
15 Hypothesis Examples

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process
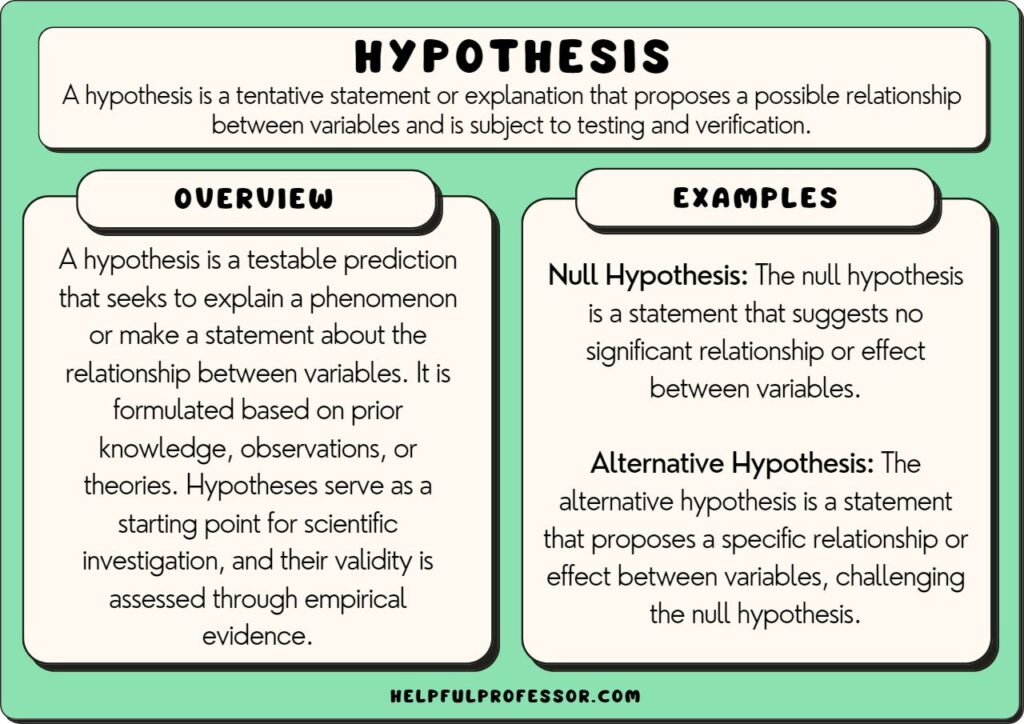
A hypothesis is defined as a testable prediction , and is used primarily in scientific experiments as a potential or predicted outcome that scientists attempt to prove or disprove (Atkinson et al., 2021; Tan, 2022).
In my types of hypothesis article, I outlined 13 different hypotheses, including the directional hypothesis (which makes a prediction about an effect of a treatment will be positive or negative) and the associative hypothesis (which makes a prediction about the association between two variables).
This article will dive into some interesting examples of hypotheses and examine potential ways you might test each one.
Hypothesis Examples
1. “inadequate sleep decreases memory retention”.
Field: Psychology
Type: Causal Hypothesis A causal hypothesis explores the effect of one variable on another. This example posits that a lack of adequate sleep causes decreased memory retention. In other words, if you are not getting enough sleep, your ability to remember and recall information may suffer.
How to Test:
To test this hypothesis, you might devise an experiment whereby your participants are divided into two groups: one receives an average of 8 hours of sleep per night for a week, while the other gets less than the recommended sleep amount.
During this time, all participants would daily study and recall new, specific information. You’d then measure memory retention of this information for both groups using standard memory tests and compare the results.
Should the group with less sleep have statistically significant poorer memory scores, the hypothesis would be supported.
Ensuring the integrity of the experiment requires taking into account factors such as individual health differences, stress levels, and daily nutrition.
Relevant Study: Sleep loss, learning capacity and academic performance (Curcio, Ferrara & De Gennaro, 2006)
2. “Increase in Temperature Leads to Increase in Kinetic Energy”
Field: Physics
Type: Deductive Hypothesis The deductive hypothesis applies the logic of deductive reasoning – it moves from a general premise to a more specific conclusion. This specific hypothesis assumes that as temperature increases, the kinetic energy of particles also increases – that is, when you heat something up, its particles move around more rapidly.
This hypothesis could be examined by heating a gas in a controlled environment and capturing the movement of its particles as a function of temperature.
You’d gradually increase the temperature and measure the kinetic energy of the gas particles with each increment. If the kinetic energy consistently rises with the temperature, your hypothesis gets supporting evidence.
Variables such as pressure and volume of the gas would need to be held constant to ensure validity of results.
3. “Children Raised in Bilingual Homes Develop Better Cognitive Skills”
Field: Psychology/Linguistics
Type: Comparative Hypothesis The comparative hypothesis posits a difference between two or more groups based on certain variables. In this context, you might propose that children raised in bilingual homes have superior cognitive skills compared to those raised in monolingual homes.
Testing this hypothesis could involve identifying two groups of children: those raised in bilingual homes, and those raised in monolingual homes.
Cognitive skills in both groups would be evaluated using a standard cognitive ability test at different stages of development. The examination would be repeated over a significant time period for consistency.
If the group raised in bilingual homes persistently scores higher than the other, the hypothesis would thereby be supported.
The challenge for the researcher would be controlling for other variables that could impact cognitive development, such as socio-economic status, education level of parents, and parenting styles.
Relevant Study: The cognitive benefits of being bilingual (Marian & Shook, 2012)
4. “High-Fiber Diet Leads to Lower Incidences of Cardiovascular Diseases”
Field: Medicine/Nutrition
Type: Alternative Hypothesis The alternative hypothesis suggests an alternative to a null hypothesis. In this context, the implied null hypothesis could be that diet has no effect on cardiovascular health, which the alternative hypothesis contradicts by suggesting that a high-fiber diet leads to fewer instances of cardiovascular diseases.
To test this hypothesis, a longitudinal study could be conducted on two groups of participants; one adheres to a high-fiber diet, while the other follows a diet low in fiber.
After a fixed period, the cardiovascular health of participants in both groups could be analyzed and compared. If the group following a high-fiber diet has a lower number of recorded cases of cardiovascular diseases, it would provide evidence supporting the hypothesis.
Control measures should be implemented to exclude the influence of other lifestyle and genetic factors that contribute to cardiovascular health.
Relevant Study: Dietary fiber, inflammation, and cardiovascular disease (King, 2005)
5. “Gravity Influences the Directional Growth of Plants”
Field: Agronomy / Botany
Type: Explanatory Hypothesis An explanatory hypothesis attempts to explain a phenomenon. In this case, the hypothesis proposes that gravity affects how plants direct their growth – both above-ground (toward sunlight) and below-ground (towards water and other resources).
The testing could be conducted by growing plants in a rotating cylinder to create artificial gravity.
Observations on the direction of growth, over a specified period, can provide insights into the influencing factors. If plants consistently direct their growth in a manner that indicates the influence of gravitational pull, the hypothesis is substantiated.
It is crucial to ensure that other growth-influencing factors, such as light and water, are uniformly distributed so that only gravity influences the directional growth.
6. “The Implementation of Gamified Learning Improves Students’ Motivation”
Field: Education
Type: Relational Hypothesis The relational hypothesis describes the relation between two variables. Here, the hypothesis is that the implementation of gamified learning has a positive effect on the motivation of students.
To validate this proposition, two sets of classes could be compared: one that implements a learning approach with game-based elements, and another that follows a traditional learning approach.
The students’ motivation levels could be gauged by monitoring their engagement, performance, and feedback over a considerable timeframe.
If the students engaged in the gamified learning context present higher levels of motivation and achievement, the hypothesis would be supported.
Control measures ought to be put into place to account for individual differences, including prior knowledge and attitudes towards learning.
Relevant Study: Does educational gamification improve students’ motivation? (Chapman & Rich, 2018)
7. “Mathematics Anxiety Negatively Affects Performance”
Field: Educational Psychology
Type: Research Hypothesis The research hypothesis involves making a prediction that will be tested. In this case, the hypothesis proposes that a student’s anxiety about math can negatively influence their performance in math-related tasks.
To assess this hypothesis, researchers must first measure the mathematics anxiety levels of a sample of students using a validated instrument, such as the Mathematics Anxiety Rating Scale.
Then, the students’ performance in mathematics would be evaluated through standard testing. If there’s a negative correlation between the levels of math anxiety and math performance (meaning as anxiety increases, performance decreases), the hypothesis would be supported.
It would be crucial to control for relevant factors such as overall academic performance and previous mathematical achievement.
8. “Disruption of Natural Sleep Cycle Impairs Worker Productivity”
Field: Organizational Psychology
Type: Operational Hypothesis The operational hypothesis involves defining the variables in measurable terms. In this example, the hypothesis posits that disrupting the natural sleep cycle, for instance through shift work or irregular working hours, can lessen productivity among workers.
To test this hypothesis, you could collect data from workers who maintain regular working hours and those with irregular schedules.
Measuring productivity could involve examining the worker’s ability to complete tasks, the quality of their work, and their efficiency.
If workers with interrupted sleep cycles demonstrate lower productivity compared to those with regular sleep patterns, it would lend support to the hypothesis.
Consideration should be given to potential confounding variables such as job type, worker age, and overall health.
9. “Regular Physical Activity Reduces the Risk of Depression”
Field: Health Psychology
Type: Predictive Hypothesis A predictive hypothesis involves making a prediction about the outcome of a study based on the observed relationship between variables. In this case, it is hypothesized that individuals who engage in regular physical activity are less likely to suffer from depression.
Longitudinal studies would suit to test this hypothesis, tracking participants’ levels of physical activity and their mental health status over time.
The level of physical activity could be self-reported or monitored, while mental health status could be assessed using standard diagnostic tools or surveys.
If data analysis shows that participants maintaining regular physical activity have a lower incidence of depression, this would endorse the hypothesis.
However, care should be taken to control other lifestyle and behavioral factors that could intervene with the results.
Relevant Study: Regular physical exercise and its association with depression (Kim, 2022)
10. “Regular Meditation Enhances Emotional Stability”
Type: Empirical Hypothesis In the empirical hypothesis, predictions are based on amassed empirical evidence . This particular hypothesis theorizes that frequent meditation leads to improved emotional stability, resonating with numerous studies linking meditation to a variety of psychological benefits.
Earlier studies reported some correlations, but to test this hypothesis directly, you’d organize an experiment where one group meditates regularly over a set period while a control group doesn’t.
Both groups’ emotional stability levels would be measured at the start and end of the experiment using a validated emotional stability assessment.
If regular meditators display noticeable improvements in emotional stability compared to the control group, the hypothesis gains credit.
You’d have to ensure a similar emotional baseline for all participants at the start to avoid skewed results.
11. “Children Exposed to Reading at an Early Age Show Superior Academic Progress”
Type: Directional Hypothesis The directional hypothesis predicts the direction of an expected relationship between variables. Here, the hypothesis anticipates that early exposure to reading positively affects a child’s academic advancement.
A longitudinal study tracking children’s reading habits from an early age and their consequent academic performance could validate this hypothesis.
Parents could report their children’s exposure to reading at home, while standardized school exam results would provide a measure of academic achievement.
If the children exposed to early reading consistently perform better acadically, it gives weight to the hypothesis.
However, it would be important to control for variables that might impact academic performance, such as socioeconomic background, parental education level, and school quality.
12. “Adopting Energy-efficient Technologies Reduces Carbon Footprint of Industries”
Field: Environmental Science
Type: Descriptive Hypothesis A descriptive hypothesis predicts the existence of an association or pattern related to variables. In this scenario, the hypothesis suggests that industries adopting energy-efficient technologies will resultantly show a reduced carbon footprint.
Global industries making use of energy-efficient technologies could track their carbon emissions over time. At the same time, others not implementing such technologies continue their regular tracking.
After a defined time, the carbon emission data of both groups could be compared. If industries that adopted energy-efficient technologies demonstrate a notable reduction in their carbon footprints, the hypothesis would hold strong.
In the experiment, you would exclude variations brought by factors such as industry type, size, and location.
13. “Reduced Screen Time Improves Sleep Quality”
Type: Simple Hypothesis The simple hypothesis is a prediction about the relationship between two variables, excluding any other variables from consideration. This example posits that by reducing time spent on devices like smartphones and computers, an individual should experience improved sleep quality.
A sample group would need to reduce their daily screen time for a pre-determined period. Sleep quality before and after the reduction could be measured using self-report sleep diaries and objective measures like actigraphy, monitoring movement and wakefulness during sleep.
If the data shows that sleep quality improved post the screen time reduction, the hypothesis would be validated.
Other aspects affecting sleep quality, like caffeine intake, should be controlled during the experiment.
Relevant Study: Screen time use impacts low‐income preschool children’s sleep quality, tiredness, and ability to fall asleep (Waller et al., 2021)
14. Engaging in Brain-Training Games Improves Cognitive Functioning in Elderly
Field: Gerontology
Type: Inductive Hypothesis Inductive hypotheses are based on observations leading to broader generalizations and theories. In this context, the hypothesis deduces from observed instances that engaging in brain-training games can help improve cognitive functioning in the elderly.
A longitudinal study could be conducted where an experimental group of elderly people partakes in regular brain-training games.
Their cognitive functioning could be assessed at the start of the study and at regular intervals using standard neuropsychological tests.
If the group engaging in brain-training games shows better cognitive functioning scores over time compared to a control group not playing these games, the hypothesis would be supported.
15. Farming Practices Influence Soil Erosion Rates
Type: Null Hypothesis A null hypothesis is a negative statement assuming no relationship or difference between variables. The hypothesis in this context asserts there’s no effect of different farming practices on the rates of soil erosion.
Comparing soil erosion rates in areas with different farming practices over a considerable timeframe could help test this hypothesis.
If, statistically, the farming practices do not lead to differences in soil erosion rates, the null hypothesis is accepted.
However, if marked variation appears, the null hypothesis is rejected, meaning farming practices do influence soil erosion rates. It would be crucial to control for external factors like weather, soil type, and natural vegetation.
The variety of hypotheses mentioned above underscores the diversity of research constructs inherent in different fields, each with its unique purpose and way of testing.
While researchers may develop hypotheses primarily as tools to define and narrow the focus of the study, these hypotheses also serve as valuable guiding forces for the data collection and analysis procedures, making the research process more efficient and direction-focused.
Hypotheses serve as a compass for any form of academic research. The diverse examples provided, from Psychology to Educational Studies, Environmental Science to Gerontology, clearly demonstrate how certain hypotheses suit specific fields more aptly than others.
It is important to underline that although these varied hypotheses differ in their structure and methods of testing, each endorses the fundamental value of empiricism in research. Evidence-based decision making remains at the heart of scholarly inquiry, regardless of the research field, thus aligning all hypotheses to the core purpose of scientific investigation.
Testing hypotheses is an essential part of the scientific method . By doing so, researchers can either confirm their predictions, giving further validity to an existing theory, or they might uncover new insights that could potentially shift the field’s understanding of a particular phenomenon. In either case, hypotheses serve as the stepping stones for scientific exploration and discovery.
Atkinson, P., Delamont, S., Cernat, A., Sakshaug, J. W., & Williams, R. A. (2021). SAGE research methods foundations . SAGE Publications Ltd.
Curcio, G., Ferrara, M., & De Gennaro, L. (2006). Sleep loss, learning capacity and academic performance. Sleep medicine reviews , 10 (5), 323-337.
Kim, J. H. (2022). Regular physical exercise and its association with depression: A population-based study short title: Exercise and depression. Psychiatry Research , 309 , 114406.
King, D. E. (2005). Dietary fiber, inflammation, and cardiovascular disease. Molecular nutrition & food research , 49 (6), 594-600.
Marian, V., & Shook, A. (2012, September). The cognitive benefits of being bilingual. In Cerebrum: the Dana forum on brain science (Vol. 2012). Dana Foundation.
Tan, W. C. K. (2022). Research Methods: A Practical Guide For Students And Researchers (Second Edition) . World Scientific Publishing Company.
Waller, N. A., Zhang, N., Cocci, A. H., D’Agostino, C., Wesolek‐Greenson, S., Wheelock, K., … & Resnicow, K. (2021). Screen time use impacts low‐income preschool children’s sleep quality, tiredness, and ability to fall asleep. Child: care, health and development, 47 (5), 618-626.

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Free Social Skills Worksheets
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 10 Reasons you’re Perpetually Single
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 20 Montessori Toddler Bedrooms (Design Inspiration)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 21 Montessori Homeschool Setups
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

- Science Notes Posts
- Contact Science Notes
- Todd Helmenstine Biography
- Anne Helmenstine Biography
- Free Printable Periodic Tables (PDF and PNG)
- Periodic Table Wallpapers
- Interactive Periodic Table
- Periodic Table Posters
- Science Experiments for Kids
- How to Grow Crystals
- Chemistry Projects
- Fire and Flames Projects
- Holiday Science
- Chemistry Problems With Answers
- Physics Problems
- Unit Conversion Example Problems
- Chemistry Worksheets
- Biology Worksheets
- Periodic Table Worksheets
- Physical Science Worksheets
- Science Lab Worksheets
- My Amazon Books
Hypothesis Examples

A hypothesis is a prediction of the outcome of a test. It forms the basis for designing an experiment in the scientific method . A good hypothesis is testable, meaning it makes a prediction you can check with observation or experimentation. Here are different hypothesis examples.
Null Hypothesis Examples
The null hypothesis (H 0 ) is also known as the zero-difference or no-difference hypothesis. It predicts that changing one variable ( independent variable ) will have no effect on the variable being measured ( dependent variable ). Here are null hypothesis examples:
- Plant growth is unaffected by temperature.
- If you increase temperature, then solubility of salt will increase.
- Incidence of skin cancer is unrelated to ultraviolet light exposure.
- All brands of light bulb last equally long.
- Cats have no preference for the color of cat food.
- All daisies have the same number of petals.
Sometimes the null hypothesis shows there is a suspected correlation between two variables. For example, if you think plant growth is affected by temperature, you state the null hypothesis: “Plant growth is not affected by temperature.” Why do you do this, rather than say “If you change temperature, plant growth will be affected”? The answer is because it’s easier applying a statistical test that shows, with a high level of confidence, a null hypothesis is correct or incorrect.
Research Hypothesis Examples
A research hypothesis (H 1 ) is a type of hypothesis used to design an experiment. This type of hypothesis is often written as an if-then statement because it’s easy identifying the independent and dependent variables and seeing how one affects the other. If-then statements explore cause and effect. In other cases, the hypothesis shows a correlation between two variables. Here are some research hypothesis examples:
- If you leave the lights on, then it takes longer for people to fall asleep.
- If you refrigerate apples, they last longer before going bad.
- If you keep the curtains closed, then you need less electricity to heat or cool the house (the electric bill is lower).
- If you leave a bucket of water uncovered, then it evaporates more quickly.
- Goldfish lose their color if they are not exposed to light.
- Workers who take vacations are more productive than those who never take time off.
Is It Okay to Disprove a Hypothesis?
Yes! You may even choose to write your hypothesis in such a way that it can be disproved because it’s easier to prove a statement is wrong than to prove it is right. In other cases, if your prediction is incorrect, that doesn’t mean the science is bad. Revising a hypothesis is common. It demonstrates you learned something you did not know before you conducted the experiment.
Test yourself with a Scientific Method Quiz .
- Mellenbergh, G.J. (2008). Chapter 8: Research designs: Testing of research hypotheses. In H.J. Adèr & G.J. Mellenbergh (eds.), Advising on Research Methods: A Consultant’s Companion . Huizen, The Netherlands: Johannes van Kessel Publishing.
- Popper, Karl R. (1959). The Logic of Scientific Discovery . Hutchinson & Co. ISBN 3-1614-8410-X.
- Schick, Theodore; Vaughn, Lewis (2002). How to think about weird things: critical thinking for a New Age . Boston: McGraw-Hill Higher Education. ISBN 0-7674-2048-9.
- Tobi, Hilde; Kampen, Jarl K. (2018). “Research design: the methodology for interdisciplinary research framework”. Quality & Quantity . 52 (3): 1209–1225. doi: 10.1007/s11135-017-0513-8
Related Posts

How to Write a Hypothesis? Types and Examples

All research studies involve the use of the scientific method, which is a mathematical and experimental technique used to conduct experiments by developing and testing a hypothesis or a prediction about an outcome. Simply put, a hypothesis is a suggested solution to a problem. It includes elements that are expressed in terms of relationships with each other to explain a condition or an assumption that hasn’t been verified using facts. 1 The typical steps in a scientific method include developing such a hypothesis, testing it through various methods, and then modifying it based on the outcomes of the experiments.
A research hypothesis can be defined as a specific, testable prediction about the anticipated results of a study. 2 Hypotheses help guide the research process and supplement the aim of the study. After several rounds of testing, hypotheses can help develop scientific theories. 3 Hypotheses are often written as if-then statements.
Here are two hypothesis examples:
Dandelions growing in nitrogen-rich soils for two weeks develop larger leaves than those in nitrogen-poor soils because nitrogen stimulates vegetative growth. 4
If a company offers flexible work hours, then their employees will be happier at work. 5
Table of Contents
- What is a hypothesis?
- Types of hypotheses
- Characteristics of a hypothesis
- Functions of a hypothesis
- How to write a hypothesis
- Hypothesis examples
- Frequently asked questions
What is a hypothesis?

A hypothesis expresses an expected relationship between variables in a study and is developed before conducting any research. Hypotheses are not opinions but rather are expected relationships based on facts and observations. They help support scientific research and expand existing knowledge. An incorrectly formulated hypothesis can affect the entire experiment leading to errors in the results so it’s important to know how to formulate a hypothesis and develop it carefully.
A few sources of a hypothesis include observations from prior studies, current research and experiences, competitors, scientific theories, and general conditions that can influence people. Figure 1 depicts the different steps in a research design and shows where exactly in the process a hypothesis is developed. 4
There are seven different types of hypotheses—simple, complex, directional, nondirectional, associative and causal, null, and alternative.
Types of hypotheses
The seven types of hypotheses are listed below: 5 , 6,7
- Simple : Predicts the relationship between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable.
Example: Exercising in the morning every day will increase your productivity.
- Complex : Predicts the relationship between two or more variables.
Example: Spending three hours or more on social media daily will negatively affect children’s mental health and productivity, more than that of adults.
- Directional : Specifies the expected direction to be followed and uses terms like increase, decrease, positive, negative, more, or less.
Example: The inclusion of intervention X decreases infant mortality compared to the original treatment.
- Non-directional : Does not predict the exact direction, nature, or magnitude of the relationship between two variables but rather states the existence of a relationship. This hypothesis may be used when there is no underlying theory or if findings contradict prior research.
Example: Cats and dogs differ in the amount of affection they express.
- Associative and causal : An associative hypothesis suggests an interdependency between variables, that is, how a change in one variable changes the other.
Example: There is a positive association between physical activity levels and overall health.
A causal hypothesis, on the other hand, expresses a cause-and-effect association between variables.
Example: Long-term alcohol use causes liver damage.
- Null : Claims that the original hypothesis is false by showing that there is no relationship between the variables.
Example: Sleep duration does not have any effect on productivity.
- Alternative : States the opposite of the null hypothesis, that is, a relationship exists between two variables.
Example: Sleep duration affects productivity.

Characteristics of a hypothesis
So, what makes a good hypothesis? Here are some important characteristics of a hypothesis. 8,9
- Testable : You must be able to test the hypothesis using scientific methods to either accept or reject the prediction.
- Falsifiable : It should be possible to collect data that reject rather than support the hypothesis.
- Logical : Hypotheses shouldn’t be a random guess but rather should be based on previous theories, observations, prior research, and logical reasoning.
- Positive : The hypothesis statement about the existence of an association should be positive, that is, it should not suggest that an association does not exist. Therefore, the language used and knowing how to phrase a hypothesis is very important.
- Clear and accurate : The language used should be easily comprehensible and use correct terminology.
- Relevant : The hypothesis should be relevant and specific to the research question.
- Structure : Should include all the elements that make a good hypothesis: variables, relationship, and outcome.

Functions of a hypothesis
The following list mentions some important functions of a hypothesis: 1
- Maintains the direction and progress of the research.
- Expresses the important assumptions underlying the proposition in a single statement.
- Establishes a suitable context for researchers to begin their investigation and for readers who are referring to the final report.
- Provides an explanation for the occurrence of a specific phenomenon.
- Ensures selection of appropriate and accurate facts necessary and relevant to the research subject.
To summarize, a hypothesis provides the conceptual elements that complete the known data, conceptual relationships that systematize unordered elements, and conceptual meanings and interpretations that explain the unknown phenomena. 1

How to write a hypothesis
Listed below are the main steps explaining how to write a hypothesis. 2,4,5
- Make an observation and identify variables : Observe the subject in question and try to recognize a pattern or a relationship between the variables involved. This step provides essential background information to begin your research.
For example, if you notice that an office’s vending machine frequently runs out of a specific snack, you may predict that more people in the office choose that snack over another.
- Identify the main research question : After identifying a subject and recognizing a pattern, the next step is to ask a question that your hypothesis will answer.
For example, after observing employees’ break times at work, you could ask “why do more employees take breaks in the morning rather than in the afternoon?”
- Conduct some preliminary research to ensure originality and novelty : Your initial answer, which is your hypothesis, to the question is based on some pre-existing information about the subject. However, to ensure that your hypothesis has not been asked before or that it has been asked but rejected by other researchers you would need to gather additional information.
For example, based on your observations you might state a hypothesis that employees work more efficiently when the air conditioning in the office is set at a lower temperature. However, during your preliminary research you find that this hypothesis was proven incorrect by a prior study.
- Develop a general statement : After your preliminary research has confirmed the originality of your proposed answer, draft a general statement that includes all variables, subjects, and predicted outcome. The statement could be if/then or declarative.
- Finalize the hypothesis statement : Use the PICOT model, which clarifies how to word a hypothesis effectively, when finalizing the statement. This model lists the important components required to write a hypothesis.
P opulation: The specific group or individual who is the main subject of the research
I nterest: The main concern of the study/research question
C omparison: The main alternative group
O utcome: The expected results
T ime: Duration of the experiment
Once you’ve finalized your hypothesis statement you would need to conduct experiments to test whether the hypothesis is true or false.
Hypothesis examples
The following table provides examples of different types of hypotheses. 10 ,11

Key takeaways
Here’s a summary of all the key points discussed in this article about how to write a hypothesis.
- A hypothesis is an assumption about an association between variables made based on limited evidence, which should be tested.
- A hypothesis has four parts—the research question, independent variable, dependent variable, and the proposed relationship between the variables.
- The statement should be clear, concise, testable, logical, and falsifiable.
- There are seven types of hypotheses—simple, complex, directional, non-directional, associative and causal, null, and alternative.
- A hypothesis provides a focus and direction for the research to progress.
- A hypothesis plays an important role in the scientific method by helping to create an appropriate experimental design.
Frequently asked questions
Hypotheses and research questions have different objectives and structure. The following table lists some major differences between the two. 9
Here are a few examples to differentiate between a research question and hypothesis.
Yes, here’s a simple checklist to help you gauge the effectiveness of your hypothesis. 9 1. When writing a hypothesis statement, check if it: 2. Predicts the relationship between the stated variables and the expected outcome. 3. Uses simple and concise language and is not wordy. 4. Does not assume readers’ knowledge about the subject. 5. Has observable, falsifiable, and testable results.
As mentioned earlier in this article, a hypothesis is an assumption or prediction about an association between variables based on observations and simple evidence. These statements are usually generic. Research objectives, on the other hand, are more specific and dictated by hypotheses. The same hypothesis can be tested using different methods and the research objectives could be different in each case. For example, Louis Pasteur observed that food lasts longer at higher altitudes, reasoned that it could be because the air at higher altitudes is cleaner (with fewer or no germs), and tested the hypothesis by exposing food to air cleaned in the laboratory. 12 Thus, a hypothesis is predictive—if the reasoning is correct, X will lead to Y—and research objectives are developed to test these predictions.
Null hypothesis testing is a method to decide between two assumptions or predictions between variables (null and alternative hypotheses) in a statistical relationship in a sample. The null hypothesis, denoted as H 0 , claims that no relationship exists between variables in a population and any relationship in the sample reflects a sampling error or occurrence by chance. The alternative hypothesis, denoted as H 1 , claims that there is a relationship in the population. In every study, researchers need to decide whether the relationship in a sample occurred by chance or reflects a relationship in the population. This is done by hypothesis testing using the following steps: 13 1. Assume that the null hypothesis is true. 2. Determine how likely the sample relationship would be if the null hypothesis were true. This probability is called the p value. 3. If the sample relationship would be extremely unlikely, reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypothesis. If the relationship would not be unlikely, accept the null hypothesis.

To summarize, researchers should know how to write a good hypothesis to ensure that their research progresses in the required direction. A hypothesis is a testable prediction about any behavior or relationship between variables, usually based on facts and observation, and states an expected outcome.
We hope this article has provided you with essential insight into the different types of hypotheses and their functions so that you can use them appropriately in your next research project.
References
- Dalen, DVV. The function of hypotheses in research. Proquest website. Accessed April 8, 2024. https://www.proquest.com/docview/1437933010?pq-origsite=gscholar&fromopenview=true&sourcetype=Scholarly%20Journals&imgSeq=1
- McLeod S. Research hypothesis in psychology: Types & examples. SimplyPsychology website. Updated December 13, 2023. Accessed April 9, 2024. https://www.simplypsychology.org/what-is-a-hypotheses.html
- Scientific method. Britannica website. Updated March 14, 2024. Accessed April 9, 2024. https://www.britannica.com/science/scientific-method
- The hypothesis in science writing. Accessed April 10, 2024. https://berks.psu.edu/sites/berks/files/campus/HypothesisHandout_Final.pdf
- How to develop a hypothesis (with elements, types, and examples). Indeed.com website. Updated February 3, 2023. Accessed April 10, 2024. https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/how-to-write-a-hypothesis
- Types of research hypotheses. Excelsior online writing lab. Accessed April 11, 2024. https://owl.excelsior.edu/research/research-hypotheses/types-of-research-hypotheses/
- What is a research hypothesis: how to write it, types, and examples. Researcher.life website. Published February 8, 2023. Accessed April 11, 2024. https://researcher.life/blog/article/how-to-write-a-research-hypothesis-definition-types-examples/
- Developing a hypothesis. Pressbooks website. Accessed April 12, 2024. https://opentext.wsu.edu/carriecuttler/chapter/developing-a-hypothesis/
- What is and how to write a good hypothesis in research. Elsevier author services website. Accessed April 12, 2024. https://scientific-publishing.webshop.elsevier.com/manuscript-preparation/what-how-write-good-hypothesis-research/
- How to write a great hypothesis. Verywellmind website. Updated March 12, 2023. Accessed April 13, 2024. https://www.verywellmind.com/what-is-a-hypothesis-2795239
- 15 Hypothesis examples. Helpfulprofessor.com Published September 8, 2023. Accessed March 14, 2024. https://helpfulprofessor.com/hypothesis-examples/
- Editage insights. What is the interconnectivity between research objectives and hypothesis? Published February 24, 2021. Accessed April 13, 2024. https://www.editage.com/insights/what-is-the-interconnectivity-between-research-objectives-and-hypothesis
- Understanding null hypothesis testing. BCCampus open publishing. Accessed April 16, 2024. https://opentextbc.ca/researchmethods/chapter/understanding-null-hypothesis-testing/#:~:text=In%20null%20hypothesis%20testing%2C%20this,said%20to%20be%20statistically%20significant
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- What is an Argumentative Essay? How to Write It (With Examples)
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)
Measuring Academic Success: Definition & Strategies for Excellence
What are scholarly sources and where can you find them , you may also like, how to write a thematic literature review, chicago style citation guide: understanding the chicago manual..., what is the purpose of an abstract why..., what are citation styles which citation style to..., what are the types of literature reviews , abstract vs introduction: what is the difference , mla format: guidelines, template and examples , machine translation vs human translation: which is reliable..., dissertation printing and binding | types & comparison , what is a dissertation preface definition and examples .
- Translators
- Graphic Designers
Please enter the email address you used for your account. Your sign in information will be sent to your email address after it has been verified.
100 Hypothesis Examples Across Various Academic Fields

A hypothesis is a statement or proposition that is made for the purpose of testing through empirical research. It represents an educated guess or prediction that can be tested through observation and experimentation. A hypothesis is often formulated using a logical construct of "if-then" statements, allowing researchers to set up experiments to determine its validity. It serves as the foundation of a scientific inquiry, providing a clear focus and direction for the study. In essence, a hypothesis is a provisional answer to a research question , which is then subjected to rigorous testing to determine its accuracy.
In this blog post, we'll explore 100 different hypothesis examples, showing you how these simple statements set the stage for discovery in various academic fields. From the mysteries of chemical reactions to the complexities of human behavior, hypotheses are used to kickstart research in numerous disciplines. Whether you're new to the world of academia or just curious about how ideas are tested, these examples will offer insight into the fundamental role hypotheses play in learning and exploration.
- If a plant is given more sunlight, then it will grow faster.
- If an animal's environment is altered, then its behavior will change.
- If a cell is exposed to a toxin, then its function will be impaired.
- If a species is introduced to a new ecosystem, then it may become invasive.
- If an antibiotic is applied to a bacterial culture, then growth will be inhibited.
- If a gene is mutated, then the corresponding protein may become nonfunctional.
- If a pond's water temperature rises, then the algae population will increase.
- If a bird species' habitat is destroyed, then its population will decrease.
- If a mammal is given a high-fat diet, then its cholesterol levels will rise.
- If human stem cells are treated with specific factors, then they will differentiate into targeted cell types.
- If the concentration of a reactant is increased, then the rate of reaction will increase.
- If a metal is placed in a solution of a salt of a less reactive metal, then a displacement reaction will occur.
- If a solution's pH is lowered, then the concentration of hydrogen ions will increase.
- If a gas is cooled at constant pressure, then its volume will decrease according to Charles's law.
- If an endothermic reaction is heated, then the equilibrium position will shift to favor the products.
- If an enzyme is added to a reaction, then the reaction rate will increase due to the lower activation energy.
- If the pressure on a gas is increased at constant temperature, then the volume will decrease according to Boyle's law.
- If a non-polar molecule is added to water, then it will not dissolve due to water's polarity.
- If a piece of litmus paper is placed in a basic solution, then the color of the paper will turn blue.
- If an electric current is passed through a salt solution, then the solution will undergo electrolysis and break down into its components.
Computer science
- If a new algorithm is applied to a sorting problem, then the computational complexity will decrease.
- If multi-factor authentication is implemented, then the security of a system will increase.
- If a machine learning model is trained with more diverse data, then its predictive accuracy will improve.
- If the bandwidth of a network is increased, then the data transmission rate will be faster.
- If a user interface is redesigned following usability guidelines, then user satisfaction and efficiency will increase.
- If a specific optimization technique is applied to a database query, then the retrieval time will be reduced.
- If a new cooling system is used in a data center, then energy consumption will decrease.
- If parallel processing is implemented in a computational task, then the processing time will be reduced.
- If a software development team adopts Agile methodologies, then the project delivery time will be shortened.
- If a more advanced error correction code is used in data transmission, then the error rate will decrease.
- If the interest rate is lowered, then consumer spending will increase.
- If the minimum wage is raised, then unemployment may increase among low-skilled workers.
- If government spending is increased, then the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) may grow.
- If taxes on luxury goods are raised, then consumption of those goods may decrease.
- If a country's currency is devalued, then its exports will become more competitive.
- If inflation is high, then the central bank may increase interest rates to control it.
- If consumer confidence is high, then spending in the economy will likely increase.
- If barriers to entry in a market are reduced, then competition will likely increase.
- If a firm engages in monopolistic practices, then consumer welfare may decrease.
- If unemployment benefits are extended, then the unemployment rate may be temporarily affected.
- If class sizes are reduced, then individual student performance may improve.
- If teachers receive ongoing professional development, then teaching quality will increase.
- If schools implement a comprehensive literacy program, then reading levels among students will rise.
- If parents are actively involved in their children's education, then students' academic achievement may increase.
- If schools provide more access to extracurricular activities, then student engagement and retention may improve.
- If educational technology is integrated into the classroom, then learning outcomes may enhance.
- If a school adopts a zero-tolerance policy on bullying, then the incidence of bullying will decrease.
- If schools provide nutritious meals, then student concentration and performance may improve.
- If a curriculum is designed to include diverse cultural perspectives, then student understanding of different cultures will increase.
- If schools implement individualized learning plans, then students with special needs will achieve better educational outcomes.
Environmental science
- If deforestation rates continue to rise, then biodiversity in the area will decrease.
- If carbon dioxide emissions are reduced, then the rate of global warming may decrease.
- If a water body is polluted with nutrients, then algal blooms may occur, leading to eutrophication.
- If renewable energy sources are used more extensively, then dependency on fossil fuels will decrease.
- If urban areas implement green spaces, then the urban heat island effect may be reduced.
- If protective measures are not implemented, then endangered species may become extinct.
- If waste recycling practices are increased, then landfill usage and waste pollution may decrease.
- If air quality regulations are enforced, then respiratory health issues in the population may decrease.
- If soil erosion control measures are not implemented, then agricultural land fertility may decrease.
- If ocean temperatures continue to rise, then coral reefs may experience more frequent bleaching events.
- If a new chemotherapy drug is administered to cancer patients, then tumor size will decrease more effectively.
- If a specific exercise regimen is followed by osteoarthritis patients, then joint mobility will improve.
- If a population is exposed to higher levels of air pollution, then respiratory diseases such as asthma will increase.
- If a novel surgical technique is utilized in cardiac surgery, then patient recovery times will be shortened.
- If a targeted screening program is implemented for a specific genetic disorder, then early detection and intervention rates will increase.
- If a community's water supply is fortified with fluoride, then dental cavity rates in children will decrease.
- If an improved vaccination schedule is followed in a pediatric population, then the incidence of preventable childhood diseases will decline.
- If nutritional supplements are provided to malnourished individuals, then general health and immune function will improve.
- If stricter infection control protocols are implemented in hospitals, then the rate of hospital-acquired infections will decrease.
- If organ transplant recipients are given a new immunosuppressant drug, then organ rejection rates will decrease.
- If a person is exposed to violent media, then their aggression levels may increase.
- If a child is given positive reinforcement, then desired behaviors will be more likely to be repeated.
- If an individual suffers from anxiety, then their performance on tasks under pressure may decrease.
- If a patient is treated with cognitive-behavioral therapy, then symptoms of depression may reduce.
- If a person lacks sleep, then their cognitive functions and decision-making abilities will decline.
- If an individual's self-esteem is increased, then their overall life satisfaction may improve.
- If a person is exposed to a traumatic event, then they may develop symptoms of PTSD.
- If social support is provided to an individual, then their ability to cope with stress will improve.
- If a group works collaboratively, then they may exhibit improved problem-solving abilities.
- If an individual is given autonomy in their work, then their job satisfaction and motivation will increase.
- If the velocity of an object is increased, then the kinetic energy will also increase.
- If the temperature of a gas is increased at constant pressure, then the volume will increase.
- If the mass of an object is doubled, then the gravitational force it exerts will also double.
- If the frequency of a wave is increased, then the energy it carries will increase.
- If a magnet's distance from a metal object is decreased, then the magnetic force will increase.
- If the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection, then the law of reflection holds true.
- If the resistance in an electrical circuit is increased, then the current will decrease.
- If the force applied to a spring is doubled, then the extension of the spring will also double.
- If a mirror is concave, then it will focus parallel rays to a point.
- If a body is in uniform circular motion, then the net force toward the center is providing the centripetal acceleration.
- If educational opportunities are equally distributed in a society, then social mobility will increase.
- If community policing strategies are implemented, then trust between law enforcement and the community may improve.
- If social media usage increases among teenagers, then face-to-face social interaction may decrease.
- If gender wage gap policies are enforced, then disparities in earnings between men and women will decrease.
- If a society emphasizes individualistic values, then community engagement and collective responsibility may decline.
- If affordable housing initiatives are implemented in urban areas, then homelessness rates may decrease.
- If a minority group is represented in media, then stereotypes and prejudices toward that group may decrease.
- If a culture promotes work-life balance, then overall life satisfaction among its citizens may increase.
- If increased funding is provided to community centers in underserved neighborhoods, then social cohesion and community engagement may improve.
- If legislation is passed to protect the rights of LGBTQ+ individuals, then discrimination and stigma may decrease in society.
In the exploration of various academic disciplines, hypotheses play a crucial role as foundational statements that guide research and inquiry. From understanding complex biological processes to navigating the nuances of human behavior in sociology, hypotheses serve as testable predictions that shape the direction of scientific investigation. The examples provided across the fields of medicine, computer science, sociology, and education illustrate the diverse applications and importance of hypotheses in shaping our understanding of the world. Whether improving medical treatments, enhancing technological systems, fostering social equality, or elevating educational practices, hypotheses remain central to scientific progress and societal advancement. By formulating clear and measurable hypotheses, researchers can continue to unravel complex phenomena, contribute to their fields, and ultimately enrich human knowledge and well-being.
Header image by Qunica .

Scientific Hypothesis
Ai generator.
Embarking on a scientific journey requires hypotheses that challenge, inspire, and guide your inquiries. The essence of any research, a well-framed hypothesis, serves as the compass that directs experiments and Thesis statement analysis. Dive into this comprehensive guide that unfolds a rich tapestry of scientific hypothesis statement examples, elucidates the steps to craft your own, and shares invaluable tips to ensure precision and relevance in your exploratory endeavors.
What is a good Scientific hypothesis statement example?
A good scientific hypothesis statement should be clear, concise, and testable. It should predict a cause-and-effect relationship between two or more variables. For instance: “If soil moisture levels decrease, then plant growth rates will also decrease.”
What is an example of a scientific hypothesis statement?
Consider a researcher studying the effects of sunlight on plant growth. The hypothesis might be: “If a plant is exposed to increased hours of sunlight, then it will grow taller than a plant that receives fewer hours of sunlight.” This Simple hypothesis sets a clear expectation (plant growth) based on a specific condition (hours of sunlight) and is easily testable through experimentation.
100 Scientific Statement Examples

Size: 205 KB
Scientific thesis statements serve as the backbone of research, setting forth clear and testable claims about phenomena. These assertions provide researchers with a focused direction and help them communicate their study’s core intent. Below are captivating examples spanning diverse scientific disciplines.
- Ecology: Increased urbanization will lead to a decrease in biodiversity in metropolitan areas.
- Genetics: Alterations in the BRCA1 gene increase susceptibility to breast cancer in women.
- Astronomy: Planets located within the habitable zone of their star system are more likely to contain traces of water.
- Chemistry: Increasing the temperature of a reaction will increase the rate at which that reaction occurs, up to a point.
- Physics: In the absence of air resistance, all objects fall at the same rate irrespective of their mass.
- Marine Biology: Coral bleaching events are directly correlated with rising sea temperatures.
- Meteorology: The increase in global temperatures has accelerated the melting rate of polar ice caps.
- Neuroscience: Chronic exposure to stress can lead to irreversible damage in the hippocampus of the brain.
- Geology: Tectonic activity along the Pacific Ring of Fire will increase the likelihood of major earthquakes in the region.
- Botany: Plants grown in higher concentrations of carbon dioxide will have faster photosynthesis rates.
- Zoology: Animals that have more intricate mating dances have a higher likelihood of attracting a mate.
- Microbiology: Bacterial resistance to antibiotics increases with the overuse of these medications.
- Biochemistry: Enzymes lose their effectiveness when subjected to temperatures beyond their optimal range.
- Psychology: Exposure to violent video games correlates with aggressive behavior in adolescents.
- Anthropology: Ancient human migration patterns can be traced through the study of mitochondrial DNA.
- Pharmacology: The introduction of Drug X will reduce symptoms of depression more effectively than currently prescribed antidepressants.
- Climatology: An increase in greenhouse gas emissions directly correlates with rising global temperatures.
- Paleontology: The mass extinction event at the end of the Cretaceous period was caused by a meteor impact.
- Mathematics: Prime numbers greater than 2 are always odd numbers.
- Biophysics: Cellular osmosis rates are influenced by the concentration gradient of solute molecules.
- Ornithology: Birds that migrate longer distances have more streamlined body shapes to enhance aerodynamic efficiency.
- Immunology: Vaccinating children against measles will drastically reduce the occurrence of the disease in the general population.
- Nanotechnology: Nanoparticles can be effectively used to target and treat specific cancer cells.
- Environmental Science: The increase in plastic waste in oceans is negatively impacting marine life.
- Molecular Biology: The transcription rate of DNA into RNA is influenced by specific protein regulators.
- Entomology: Insect species that undergo metamorphosis have a higher survival rate than those that don’t.
- Genomics: Identifying specific gene markers can help predict susceptibility to Type 2 Diabetes.
- Agronomy: Crop yields improve with the rotation of specific plant species.
- Astrophysics: Black holes can be identified by observing the radiation emitted at their event horizon.
- Material Science: The tensile strength of a metal increases with the addition of specific alloys.
- Toxicology: Prolonged exposure to pollutant X increases the risk of respiratory diseases in urban dwellers.
- Endocrinology: Hormone imbalances can lead to metabolic syndromes in mammals.
- Space Science: The existence of exoplanets around binary star systems suggests diverse planetary formation processes.
- Physiology: High-intensity interval training (HIIT) increases metabolic rates more significantly than steady-state cardio exercises.
- Quantum Mechanics: Particles can display both wave-like and particle-like behavior under specific observational conditions.
- Pedology: Soil health directly influences the nutritional quality of food crops grown in that soil.
- Mycology: Fungi play a critical role in forest ecosystems by decomposing organic matter and forming symbiotic relationships with trees.
- Virology: Viruses that mutate rapidly pose higher challenges for vaccine development.
- Hydrology: Urban development and deforestation increase the risk of flash floods due to reduced soil absorption capacities.
- Structural Biology: The 3D arrangement of proteins influences their functionality and interaction with other molecules.
- Thermodynamics: An isolated system will always move towards a state of maximum entropy.
- Arachnology: Spider silk’s tensile strength can rival that of steel when adjusted for thickness.
- Paleobotany: The presence of certain ancient pollen types can indicate past climatic conditions of a region.
- Oceanography: Ocean acidification is causing significant disruptions to marine food chains.
- Spectroscopy: Molecules can be identified based on the absorption and emission spectra of light they produce.
- Cytology: Cell division rates can be influenced by the surrounding micro-environment and external growth factors.
- Ethology: Animal behaviors, such as nesting and migration, often correlate with seasonal changes.
- Optics: Light’s behavior changes when passing through materials with different refractive indices.
- Volcanology: Certain gas emissions from volcanoes can serve as early indicators of potential eruptions.
- Bacteriology: Beneficial gut bacteria play a role in digestion and overall human health.
- Nephrology: High sodium intake correlates with increased risk factors for chronic kidney diseases.
- Chronobiology: The human circadian rhythm influences sleep patterns, alertness, and hormone production.
- Rheology: The viscosity of a fluid changes under different temperatures and pressures.
- Aerodynamics: Wing shapes in aircraft influence fuel efficiency and maneuverability.
- Seismology: Earthquake aftershocks can be predicted based on the magnitude of the primary quake.
- Mineralogy: Specific minerals can be identified by their unique crystalline structures and optical properties.
- Pathology: The progression of disease Y is accelerated by genetic predisposition.
- Cosmology: The observed redshift of distant galaxies supports the theory of the expanding universe.
- Dermatology: UV exposure is the primary factor leading to premature skin aging.
- Epidemiology: Vaccination rates correlate inversely with the incidence of infectious diseases in a population.
- Gastroenterology: Diets high in processed sugars correlate with an increased risk of gastrointestinal disorders.
- Forestry: Old growth forests store more carbon per acre than younger, reforested areas.
- Astrobiology: The presence of methane on Mars might suggest microbial life below its surface.
- Hematology: Individuals with blood type O are universal donors for blood transfusions.
- Gerontology: Caloric restriction can extend lifespan in certain organisms.
- Ichthyology: Overfishing in a specific region leads to a decline in the diversity of marine species.
- Limnology: Freshwater lakes with high nutrient runoffs are more susceptible to algal blooms.
- Mammalogy: The echolocation frequency of bats is adapted to their specific prey type.
- Nuclear Physics: The stability of an atomic nucleus depends on the ratio of its protons to neutrons.
- Odonatology: Dragonfly wing patterns play a significant role in mate selection and territorial disputes.
- Petrology: The mineral composition of igneous rocks can indicate the conditions under which they formed.
- Radiology: Modern MRI techniques can detect neural anomalies leading to specific cognitive disorders.
- Statistical Physics: The behavior of macroscopic systems can be predicted by understanding the statistical behaviors of its microscopic constituents.
- Urology: High fluid intake can reduce the risk of kidney stone formation.
- Xenobiology: (Hypothetical) If life exists on exoplanets, it might not be carbon-based, leading to diverse biochemistries.
- Zymology: The fermentation rate of yeast is influenced by sugar concentration and ambient temperature.
- Dendrology: Tree ring patterns can serve as indicators of past climatic conditions.
- Electrophysiology: Neuronal firing rates can be modulated by external electrical stimulation.
- Fossil Fuels: The over-reliance on fossil fuels directly correlates with increased atmospheric CO2 levels.
- Herpetology: Amphibian populations are declining globally due to a combination of habitat loss, pollution, and fungal diseases.
- Kinesiology: Proper biomechanics during physical activities can reduce the risk of injury.
- Lepidopterology: Moth species that mimic unpalatable butterfly species have higher survival rates against predators.
- Mycorrhizae: Fungal and plant root symbiotic relationships enhance nutrient absorption.
- Neuropharmacology: Drug Z shows potential in slowing the progression of Alzheimer’s disease.
- Ornithological Behavior: Birds adjust their migratory patterns in response to changes in food availability.
- Paleoecology: Fossilized pollen and spores can provide clues about ancient ecosystems and climate conditions.
- Quantum Biology: Quantum effects might play a role in efficient energy transfer during photosynthesis.
- Raptor Biology: Urban environments affect the hunting strategies of birds of prey.
- Symbiosis: Mutualistic relationships between species X and Y lead to a more efficient nutrient cycle.
- Tectonics: The movement of tectonic plates influences global climatic patterns over geologic time scales.
- Vertebrate Zoology: The skeletal adaptations of burrowing animals provide increased strength and flexibility for underground movement.
- Weather Patterns: La Niña conditions in the Pacific Ocean correlate with increased rainfall in the Southwestern United States.
- X-ray Crystallography: Protein structures determined through X-ray diffraction techniques provide insights into molecular interactions and functionality.
- Yeast Genetics: Manipulating specific genes in yeast can enhance their fermentation efficiency, impacting biofuel production.
- Zoonotic Diseases: Human encroachment into wild habitats increases the risk of zoonotic disease transmission.
- Agroforestry: Integrating trees into farmlands enhances biodiversity, improves soil quality, and can increase crop yields.
- Bioinformatics: Computational tools in analyzing DNA sequences can predict potential functions of unknown genes.
- Climatology: The ongoing rise in global average temperatures suggests a significant anthropogenic influence on the climate.
- Dermatophytosis: Fungi causing skin infections in humans show increasing resistance to traditional antifungal treatments.
- Ecotourism: Sustainable ecotourism practices can aid in conservation efforts and boost local economies.
Scientific Hypothesis Statement Examples for Research
Scientific hypothesis for research serve as tentative explanations for specific phenomena, which can be tested through experiments or observations. They’re foundational in guiding the direction of scientific inquiry.
- Ozone Depletion: The depletion of ozone in Earth’s atmosphere is majorly contributed by human-made chemicals like CFCs.
- Plant Growth: The rate of plant growth in a hydroponic system is faster compared to traditional soil gardening.
- Aerodynamics: Modified wingtip designs reduce drag and improve fuel efficiency in aircraft.
- Brain Plasticity: Regular cognitive exercises can slow the degenerative processes in aging brains.
- Marine Biology: Coral reefs that experience frequent temperature fluctuations are more resilient to coral bleaching events.
- Chemistry: The rate of chemical reaction X increases with a rise in temperature up to a certain point.
- Geology: Regions with more frequent earthquakes have a thinner lithosphere.
- Endocrinology: Consuming foods high in sugar leads to a rapid spike in insulin levels.
- Environmental Science: Urban areas with more green spaces have lower levels of air pollution.
- Quantum Mechanics: Particle behavior at the quantum level is influenced by the act of observation.
Scientific Investigation Hypothesis Statement Examples
Hypotheses in scientific investigations are proposed explanations or predictions that are directly testable, usually through experiments or special observational techniques.
- Astronomy: The brightness variation of star X is due to the presence of a large exoplanet.
- Microbiology: The presence of bacteria Y in water sources correlates with the onset of disease Z in communities.
- Genetics: Gene A in fruit flies is responsible for wing color variation.
- Neurology: The prolonged use of digital devices causes changes in the sleep patterns of adolescents.
- Ecology: Introduction of a predator in ecosystem B will reduce the population of herbivores.
- Physics: Materials with a higher rate of thermal conductivity cool down faster when exposed to the same conditions.
- Psychology: Exposure to nature reduces levels of stress and anxiety in adults.
- Volcanology: Active volcanoes with higher silica content in their magma are more likely to erupt explosively.
- Anthropology: Early human migrations were influenced by climate changes.
- Botany: Plants exposed to music grow faster than those that aren’t.
Scientific Null Hypothesis Statement Examples
Null hypothesis assert that there is no significant difference or effect, serving as a default stance in research until evidence suggests otherwise.
- Medicine: Treatment A has no significant effect on the recovery rate of patients compared to the placebo.
- Behavioral Science: There is no measurable difference in test scores between students taught with method X versus method Y.
- Genetics: There is no relationship between gene B and the trait C in species D.
- Climatology: Changes in global temperature do not depend on the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
- Pharmacology: Drug E does not significantly alter blood pressure levels more than the standard medication.
- Zoology: There is no difference in the lifespans of species F in the wild versus in captivity.
- Agriculture: Fertilizer G doesn’t increase crop yields more than the traditional fertilizer.
- Physics: Changing the material of wire H does not affect its electrical conductivity.
- Marine Science: The presence of pollutant I has no significant impact on fish reproduction rates.
- Paleontology: The morphology of fossil J is not influenced by the environment it once inhabited.
Testable Scientific Hypothesis Statement Examples
A testable hypothesis is an actionable statement that can be examined and evaluated through empirical means, ensuring clarity and precision in scientific endeavors.
- Meteorology: Increased cloud cover over region K results in decreased daytime temperatures.
- Physiology: Regular exercise increases bone density in adults over the age of 50.
- Geography: River meandering intensity is directly related to the gradient of the terrain.
- Chemical Engineering: Catalyst L enhances the efficiency of reaction M by at least 20%.
- Ornithology: Birds of species N change their migration patterns due to shifts in global temperature.
- Material Science: Alloy O has twice the tensile strength of its primary metal component.
- Sociology: Communities with more recreational areas report higher levels of general well-being.
- Optics: Lens P refracts light at a different angle than lens Q, affecting image clarity.
- Forensics: The presence of substance R is indicative of a specific cause of death.
- Endocrinology: Hormone S levels are directly proportional to the intensity of emotion T.
Scientific Hypothesis Statement Examples for Action Research
In action research, hypotheses often focus on interventions and their outcomes, allowing for iterative improvements in practice based on findings.
- Education: Implementing multimedia tools in classroom U enhances student engagement and understanding.
- Urban Planning: Introducing green corridors in city V reduces the urban heat island effect.
- Healthcare: Incorporating mindfulness exercises in daily routines reduces burnout rates among nurses.
- Agriculture: Using natural predator W reduces pest populations without affecting crop health.
- Community Development: Local art initiatives boost community morale and reduce vandalism rates.
- Business: Employee training program X increases sales by at least 15% in the subsequent quarter.
- Conservation: Implementing recycling program Y in city Z increases waste diversion by 30%.
- Transportation: Carpool initiatives reduce traffic congestion during peak hours.
- Mental Health: Cognitive-behavioral therapy techniques reduce symptom severity in patients with phobias.
- Technology: Introduction of software A in company B enhances workflow efficiency by 25%.
Alternative Hypothesis Statement Examples in Scientific Study
The alternative hypothesis posits a potential relationship or effect, opposing the null hypothesis and indicating a significant result in research.
- Oceanography: Deep-sea mining significantly affects the biodiversity of marine ecosystems.
- Epidemiology: Vaccination rates are inversely related to the incidence of disease C in population D.
- Astronomy: The luminosity of star E is influenced by the presence of nearby celestial bodies.
- Toxicology: Exposure to chemical F at concentration G leads to health complications H.
- Microbiology: The growth rate of bacteria I is inhibited by the presence of antibiotic J.
- Hydrology: River K’s flow rate is influenced by the lunar cycle.
- Seismology: Tectonic activity L is related to the occurrence of supermoons.
- Anthropology: Cultural practices M in tribe N evolved due to environmental pressures O.
- Quantum Physics: The behavior of particle P is determined by the presence of field Q.
- Biochemistry: The activity of enzyme R is enhanced in the presence of compound S.
Scientific Development Hypothesis Statement Examples
These hypotheses address the developmental processes in various fields of science, focusing on growth, evolution, and stages of progression.
- Embryology: Exposure to substance T during the embryonic stage leads to developmental anomalies in species U.
- Evolution: Species V evolved specific traits in response to predation pressures.
- Cognitive Science: Neural connections in the brain’s W region develop faster in children exposed to bilingual environments.
- Plant Science: Plant X’s growth phases are influenced by light duration and intensity.
- Endocrinology: The development of gland Y in adolescents is influenced by nutritional factors.
- Neuroscience: Neuron type Z in the brain develops in response to sensory stimuli during early childhood.
- Genetics: Certain genetic markers indicate a predisposition to developmental disorders A.
- Palaeontology: Dinosaur species B developed feathers for thermoregulation before they were used for flight.
- Pharmacology: The development of drug resistance in bacteria C is influenced by the misuse of antibiotics.
- Sociology: Social structures D in ancient civilizations developed in response to geographic and climatic challenges.
What is a hypothesis in the scientific method?
A s cience hypothesis is a fundamental component of the scientific method, serving as a bridge between the formulation of research questions and the execution of experiments or observations. It is a proposed explanation or prediction about a specific phenomenon, based on prior knowledge, observation, or reasoning, which can be tested and either confirmed or refuted.
The role of a hypothesis in the scientific method can be broken down into several key points:
- Foundation for Research: It provides a clear focus and direction for the research by stipulating what the researcher expects to find or verify.
- Testability: For a hypothesis to be considered scientific, it must be testable through empirical methods (observations or experiments).
- Falsifiability: A scientific hypothesis must also be falsifiable, meaning there should be potential outcomes of the research that would prove the hypothesis wrong. This is a critical aspect of the scientific method, ensuring that hypotheses are not merely speculative.
- Predictive Power: A hypothesis often predicts specific outcomes, allowing for the design of experiments to test these predictions.
- Refinement of Knowledge: Once a hypothesis is tested, it can either be supported, refuted, or require modification, contributing to the evolving body of scientific knowledge.
How do you write a hypothesis statement for Scientific Research – Step by Step Guide
- Identify the Research Question: Before you can write a hypothesis, you need to pinpoint what you’re trying to find out. This could arise from observations, literature reviews, or gaps in current knowledge.
- Conduct Preliminary Research: Get familiar with existing literature and studies on the topic to ensure your hypothesis is novel and relevant.
- Determine the Variables: Identify the independent variable (what you will change) and the dependent variable (what you will observe or measure).
- Formulate the Hypothesis: Write a clear, concise statement that predicts the relationship or effect between the variables. Ensure it’s testable and falsifiable.
- Ensure Clarity: The hypothesis should be specific and unambiguous, so that anyone reading it understands your prediction.
- Check Falsifiability: Ensure there are potential outcomes that could prove your hypothesis incorrect.
- Re-evaluate and Refine: Go back to existing literature or seek peer feedback to ensure your hypothesis is sound and relevant.
Tips for Writing a Scientific Hypothesis Statement
- Be Concise: A hypothesis should be a clear and concise statement, not a question or a vague idea.
- Use Clear Language: Avoid jargon or overly complex language. The statement should be understandable to someone outside of the specific research field.
- Ensure It’s Testable: A hypothesis should make a claim that can be supported or refuted through experimentation or observation.
- Prioritize Falsifiability: While it might be tempting to craft a hypothesis that’s sure to be proven right, it’s essential that there are ways it could be proven wrong.
- Avoid Absolutes: Steer clear of words like “always” or “never” as they can make your hypothesis untestable. Instead, opt for terms that indicate a relationship or effect.
- Stay Relevant: Your hypothesis should be pertinent to the research question and reflect current scientific understanding.
- Seek Feedback: Before finalizing your hypothesis, it can be beneficial to get feedback from peers, mentors, or experts in the field.
- Be Prepared to Revise: As you delve deeper into your research, you may find that your original hypothesis needs refining or modification. This is a natural part of the scientific process.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
- Science, Tech, Math ›
- Chemistry ›
- Scientific Method ›
What Are Examples of a Hypothesis?
- Scientific Method
- Chemical Laws
- Periodic Table
- Projects & Experiments
- Biochemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Medical Chemistry
- Chemistry In Everyday Life
- Famous Chemists
- Activities for Kids
- Abbreviations & Acronyms
- Weather & Climate
- Ph.D., Biomedical Sciences, University of Tennessee at Knoxville
- B.A., Physics and Mathematics, Hastings College
A hypothesis is an explanation for a set of observations. Hypothesis examples can help you understand how this scientific method works.
Although you could state a scientific hypothesis in various ways, most hypotheses are either "If, then" statements or forms of the null hypothesis. The null hypothesis is sometimes called the "no difference" hypothesis. The null hypothesis is good for experimentation because it's simple to disprove. If you disprove a null hypothesis, that is evidence for a relationship between the variables you are examining.
Hypotheses Examples: Null
- All daisies have the same number of petals.
- Hyperactivity is unrelated to eating sugar.
- The number of pets in a household is unrelated to the number of people living in it.
- A person's preference for a shirt is unrelated to its color.
Hypotheses Examples: If, Then
- If you get at least 6 hours of sleep, you will do better on tests than if you get less sleep.
- If you drop a ball, it will fall toward the ground.
- If you drink coffee before going to bed, then it will take longer to fall asleep.
- If you cover a wound with a bandage, then it will heal with less scarring.
Improving a Hypothesis to Make It Testable
You may wish to revise your first hypothesis to make it easier to design an experiment to test. For example, let's say you have a bad breakout the morning after eating a lot of greasy food. You may wonder if there is a correlation between eating greasy food and getting pimples. You propose the hypothesis example:
Eating greasy food causes pimples.
Next, you need to design an experiment to test this hypothesis. Let's say you decide to eat greasy food every day for a week and record the effect on your face. Then, as a control, you'll avoid greasy food for the next week and see what happens. Now, this is not a good experiment because it does not take into account other factors such as hormone levels, stress, sun exposure, exercise, or any number of other variables that might conceivably affect your skin.
The problem is that you cannot assign cause to your effect . If you eat french fries for a week and suffer a breakout, can you definitely say it was the grease in the food that caused it? Maybe it was the salt. Maybe it was the potato. Maybe it was unrelated to diet. You can't prove your hypothesis. It's much easier to disprove a hypothesis.
So, let's restate the hypothesis to make it easier to evaluate the data:
Getting pimples is unaffected by eating greasy food.
So, if you eat fatty food every day for a week and suffer breakouts and then don't break out the week that you avoid greasy food, you can be pretty sure something is up. Can you disprove the hypothesis? Probably not, since it is so hard to assign cause and effect. However, you can make a strong case that there is some relationship between diet and acne.
If your skin stays clear for the entire test, you may decide to accept your hypothesis . Again, you didn't prove or disprove anything, which is fine
- Null Hypothesis Examples
- The Role of a Controlled Variable in an Experiment
- Random Error vs. Systematic Error
- What Is a Testable Hypothesis?
- What Are the Elements of a Good Hypothesis?
- Scientific Hypothesis Examples
- What Is a Hypothesis? (Science)
- Scientific Method Vocabulary Terms
- Scientific Method Flow Chart
- Understanding Simple vs Controlled Experiments
- Six Steps of the Scientific Method
- What Is an Experimental Constant?
- What Is the Difference Between a Control Variable and Control Group?
- What Is a Controlled Experiment?
- Scientific Variable
- DRY MIX Experiment Variables Acronym

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Sep 8, 2023 · A hypothesis is defined as a testable prediction, and is used primarily in scientific experiments as a potential or predicted outcome that scientists attempt to prove or disprove (Atkinson et al., 2021; Tan, 2022). In
Nov 24, 2014 · A hypothesis is a prediction of the outcome of a test. It forms the basis for designing an experiment in the scientific method. A good hypothesis is testable, meaning it makes a prediction you can check with observation or experimentation. Here are different hypothesis examples. Null Hypothesis Examples
Jul 12, 2024 · What is Experimental Hypothesis? An experimental hypothesis, often referred to simply as a hypothesis, is a precise, testable statement about the expected outcome of an experiment or a research study. It predicts a relationship between two or more variables that can be tested through controlled experiments.
Feb 25, 2021 · A hypothesis is a reasoned explanation that is not yet confirmed by the scientific method. It is standard practice to formulate a hypothesis as a starting point of research. This is then refuted, confirmed or reframed based on evidence. The following are illustrative examples of a hypothesis.
Apr 27, 2024 · An incorrectly formulated hypothesis can affect the entire experiment leading to errors in the results so it’s important to know how to formulate a hypothesis and develop it carefully. A few sources of a hypothesis include observations from prior studies, current research and experiences, competitors, scientific theories, and general ...
Jul 29, 2023 · A hypothesis is a statement or proposition that is made for the purpose of testing through empirical research. It represents an educated guess or prediction that can be tested through observation and experimentation. A hypothesis is often formulated using a logical construct of "if-then" statements, allowing researchers to set up experiments to determine its validity. It serves as the ...
Dec 8, 2019 · A hypothesis is an educated guess about what you think will happen in a scientific experiment, based on your observations. Before conducting the experiment, you propose a hypothesis so that you can determine if your prediction is supported.
Jul 23, 2024 · What is an example of a hypothesis statement in science? Example of a hypothesis statement in science: “If the temperature of water increases, then the rate of plant growth will also increase.” This hypothesis predicts a cause-and-effect relationship between water temperature and plant growth, which can be tested through controlled experiments.
Jul 23, 2024 · The essence of any research, a well-framed hypothesis, serves as the compass that directs experiments and Thesis statement analysis. Dive into this comprehensive guide that unfolds a rich tapestry of scientific hypothesis statement examples, elucidates the steps to craft your own, and shares invaluable tips to ensure precision and relevance in ...
Aug 17, 2024 · You may wish to revise your first hypothesis to make it easier to design an experiment to test. For example, let's say you have a bad breakout the morning after eating a lot of greasy food. You may wonder if there is a correlation between eating greasy food and getting pimples. You propose the hypothesis example: