What fraction of the dance is left for the class to learn on Wednesday? \(\frac{□}{□}\)
Explanation: The fraction of left for the class to learn on Wednesday is \(\frac{3}{5}\).
Page No. 388
Answer: Both Samantha and Kim’s statements make sense. Because both models have an equal number of fractions for each diagram.
Question 10. Draw a model you could use to add \(\frac{1}{4}+\frac{1}{2}\). Type below: ___________
Answer: \(\frac{3}{8}+\frac{2}{8}\) = \(\frac{5}{8}\)
Conclusion:
By downloading the Go Math Grade 4 Answer Key Chapter 6 Fraction Equivalence and Comparison PDF, students of grade 4 will aid you to understand different topics in Chapter 6 easily. Prepare well with the help of Go Math Grade 4 Answer Key PDFand solve each and every question properly. For more help utilize this Go Math Grade 4 Solution Key Chapter 6 Fraction Equivalence and Comparison PDF and gain what you require.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO