

Review Paper Format: How To Write A Review Article Fast
This guide aims to demystify the review paper format, presenting practical tips to help you accelerate the writing process.
From understanding the structure to synthesising literature effectively, we’ll explore how to create a compelling review article swiftly, ensuring your work is both impactful and timely.
Whether you’re a seasoned researcher or a budding scholar, these info on review paper format and style will streamline your writing journey.
Research Paper, Review Paper Format
What is a review paper.
Diving into the realm of scholarly communication, you might have stumbled upon a research review article.
This unique genre serves to synthesise existing data, offering a panoramic view of the current state of knowledge on a particular topic.

Unlike a standard research article that presents original experiments, a review paper delves into published literature, aiming to:
- clarify, and
- evaluate previous findings.
Imagine you’re tasked to write a review article. The starting point is often a burning research question. Your mission? To scour various journals, piecing together a well-structured narrative that not only summarises key findings but also identifies gaps in existing literature.
This is where the magic of review writing shines – it’s about creating a roadmap for future research, highlighting areas ripe for exploration.
Review articles come in different flavours, with systematic reviews and meta-analyses being the gold standards. The methodology here is meticulous, with a clear protocol for selecting and evaluating studies.
This rigorous approach ensures that your review is more than just an overview; it’s a critical analysis that adds depth to the understanding of the subject.
Crafting a good review requires mastering the art of citation. Every claim or observation you make needs to be backed by relevant literature. This not only lends credibility to your work but also provides a treasure trove of information for readers eager to delve deeper.
Types Of Review Paper
Not all review articles are created equal. Each type has its methodology, purpose, and format, catering to different research needs and questions. Here’s a couple of types of review paper for you to look at:
Systematic Review Paper
First up is the systematic review, the crème de la crème of review types. It’s known for its rigorous methodology, involving a detailed plan for:
- identifying,
- selecting, and
- critically appraising relevant research.
The aim? To answer a specific research question. Systematic reviews often include meta-analyses , where data from multiple studies are statistically combined to provide more robust conclusions.
This review type is a cornerstone in evidence-based fields like healthcare.
Literature Review Paper
Then there’s the literature review, a broader type you might encounter.
Here, the goal is to give an overview of the main points and debates on a topic, without the stringent methodological framework of a systematic review.
Literature reviews are great for getting a grasp of the field and identifying where future research might head. Often reading literature review papers can help you to learn about a topic rather quickly.

Narrative Reviews
Narrative reviews allow for a more flexible approach. Authors of narrative reviews draw on existing literature to provide insights or critique a certain area of research.
This is generally done with a less formal structure than systematic reviews. This type is particularly useful for areas where it’s difficult to quantify findings across studies.
Scoping Reviews
Scoping reviews are gaining traction for their ability to map out the existing literature on a broad topic, identifying:
- key concepts,
- theories, and
Unlike systematic reviews, scoping reviews have a more exploratory approach, which can be particularly useful in emerging fields or for topics that haven’t been comprehensively reviewed before.
Each type of review serves a unique purpose and requires a specific skill set. Whether you’re looking to summarise existing findings, synthesise data for evidence-based practice, or explore new research territories, there’s a review type that fits the bill.
Knowing how to write, read, and interpret these reviews can significantly enhance your understanding of any research area.
What Are The Parts In A Review Paper
A review paper format has a pretty set structure, with minor changes here and there to suit the topic covered. The review paper format not only organises your thoughts but also guides your readers through the complexities of your topic.
Title & Abstract
Starting with the title and abstract, you set the stage. The title should be a concise indicator of the content, making it easier for others to quickly tell what your article content is about.
As for the abstract, it should act as a descriptive summary, offering a snapshot of your review’s scope and findings.
Introduction
The introduction lays the groundwork, presenting the research question that drives your review. It’s here you:
- justify the importance of your review,
- delineating the current state of knowledge and
- highlighting gaps.
This section aims to articulate the significance of the topic and your objective in exploring it.
Methodology
The methodology section is the backbone of systematic reviews and meta-analyses, detailing the research methods employed to select, assess, and synthesise studies.

This transparency allows readers to gauge the rigour and reproducibility of your review. It’s a testament to the integrity of your work, showing how you’ve minimised bias.
The heart of your review lies in the body, where you:
- analyse, and
- critique existing literature .
This is where you synthesise evidence, draw connections, and present both sides of any argument. Well-structured paragraphs and clear subheadings guide readers through your analysis, offering insights and fostering a deeper understanding of the subject.
Discussion & Conclusion
The discussion or conclusion section is where you weave together the main points, reflecting on what your findings mean for the field.
It’s about connecting the dots, offering a synthesis of evidence that answers your initial research question. This part often hints at future research directions, suggesting areas that need further exploration due to gaps in existing knowledge.
Review paper format usually includes the citation list – it is your nod to the scholarly community, acknowledging the contributions of others.
Each citation is a thread in the larger tapestry of academic discourse, enabling readers to delve deeper into the research that has shaped your review.
Tips To Write An Review Article Fast
Writing a review article quickly without sacrificing quality might seem like a tall order, but with the right approach, it’s entirely achievable.
Clearly Define Your Research Question
Clearly define your research question. A focused question not only narrows down the scope of your literature search but also keeps your review concise and on track.
By honing in on a specific aspect of a broader topic, you can avoid the common pitfall of becoming overwhelmed by the vast expanse of available literature. This specificity allows you to zero in on the most relevant studies, making your review more impactful.
Efficient Literature Searching
Utilise databases specific to your field and employ advanced search techniques like Boolean operators. This can drastically reduce the time you spend sifting through irrelevant articles.
Additionally, leveraging citation chains—looking at who has cited a pivotal paper in your area and who it cites—can uncover valuable sources you might otherwise miss.
Organise Your Findings Systematically
Developing a robust organisation strategy is key. As you gather sources, categorize them based on themes or methodologies.
This not only aids in structuring your review but also in identifying areas where research is lacking or abundant. Organize your findings based on the review paper format.
Tools like citation management software can be invaluable here, helping you keep track of your sources and their key points. We list out some of the best AI tools for academic research here.

Build An Outline Before Writing
Don’t underestimate the power of a well-structured outline. A clear blueprint of your article can guide your writing process, ensuring that each section flows logically into the next.
This roadmap not only speeds up the writing process by providing a clear direction but also helps maintain coherence, ensuring your review article delivers a compelling narrative that advances understanding in your field.
Start Writing With The Easiest Sections
When it’s time to write, start with sections you find easiest. This might be the methodology or a particular thematic section where you feel most confident.
Getting words on the page can build momentum, making it easier to tackle more challenging sections later.
Remember, your first draft doesn’t have to be perfect; the goal is to start articulating your synthesis of the literature.
Learn How To Write An Article Review
Mastering the review paper format is a crucial step towards efficient academic writing. By adhering to the structured components outlined, you can streamline the creation of a compelling review article.
Embracing these guidelines not only speeds up the writing process but also enhances the clarity and impact of your work, ensuring your contributions to scholarly discourse are both valuable and timely.
A review paper serves to synthesise existing data, offering a panoramic view of the current state of knowledge on a particular topic
A Review Paper Format Usually Contains What Sections?
You usually will see sections like introduction, literature review, methodology, analysis and findings, discussions, citation and conclusion.
How To Write A Review Paper Fast?
The key is to organize, pre-plan things out before writing it.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider

- Interesting
- Scholarships
- UGC-CARE Journals
How to Write a Best Review Paper to Get More Citation
Review Paper Writing Guide
Are you new to academia? Do you want to learn how to write a good review paper to get in-depth knowledge about your domain? you are at the right place. In this article, you will learn how to write the best review paper in a step-by-step systematic procedure with a sample review article format to get more Citation.
What is a Review Paper?
A review paper, or a literature review , is a thorough, analytical examination of previously published literature. It also provides an overview of current research works on a particular topic in chronological order.
- The main objective of writing a review paper is to evaluate the existing data or results, which can be done through analysis, modeling, classification, comparison, and summary.
- Review papers can help to identify the research gaps, to explore potential areas in a particular field.
- It helps to come out with new conclusions from already published works.
- Any scholar or researcher or scientist who wants to carry out research on a specific theme, first read the review articles relevant to that research area to understand the research gap for arriving at the problem statement.
- Writing a review article provides clarity, novelty, and contribution to the area of research and it demands a great level of in-depth understanding of the subject and a well-structured arrangement of discussions and arguments.
- Some journals publish only review papers, and they do not accept research articles. It is important to check the journal submission guidelines.
Difference Between a Review Paper and a Research Paper
The difference between a review paper and a research paper is presented below.
6 T ypes of Review Papers
The review papers are classified in to six main categories based on the theme and it is presented in the figure below.
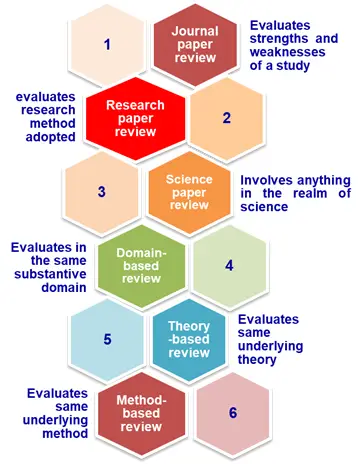
Purpose of Review Paper
The purpose of a review paper is to assess a particular research question, theoretical or practical approach which provides readers with in-depth knowledge and state-of-the-art understanding of the research area.
The purpose of the review paper can vary based on their specific type and research needs.
- Provide a unified, collective overview of the current state of knowledge on a specific research topic and provide an inclusive foundation on a research theme.
- Identify ambiguity, and contradictions in existing results or data.
- Highlight the existing methodological approaches, research techniques, and unique perceptions.
- Develop theoretical outlines to resolve and work on published research.
- Discuss research gaps and future perspectives.
Criteria for Good Review Paper
A good review paper needs to achieve three important criteria. ( Palmatier et al 2017 ).
- First, the area of research should be suitable for writing a review paper so that the author finds sufficient published literature.
- The review paper should be written with suitable literature, detailed discussion, sufficient data/results to support the interpretation, and persuasive language style.
- A completed review paper should provide substantial new innovative ideas to the readers based on the comparison of published works.
Review papers are widely read by many researchers and it helps to get more citations for author. So, it is important to learn how to write a review paper and find a journal to publish .
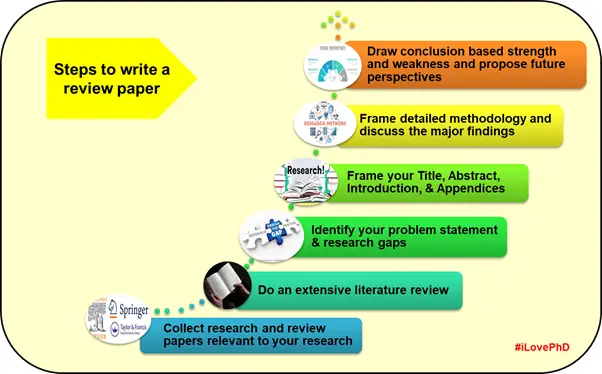
Step-by-Step Systematic Procedure to Write a Review Paper
Time needed: 20 days and 7 hours
The systematic procedural steps to write the best review paper are as follows:
Select a suitable area in your research field formulate clear objectives, and prepare the specific research hypotheses that are to be explored.
Designing your research work is an important step for any researcher. Based on the objectives, develop a clear methodology or protocol to review a review paper.
Thorough analysis and understanding of different published works help the author to identify suitable and relevant data/results that will be used to write the paper.
The degree of analysis to evaluate the collected data varies by extensive review. The examination of trends, patterns, ideas, comparisons, and relationships in the study provides deeper knowledge on that area of research .
Interpretation of results is very important for a good review paper. The author should present the discussion systematically without any ambiguity. The results can be presented in descriptive form, tables, and figures. The new insights should have an in-depth discussion of the topic in line with fundamentals. Finally, the author is expected to present the limitations of the existing study with future perspectives.
Sample Review Article Format
Title, abstract, keywords.
Write an effective and suitable title, abstract, and keywords relevant to your review paper. This will maximize the visibility of your paper online for the readers to find your work. Your title and abstract should be clear, concise, appropriate, and informative.
Introduction
Present a detailed introduction to your research which is published in chronological order in your own words. Don’t summarize the published literature. The introduction should encourage the readers to read your paper.
Various topics to discuss the critical issues
Make sure you present a critical discussion, not a descriptive summary of the topic. If there is contradictory research in your area of research, verify to include an element of debate and present both sides of the argument. A good review paper can resolve the conflict between contradictory works.
Conclusion and Future Perspectives
The written review paper should achieve your objectives. Hence, the review paper should leave the reader with a clear understanding of the following questions:
What they can understand from the review paper?
What still remains a requirement of further investigation in the research area?
This can include making suggestions for future scope on the theme as part of your conclusion.
Acknowledgment
The authors can submit a brief acknowledgment of any financial, instrumentation, and academic support received about research work.
Citing references at appropriate places in the article is necessary and important to avoid plagiarism. Each journal has its referencing style. Therefore, the references need to be listed at the end of the manuscript. The number of references in the review paper is usually higher than in a research paper .
I hope this article will give you a clear idea of how to write a review paper. Please give your valuable comments.
iLovePhD Learn to Research Find Journals to Publish

- Academic Citations
- Academic Writing
- academic writing tips
- basics of research
- Citation Boost
- citation management
- Citation Strategies
- easy review paper writing
- effective writing
- example of review paper
- how to write a literature review
- how to write a review article
- how to write a review paper
- improve your review paper
- Literature Review
- literature review tutorial
- Paper Impact
- Paper Writing
- qualitative research methods
- Research Paper
- Research Paper Writing
- research strategies
- review article
- review paper
- review paper writing guide
- Sample Review Paper
- Scholarly writing
- Scientific Review
- step-by-step review paper
- Types of Review Paper
- write a review paper for college
599 Scopus Indexed Computer Science & Engineering Journals for Fast Publication – 2025
Download ugc care list of journals 2025 pdf, dissertation vs thesis.
Nice thank you for your clarification
How to write a review paper on the relevant of science to education
This blog is very informative. Is it true that an increase in the number of citations improves the quality and impact of a review paper?
Thanks for your ideas. Really helpful
it was very well information
As the best PhD Guidance, we just want to make this PhD journey somewhat smoother. HIGS offers the best PhD help & support for clients across the globe from various subject lines. We will help you with part-time and full-time PhD. At every stage of the research work, we make sure that your work has been completed within a given timeframe and at the lowest possible rate. Our team will help you from the stage of PhD admission to the guideship process. We help you in admission, proposal writing, review paper writing, thesis writing, editing, journal publication, implementation, viva process, guideship, and more. “HIGS- the best PhD guidance & services always stands with you in achieving your research goal through your most prestigious PhD degree”
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Log in to leave a comment
Most Popular
2025 guidelines for thesis structure in academia, a simple thesis outline for your research, 480 ugc care list of journals – science – 2025, dbt research associateship in biotechnology for 2024-2025, call for proposal under innovation & stem demonstration, what is research design and how to frame it, 10 ai tricks to supercharge your research paper, best for you, 24 best online plagiarism checker free – 2024, what is a phd a comprehensive guide for indian scientists and aspiring researchers, popular posts, top 100 journal publications in the world 2024, popular category.
- POSTDOC 317
- Interesting 262
- Journals 237
- Fellowship 136
- Research Methodology 103
- All Scopus Indexed Journals 94
Mail Subscription

iLovePhD is a research education website to know updated research-related information. It helps researchers to find top journals for publishing research articles and get an easy manual for research tools. The main aim of this website is to help Ph.D. scholars who are working in various domains to get more valuable ideas to carry out their research. Learn the current groundbreaking research activities around the world, love the process of getting a Ph.D.
Contact us: [email protected]

Google News
Copyright © 2024 iLovePhD. All rights reserved
- Artificial intelligence
higheredinreview.org
best academic paper tips
- Search for:
What Is a Review Paper? Everything You Need to Know
What is a review paper? The first time handling a review paper may come with its fair share of confusion. Although you may be familiar with a research paper, the review paper often evokes multiple questions from students.
If you have any confusion regarding the review paper, this article will analyse the review paper and compare it with common academic assignments. The article will, therefore, highlight the nuances of a review article, helping you overcome any confusion and submit an outstanding paper.
What is a review article in research?
A review article is an academic paper summarizing the existing knowledge within a field. This paper analyses various sources on a topic to show the extent of research in a given niche, thus, helping a reader get a clear perspective of advancements in research.
Often, the review paper ranges between three thousand and five thousand words and offers a balanced perspective of the topic.
Review paper vs research paper
A review paper and the research paper differ in that the review paper is based on other published works whereas a research paper is based on original research and the analysis of raw data.
As such, the research paper seeks to answer various research questions by conducting experiments to investigate a given phenomenon. This is in contrast with the review paper that only seeks to establish the extent of research within a given topic.
Literature review vs research paper
Like the review paper, the literature review differs from the research paper based on its purpose. The literature review is a section of a research paper that gauges all the sources related to a field to highlight research gaps.
The literature review also offers a summary of existing knowledge and, unlike the research paper, does not tackle original insights into the field.
How to review a paper
The approach taken to write a review paper is a great determinant of the quality of your paper and your writing experience. Some of the steps to consider when writing a review paper include:
- Skim through the paper
Before evaluating the key points in your paper, gauge the paper to identify the main question, the relevance of the research paper to the field, the consistency of the conclusions, and flaws in various arguments.
In this step, you may consider searching for counterarguments to the topic for easy analysis of various inconsistencies within the paper.
- Gauge each section of the paper
After skimming through each section of the paper, gauge each chapter to identify the flaws in the argument and provide the reasoning for various conflicting arguments.
- Outline your review paper
After familiarizing yourself with the literature under study, develop an outline of the major claims you intend to tackle within your review paper. the outline will allow you to organize your arguments and also help you overcome confusion as you write your paper.
- Draft and edit your paper
After outlining your paper, write the first draft and review it to rid your paper of errors that may compromise your final score. You may consider reaching out for expert help to pinpoint the errors that you might have easily glossed over.
Review paper outline
The review paper outline is divided into an introduction, a body, a discussion, and a conclusion. The introduction covers a fifth of the paper’s wordcount and carries the hook and relevance of the research.
The body expands on the evidence of your work and the arguments contained within the item under review. Your conclusion then summarizes your paper, highlighting the state of research on a topic and recommending the research that’s needed to tackle the gaps within the existing research.
We hope that this guide on the review article vs research article has answered any questions you had regarding the review paper. You must read a paper review example to better familiarize yourself with the review paper.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
© 2023 higheredinreview.org
An official website of the United States government
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
How to write a review article?
Ömer gülpınar, adil güçal güçlü.
- Author information
- Article notes
- Copyright and License information
Correspondence: Adil Güçal Güçlü, Department of Urology, Faculty of Medicine İbni Sina Hospital, Ankara University, 06100 Ankara, Turkey, Phone: +90 312 508 22 58, E-mail: [email protected]
Received 2013 Mar 6; Accepted 2013 May 23.
In the medical sciences, the importance of review articles is rising. When clinicians want to update their knowledge and generate guidelines about a topic, they frequently use reviews as a starting point. The value of a review is associated with what has been done, what has been found and how these findings are presented. Before asking ‘how,’ the question of ‘why’ is more important when starting to write a review. The main and fundamental purpose of writing a review is to create a readable synthesis of the best resources available in the literature for an important research question or a current area of research. Although the idea of writing a review is attractive, it is important to spend time identifying the important questions. Good review methods are critical because they provide an unbiased point of view for the reader regarding the current literature. There is a consensus that a review should be written in a systematic fashion, a notion that is usually followed. In a systematic review with a focused question, the research methods must be clearly described. A ‘methodological filter’ is the best method for identifying the best working style for a research question, and this method reduces the workload when surveying the literature. An essential part of the review process is differentiating good research from bad and leaning on the results of the better studies. The ideal way to synthesize studies is to perform a meta-analysis. In conclusion, when writing a review, it is best to clearly focus on fixed ideas, to use a procedural and critical approach to the literature and to express your findings in an attractive way.
Keywords: How to write, review, writing
The importance of review articles in health sciences is increasing day by day. Clinicians frequently benefit from review articles to update their knowledge in their field of specialization, and use these articles as a starting point for formulating guidelines. [ 1 , 2 ] The institutions which provide financial support for further investigations resort to these reviews to reveal the need for these researches. [ 3 ] As is the case with all other researches, the value of a review article is related to what is achieved, what is found, and the way of communicating this information. A few studies have evaluated the quality of review articles. Murlow evaluated 50 review articles published in 1985, and 1986, and revealed that none of them had complied with clear-cut scientific criteria. [ 4 ] In 1996 an international group that analyzed articles, demonstrated the aspects of review articles, and meta-analyses that had not complied with scientific criteria, and elaborated QUOROM (QUality Of Reporting Of Meta-analyses) statement which focused on meta-analyses of randomized controlled studies. [ 5 ] Later on this guideline was updated, and named as PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses). [ 6 ]
Review articles are divided into 2 categories as narrative, and systematic reviews. Narrative reviews are written in an easily readable format, and allow consideration of the subject matter within a large spectrum. However in a systematic review, a very detailed, and comprehensive literature surveying is performed on the selected topic. [ 7 , 8 ] Since it is a result of a more detailed literature surveying with relatively lesser involvement of author’s bias, systematic reviews are considered as gold standard articles. Systematic reviews can be diivded into qualitative, and quantitative reviews. In both of them detailed literature surveying is performed. However in quantitative reviews, study data are collected, and statistically evaluated (ie. meta-analysis). [ 8 ]
Before inquring for the method of preparation of a review article, it is more logical to investigate the motivation behind writing the review article in question. The fundamental rationale of writing a review article is to make a readable synthesis of the best literature sources on an important research inquiry or a topic. This simple definition of a review article contains the following key elements:
The question(s) to be dealt with
Methods used to find out, and select the best quality researches so as to respond to these questions.
To synthetize available, but quite different researches
For the specification of important questions to be answered, number of literature references to be consulted should be more or less determined. Discussions should be conducted with colleagues in the same area of interest, and time should be reserved for the solution of the problem(s). Though starting to write the review article promptly seems to be very alluring, the time you spend for the determination of important issues won’t be a waste of time. [ 9 ]
The PRISMA statement [ 6 ] elaborated to write a well-designed review articles contains a 27-item checklist ( Table 1 ). It will be reasonable to fulfill the requirements of these items during preparation of a review article or a meta-analysis. Thus preparation of a comprehensible article with a high-quality scientific content can be feasible.
PRISMA statement: A 27-item checklist
Contents and format
Important differences exist between systematic, and non-systematic reviews which especially arise from methodologies used in the description of the literature sources. A non-systematic review means use of articles collected for years with the recommendations of your colleagues, while systematic review is based on struggles to search for, and find the best possible researches which will respond to the questions predetermined at the start of the review.
Though a consensus has been reached about the systematic design of the review articles, studies revealed that most of them had not been written in a systematic format. McAlister et al. analyzed review articles in 6 medical journals, and disclosed that in less than one fourth of the review articles, methods of description, evaluation or synthesis of evidence had been provided, one third of them had focused on a clinical topic, and only half of them had provided quantitative data about the extend of the potential benefits. [ 10 ]
Use of proper methodologies in review articles is important in that readers assume an objective attitude towards updated information. We can confront two problems while we are using data from researches in order to answer certain questions. Firstly, we can be prejudiced during selection of research articles or these articles might be biased. To minimize this risk, methodologies used in our reviews should allow us to define, and use researches with minimal degree of bias. The second problem is that, most of the researches have been performed with small sample sizes. In statistical methods in meta-analyses, available researches are combined to increase the statistical power of the study. The problematic aspect of a non-systematic review is that our tendency to give biased responses to the questions, in other words we apt to select the studies with known or favourite results, rather than the best quality investigations among them.
As is the case with many research articles, general format of a systematic review on a single subject includes sections of Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion ( Table 2 ).
Structure of a systematic review
Preparation of the review article
Steps, and targets of constructing a good review article are listed in Table 3 . To write a good review article the items in Table 3 should be implemented step by step. [ 11 – 13 ]
Steps of a systematic review
The research question
It might be helpful to divide the research question into components. The most prevalently used format for questions related to the treatment is PICO (P - Patient, Problem or Population; I-Intervention; C-appropriate Comparisons, and O-Outcome measures) procedure. For example In female patients (P) with stress urinary incontinence, comparisons (C) between transobturator, and retropubic midurethral tension-free band surgery (I) as for patients’ satisfaction (O).
Finding Studies
In a systematic review on a focused question, methods of investigation used should be clearly specified.
Ideally, research methods, investigated databases, and key words should be described in the final report. Different databases are used dependent on the topic analyzed. In most of the clinical topics, Medline should be surveyed. However searching through Embase and CINAHL can be also appropriate.
While determining appropriate terms for surveying, PICO elements of the issue to be sought may guide the process. Since in general we are interested in more than one outcome, P, and I can be key elements. In this case we should think about synonyms of P, and I elements, and combine them with a conjunction AND.
One method which might alleviate the workload of surveying process is “methodological filter” which aims to find the best investigation method for each research question. A good example of this method can be found in PubMed interface of Medline. The Clinical Queries tool offers empirically developed filters for five different inquiries as guidelines for etiology, diagnosis, treatment, prognosis or clinical prediction.
Evaluation of the Quality of the Study
As an indispensable component of the review process is to discriminate good, and bad quality researches from each other, and the outcomes should be based on better qualified researches, as far as possible. To achieve this goal you should know the best possible evidence for each type of question The first component of the quality is its general planning/design of the study. General planning/design of a cohort study, a case series or normal study demonstrates variations.
A hierarchy of evidence for different research questions is presented in Table 4 . However this hierarchy is only a first step. After you find good quality research articles, you won’t need to read all the rest of other articles which saves you tons of time. [ 14 ]
Determination of levels of evidence based on the type of the research question
Formulating a Synthesis
Rarely all researches arrive at the same conclusion. In this case a solution should be found. However it is risky to make a decision based on the votes of absolute majority. Indeed, a well-performed large scale study, and a weakly designed one are weighed on the same scale. Therefore, ideally a meta-analysis should be performed to solve apparent differences. Ideally, first of all, one should be focused on the largest, and higher quality study, then other studies should be compared with this basic study.
Conclusions
In conclusion, during writing process of a review article, the procedures to be achieved can be indicated as follows: 1) Get rid of fixed ideas, and obsessions from your head, and view the subject from a large perspective. 2) Research articles in the literature should be approached with a methodological, and critical attitude and 3) finally data should be explained in an attractive way.
- 1. Oxman AD, Cook DJ, Guyatt GH. Users’ guides to the medical 1 literature. VI. How to use an overview. Evidence-Based Medicine Working Group. JAMA. 1994;272:1367–71. doi: 10.1001/jama.272.17.1367. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 2. Swingler GH, Volmink J, Ioannidis JP. Number of published systematic 2 reviews and global burden of disease: database analysis. BMJ. 2003;327:1083–4. doi: 10.1136/bmj.327.7423.1083. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 3. Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Randomized controlled trials 3 registration/application checklist (12/2006) 2006. www.cihrirsc.gc.ca/e/documents/rct_reg_e.pdf (accessed 19 May 2009).
- 4. Mulrow CD. The medical review article: state of the science. Ann Intern Med. 1987;106:485–8. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-106-3-485. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 5. Moher D, Cook DJ, Eastwood S, Olkin I, Rennie D, Stroup DF. Improving the quality of reports of meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials: the QUOROM statement. Quality of Reporting of Meta-analyses. Lancet. 1999;354:1896–900. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(99)04149-5. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 6. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ. 2009;339:b2535. doi: 10.1136/bmj.b2535. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 7. Collins JA, Fauser B. Balancing the strengths of systematicand narrative reviews. Hum Reprod Update. 2005;11:103–4. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmh058. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 8. Green BN, Johnson CD, Adams A. Writing narrative literaturereviews for peer-reviewed journals: secrets of the trade. J SportsChiropract Rehabil. 2001;15:5–19. doi: 10.1016/S0899-3467(07)60142-6. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 9. Booth WC, Colomb GG, Williams JM. 2003 Series : Chicago Guides to Writing, Editing and Publishing. 2nd edn. Chicago: The Universty of Chicago Press; 2003. The craft of research. [ Google Scholar ]
- 10. McAlister FA, Clark HD, van Walraven C, Straus SE, Lawson FM, Moher D, et al. The medical review article revisited: has the science improved? Ann Intern Med. 1999;131:947–51. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-131-12-199912210-00007. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 11. Glasziou P, Irwig P, Bain C, Colditz G. Systematic reviews in health care: a practical guide. Cambridge University Press; 2001. [ Google Scholar ]
- 12. Khan KS, Kunz R, Kleijnen J, Antes G. Systematic reviews to support evidence based medicine How to review and apply finding of health care research. London: RSM Press; 2003. [ Google Scholar ]
- 13. Mulrow C, Cook D, editors. Systematic reviews: synthesis of best evidence for health care decisions. Philadelphia: American Collage of Phtsicians; 1998. [ Google Scholar ]
- 14. Glasziou PP, Vandenbroucke J, Chalmers I. Assessing the quality of research. BMJ. 2004;328:39–41. doi: 10.1136/bmj.328.7430.39. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- View on publisher site
- PDF (239.9 KB)
- Collections
Similar articles
Cited by other articles, links to ncbi databases.
- Download .nbib .nbib
- Format: AMA APA MLA NLM
Add to Collections
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and Templates
Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and Templates
Table of Contents

Research Paper Formats
The format of a research paper is essential for maintaining consistency, clarity, and readability, enabling readers to understand the research findings effectively. Different disciplines follow specific formats and citation styles, such as APA, MLA, Chicago, and IEEE. Knowing the requirements for each format ensures that researchers present their work in a professional and organized manner.
Why Research Paper Format is Important
- Consistency : A standardized format ensures that each paper has a similar structure, making it easier for readers to locate information.
- Credibility : Following a professional format enhances the credibility of the work, making it look polished and reliable.
- Guidelines for Citations : Proper format helps in organizing references and citing sources accurately, which is crucial for avoiding plagiarism.
- Reader Comprehension : An organized format improves readability, enabling readers to follow the research arguments and findings effortlessly.
Types of Research Paper Formats
1. apa format (american psychological association).
- Discipline : Commonly used in social sciences, psychology, education, and business.
- Title Page : Includes title, author’s name, affiliation, course, instructor, and date.
- Abstract : A brief summary of the research, usually around 150-250 words.
- Main Body : Contains sections such as introduction, method, results, discussion, and conclusion.
- References : Lists all sources cited in the paper in APA style.
- Double-spaced, Times New Roman 12-point font.
- One-inch margins on all sides.
- In-text citations include author’s last name and year (e.g., Smith, 2020).
2. MLA Format (Modern Language Association)
- Discipline : Commonly used in humanities, literature, and cultural studies.
- Header : Author’s name, instructor’s name, course, and date.
- Title : Centered on the first page, no separate title page required.
- Main Body : Sections for introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion.
- Works Cited : Lists all references in MLA style.
- One-inch margins, with in-text citations including the author’s last name and page number (e.g., Smith 45).
3. Chicago Format (Chicago Manual of Style)
- Discipline : Used in history, business, fine arts, and sometimes social sciences.
- Title Page : Includes the title, author’s name, and institutional affiliation.
- Abstract (Optional) : Brief summary, sometimes included depending on requirements.
- Main Body : Includes introduction, main sections, and conclusion.
- Footnotes/Endnotes : Citations are either in the form of footnotes or endnotes.
- Bibliography : Lists all sources in Chicago style.
- One-inch margins, with footnotes or endnotes for in-text citations.
4. IEEE Format (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers)
- Discipline : Primarily used in engineering, computer science, and technical fields.
- Title Page : Includes title, author’s name, affiliations, and acknowledgment.
- Abstract : Brief summary, typically 100-150 words.
- Main Body : Sections such as introduction, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion.
- References : Numbered list of references, with citations in brackets (e.g., [1], [2]).
- Double-column layout, single-spaced, Times New Roman 10-point font.
- One-inch margins, with citations indicated by numbers in brackets within the text.
5. Harvard Format
- Discipline : Widely used in academic publications, particularly in the UK.
- Title Page : Title, author’s name, date, and affiliation.
- Abstract : Summary of the research.
- Main Body : Sections such as introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion.
- References : Alphabetized list in Harvard style.
- One-inch margins, with in-text citations including the author’s last name, year, and page number if applicable (e.g., Smith, 2020).
General Template for Research Paper
Here is a general template applicable across various formats, especially useful if a specific format isn’t required. Researchers can adjust sections based on the format style guide they need to follow.
- Paper Title
- Author’s Name(s)
- Institutional Affiliation
- Brief summary of the research, key findings, and significance.
- Typically 150-250 words.
- Background of the study and research questions.
- Purpose and significance of the research.
- Summary of existing research relevant to the topic.
- Identification of gaps in the literature.
- Detailed explanation of research methods and procedures.
- Description of sample, data collection, and analysis techniques.
- Presentation of findings, often with tables, charts, or graphs.
- Clear and objective reporting of data.
- Interpretation of findings.
- Comparison with other studies, implications, and potential limitations.
- Summary of the research and its contributions.
- Suggestions for future research.
- Complete list of all sources cited in the paper.
- Follow the specific citation style format (APA, MLA, etc.).
- Appendices (if required)
- Additional information, data, or materials relevant to the study but not included in the main text.
Tips for Formatting a Research Paper
- Check Formatting Guidelines : Each journal or institution may have specific requirements, so always refer to the official guidelines.
- Use Consistent Citations : Ensure all in-text citations and references follow the same format, matching the required style.
- Use Headings and Subheadings : Organize sections with clear headings to improve readability and structure.
- Proofread for Formatting Errors : Small formatting errors can detract from the professionalism of the paper, so carefully review layout and style.
- Use Templates in Word Processors : Many word processors offer built-in templates for APA, MLA, and other styles, helping streamline the formatting process.
Example of Research Paper Formatting in APA
Title Page Impact of Social Media on Adolescent Mental Health Author Name University Name Course Name, Instructor Name Date
Abstract This study explores the impact of social media use on adolescent mental health, focusing on levels of anxiety and depression. Data were collected from high school students through a survey. Results suggest a positive correlation between social media use and anxiety, highlighting the need for guidelines on healthy social media habits. (Word count: 150)
Main Body Introduction Discusses the background of social media’s popularity and its psychological effects on teenagers.
Methodology Details the survey process, sample selection, and data analysis techniques.
Results Presents survey findings on the levels of anxiety and depression associated with social media usage.
Discussion Interprets findings in light of previous research and discusses potential implications.
Conclusion Summarizes the key findings, suggesting areas for future study.
References Lists all references in APA format, alphabetically by author.
A research paper’s format is essential for presenting information clearly and professionally. By following specific guidelines, such as APA, MLA, or IEEE, researchers ensure that their work is accessible and credible. Using templates and formatting tips, researchers can structure their papers effectively, improving readability and impact.
- American Psychological Association. (2020). Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.). American Psychological Association.
- Gibaldi, J. (2016). MLA Handbook (8th ed.). Modern Language Association of America.
- University of Chicago Press. (2017). The Chicago Manual of Style (17th ed.). University of Chicago Press.
- IEEE Standards Association. (2020). IEEE Citation Reference . IEEE.
- Pears, R., & Shields, G. (2019). Cite Them Right: The Essential Referencing Guide . Red Globe Press.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Significance of the Study – Examples and Writing...

Appendices – Writing Guide, Types and Examples

How to Publish a Research Paper – Step by Step...

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Abstract – Writing Guide and...

Theoretical Framework – Types, Examples and...
COMMUNICATION IN THE BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES Department of Biology
LITERATURE REVIEW PAPER
WHAT IS A REVIEW PAPER?
CHOOSING A TOPIC
RESEARCHING A TOPIC
HOW TO WRITE THE PAPER
The purpose of a review paper is to succinctly review recent progress in a particular topic. Overall, the paper summarizes the current state of knowledge of the topic. It creates an understanding of the topic for the reader by discussing the findings presented in recent research papers .
A review paper is not a "term paper" or book report . It is not merely a report on some references you found. Instead, a review paper synthesizes the results from several primary literature papers to produce a coherent argument about a topic or focused description of a field.
Examples of scientific reviews can be found in:
Current Opinion in Cell Biology
Current Opinion in Genetics & Development
Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology
Annual Review of Physiology
Trends in Ecology & Evolution
You should read articles from one or more of these sources to get examples of how your paper should be organized.
Scientists commonly use reviews to communicate with each other and the general public. There are a wide variety of review styles from ones aimed at a general audience (e.g., Scientific American ) to those directed at biologists within a particular subdiscipline (e.g., Annual Review of Physiology ).
A key aspect of a review paper is that it provides the evidence for a particular point of view in a field. Thus, a large focus of your paper should be a description of the data that support or refute that point of view. In addition, you should inform the reader of the experimental techniques that were used to generate the data.
The emphasis of a review paper is interpreting the primary literature on the subject. You need to read several original research articles on the same topic and make your own conclusions about the meanings of those papers.
Click here for advice on choosing a topic.
Click here for advice on doing research on your topic.
HOW TO WRITE THE PAPER
Overview of the Paper: Your paper should consist of four general sections:
Review articles contain neither a materials and methods section nor an abstract.
Organizing the Paper: Use topic headings. Do not use a topic heading that reads, "Body of the paper." Instead the topic headings should refer to the actual concepts or ideas covered in that section.
Example
What Goes into Each Section:
Home

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Sep 7, 2024 · Review paper format usually includes the citation list – it is your nod to the scholarly community, acknowledging the contributions of others. Each citation is a thread in the larger tapestry of academic discourse, enabling readers to delve deeper into the research that has shaped your review. Tips To Write An Review Article Fast
Format for a review paper Title page: Title-- reflecting topic of review Your Name Date Abstract: An abstract should be of approximately 200-300 words. Provide a brief summary of the review question being addressed or rationale for the review, the major studies reviewed, and conclusions drawn. Please do not cite references in the Abstract.
Jan 10, 2019 · the knowledge gaps and research needs brought to light by a critical review of the relevant literature and then ensuring that their research design, methods, results, and conclusions follow logically from these objectives (Maier, 2013). There exist a number of papers devoted to instruction on how to write a good review paper. Among the most
Apr 17, 2015 · Review research is done on other research and covers concepts, experiments and data handled previously [29]. The most common form of review research is in the form of a literature review being 60% ...
Mar 31, 2024 · Some journals publish only review papers, and they do not accept research articles. It is important to check the journal submission guidelines. Difference Between a Review Paper and a Research Paper. The difference between a review paper and a research paper is presented below.
As such, the research paper seeks to answer various research questions by conducting experiments to investigate a given phenomenon. This is in contrast with the review paper that only seeks to establish the extent of research within a given topic. Literature review vs research paper. Like the review paper, the literature review differs from the ...
Jul 1, 2014 · Writing a literature review in the pre or post-qualification, will be required to undertake a literature review, either as part of a course of study, as a key step in the research process.
Review articles are divided into 2 categories as narrative, and systematic reviews. Narrative reviews are written in an easily readable format, and allow consideration of the subject matter within a large spectrum. However in a systematic review, a very detailed, and comprehensive literature surveying is performed on the selected topic.
Mar 26, 2024 · Proofread for Formatting Errors: Small formatting errors can detract from the professionalism of the paper, so carefully review layout and style. Use Templates in Word Processors: Many word processors offer built-in templates for APA, MLA, and other styles, helping streamline the formatting process. Example of Research Paper Formatting in APA
A review paper is not a "term paper" or book report. It is not merely a report on some references you found. Instead, a review paper synthesizes the results from several primary literature papers to produce a coherent argument about a topic or focused description of a field. Examples of scientific reviews can be found in: Scientific American