- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Organisational Behaviour
- Human Resource Management
- Entrepreneurship

Tabular Presentation of Data: Meaning, Objectives, Features and Merits
What is tabulation.
The systematic presentation of numerical data in rows and columns is known as Tabulation . It is designed to make presentation simpler and analysis easier. This type of presentation facilitates comparison by putting relevant information close to one another, and it helps in further statistical analysis and interpretation. One of the most important devices for presenting the data in a condensed and readily comprehensible form is tabulation. It aims to provide as much information as possible in the minimum possible space while maintaining the quality and usefulness of the data.
“Tabulation involves the orderly and systematic presentation of numerical data in a form designed to elucidate the problem under consideration.” – L.R. Connor
Objectives of Tabulation
The aim of tabulation is to summarise a large amount of numerical information into the simplest form. The following are the main objectives of tabulation:
- To make complex data simpler: The main aim of tabulation is to present the classified data in a systematic way. The purpose is to condense the bulk of information (data) under investigation into a simple and meaningful form.
- To save space: Tabulation tries to save space by condensing data in a meaningful form while maintaining the quality and quantity of the data.
- To facilitate comparison: It also aims to facilitate quick comparison of various observations by providing the data in a tabular form.
- To facilitate statistical analysis: Tabulation aims to facilitate statistical analysis because it is the stage between data classification and data presentation. Various statistical measures, including averages, dispersion, correlation, and others, are easily calculated from data that has been systematically tabulated.
- To provide a reference: Since data may be easily identifiable and used when organised in tables with titles and table numbers, tabulation aims to provide a reference for future studies.
Features of a Good Table
Tabulation is a very specialised job. It requires a thorough knowledge of statistical methods, as well as abilities, experience, and common sense. A good table must have the following characteristics:
- Title: The top of the table must have a title and it needs to be very appealing and attractive.
- Manageable Size: The table shouldn’t be too big or too small. The size of the table should be in accordance with its objectives and the characteristics of the data. It should completely cover all significant characteristics of data.
- Attractive: A table should have an appealing appearance that appeals to both the sight and the mind so that the reader can grasp it easily without any strain.
- Special Emphasis: The data to be compared should be placed in the left-hand corner of columns, with their titles in bold letters.
- Fit with the Objective: The table should reflect the objective of the statistical investigation.
- Simplicity: To make the table easily understandable, it should be simple and compact.
- Data Comparison: The data to be compared must be placed closely in the columns.
- Numbered Columns and Rows: When there are several rows and columns in a table, they must be numbered for reference.
- Clarity: A table should be prepared so that even a layman may make conclusions from it. The table should contain all necessary information and it must be self-explanatory.
- Units: The unit designations should be written on the top of the table, below the title. For example, Height in cm, Weight in kg, Price in ₹, etc. However, if different items have different units, then they should be mentioned in the respective rows and columns.
- Suitably Approximated: If the figures are large, then they should be rounded or approximated.
- Scientifically Prepared: The preparation of the table should be done in a systematic and logical manner and should be free from any kind of ambiguity and overlapping.
Components of a Table
A table’s preparation is an art that requires skilled data handling. It’s crucial to understand the components of a good statistical table before constructing one. A table is created when all of these components are put together in a systematic order. In simple terms, a good table should include the following components:
1. Table Number:
Each table needs to have a number so it may be quickly identified and used as a reference.
- If there are many tables, they should be numbered in a logical order.
- The table number can be given at the top of the table or the beginning of the table title.
- The table is also identified by its location using subscripted numbers like 1.2, 2.1, etc. For instance, Table Number 3.1 should be seen as the first table of the third chapter.
Each table should have a suitable title. A table’s contents are briefly described in the title.
- The title should be simple, self-explanatory, and free from ambiguity.
- A title should be brief and presented clearly, usually below the table number.
- In certain cases, a long title is preferable for clarification. In these cases, a ‘Catch Title’ may be placed above the ‘Main Title’. For instance , the table’s contents might come after the firm’s name, which appears as a catch title.
- Contents of Title: The title should include the following information: (i) Nature of data, or classification criteria (ii) Subject-matter (iii) Place to which the data relates (iv) Time to which the data relates (v) Source to which the data belongs (vi) Reference to the data, if available.
3. Captions or Column Headings:
A column designation is given to explain the figures in the column at the top of each column in a table. This is referred to as a “Column heading” or “Caption”.
- Captions are used to describe the names or heads of vertical columns.
- To save space, captions are generally placed in small letters in the middle of the columns.
4. Stubs or Row Headings:
Each row of the table needs to have a heading, similar to a caption or column heading. The headers of horizontal rows are referred to as stubs. A brief description of the row headers may also be provided at the table’s left-hand top.
5. Body of Table:
The table’s most crucial component is its body, which contains data (numerical information).
- The location of any one figure or data in the table is fixed and determined by the row and column of the table.
- The columns and rows in the main body’s arrangement of numerical data are arranged from top to bottom.
- The size and shape of the main body should be planned in accordance with the nature of the figures and the purpose of the study.
- As the body of the table summarises the facts and conclusions of the statistical investigation, it must be ensured that the table does not have irrelevant information.
6. Unit of Measurement:
If the unit of measurement of the figures in the table (real data) does not change throughout the table, it should always be provided along with the title.
- However, these units must be mentioned together with stubs or captions if rows or columns have different units.
- If there are large figures, they should be rounded up and the rounding method should be stated.
7. Head Notes:
If the main title does not convey enough information, a head note is included in small brackets in prominent words right below the main title.
- A head-note is included to convey any relevant information.
- For instance, the table frequently uses the units of measurement “in million rupees,” “in tonnes,” “in kilometres,” etc. Head notes are also known as Prefatory Notes .
8. Source Note:
A source note refers to the place where information was obtained.
- In the case of secondary data, a source note is provided.
- Name of the book, page number, table number, etc., from which the data were collected should all be included in the source. If there are multiple sources, each one must be listed in the source note.
- If a reader wants to refer to the original data, the source note enables him to locate the data. Usually, the source note appears at the bottom of the table. For example, the source note may be: ‘Census of India, 2011’.
- Importance: A source note is useful for three reasons: -> It provides credit to the source (person or group), who collected the data; -> It provides a reference to source material that may be more complete; -> It offers some insight into the reliability of the information and its source.
9. Footnotes:
The footnote is the last part of the table. The unique characteristic of the data content of the table that is not self-explanatory and has not previously been explained is mentioned in the footnote.
- Footnotes are used to provide additional information that is not provided by the heading, title, stubs, caption, etc.
- When there are many footnotes, they are numbered in order.
- Footnotes are identified by the symbols *, @, £, etc.
- In general, footnotes are used for the following reasons: (i) To highlight any exceptions to the data (ii)Any special circumstances affecting the data; and (iii)To clarify any information in the data.
.webp)
Merits of Tabular Presentation of Data
The following are the merits of tabular presentation of data:
- Brief and Simple Presentation: Tabular presentation is possibly the simplest method of data presentation. As a result, information is simple to understand. A significant amount of statistical data is also presented in a very brief manner.
- Facilitates Comparison: By grouping the data into different classes, tabulation facilitates data comparison.
- Simple Analysis: Analysing data from tables is quite simple. One can determine the data’s central tendency, dispersion, and correlation by organising the data as a table.
- Highlights Characteristics of the Data: Tabulation highlights characteristics of the data. As a result of this, it is simple to remember the statistical facts.
- Cost-effective: Tabular presentation is a very cost-effective way to convey data. It saves time and space.
- Provides Reference: As the data provided in a tabular presentation can be used for other studies and research, it acts as a source of reference.
Similar Reads
- CBSE Class 11 Statistics for Economics Notes Economic statistics is a topic in applied statistics that concerns the collection, organization, and presentation of data. GeeksforGeeks Class 11 Statistics for Economics Notes have been designed according to the CBSE Syllabus for Class 11. These revision notes consist of detailed Chapterwise import 8 min read
Chapter 1: Concept of Economics and Significance of Statistics in Economics
- Statistics for Economics | Functions, Importance, and Limitations What is Statistics?The word Statistics is derived from the Greek word 'Statistique,' the Latin word 'Status,' the Italian word 'Statista,' and the German word 'Statistic.' Statistics is defined as the study, collection, analysis, interpretation, and organization of data for different ultimate object 8 min read
Chapter 2: Collection of Data
- Data Collection Methods | Primary and Secondary Data Data Collection refers to the systematic process of gathering, measuring, and analyzing information from various sources to get a complete and accurate picture of an area of interest. Data collection is a critical step in any research or data-driven decision-making process, ensuring the accuracy and 11 min read
- Sources of Data Collection | Primary and Secondary Sources Data Collection refers to the systematic process of gathering, measuring, and analyzing information from various sources to get a complete and accurate picture of an area of interest. Different sources of data collection include Primary Sources and Secondary Sources. What is Data?Data is a collectio 8 min read
- Direct Personal Investigation: Meaning, Suitability, Merits, Demerits and Precautions What is Direct Personal Investigation?Direct Personal Investigation or Personal Interview is a method of collecting primary data through which the investigator contacts the informant directly to collect data by conducting on-the-spot enquiry. He/she goes to the field personally, contacts the respond 4 min read
- Indirect Oral Investigation : Suitability, Merits, Demerits and Precautions What is Indirect Oral Investigation?Indirect Oral Investigation is a method of collecting primary data through which the investigator approaches third parties who are in the possession of required information about the subject of enquiry. It is used when the area of investigation is large or the res 4 min read
- Difference between Direct Personal Investigation and Indirect Oral Investigation Direct Personal Investigation and Indirect Oral Investigation are two of the many methods of collecting primary data. What is Direct Personal Investigation? Direct Personal Investigation or Personal Interview is a method of collecting primary data through which the investigator contacts the informan 3 min read
- Information from Local Source or Correspondents: Meaning, Suitability, Merits, and Demerits Data is the collection of measurements and facts and a tool that helps an individual or a group of individuals reach a sound conclusion by providing them with some information. It helps the analyst understand, analyze, and interpret different socio-economic problems like unemployment, poverty, infla 3 min read
- Questionnaires and Schedules Method of Data Collection Questionnaires & Schedule method of data collection : The questionnaires are the fundamental instrument for gathering information in review research. Fundamentally, it is a bunch of standardized questions, frequently called items, which follow a decent plan to gather individual information aroun 6 min read
- Difference between Questionnaire and Schedule Questionnaires and Schedules are two methods of collecting primary data and are different from each other in many ways. What is a Questionnaire? A questionnaire is a research instrument used by any researcher as a tool to collect data or gather information from any source or subject of his or her in 3 min read
- Qualities of a Good Questionnaire and Types of Questionnaires Meaning of QuestionnaireA questionnaire is a research instrument used by any researcher as a tool to collect data or gather information from any source or subject of his or her interest from the respondents. It has a specific goal to understand topics from the respondent's point of view. It consists 5 min read
- What are the Published Sources of Collecting Secondary Data? What is Data?Data is the collection of measurements and facts and a tool that helps an individual or a group of individuals reach a sound conclusion by providing them with some information. It helps the analyst understand, analyse, and interpret different socio-economic problems like unemployment, p 3 min read
- What Precautions should be taken before using Secondary Data? In the plural sense, Statistics refers to facts or quantitative information that can be used to draw significant conclusions. Hence, for a student of Economics, the main purpose to collect data is to recognize, evaluate, and describe a social issue. For example, the problem of poverty or the problem 3 min read
- Two Important Sources of Secondary Data: Census of India and Reports & Publications of NSSO Data is the collection of measurement and facts and a tool that help an individual or a group of individuals reach a sound conclusion by providing them with some information. It helps the analyst understand, analyze, and interpret different socio-economic problems like unemployment, poverty, inflati 3 min read
- What is National Sample Survey Organisation (NSSO)? National Sample Survey (NSS) was set up on the recommendations of the National Income Committee in 1950 and was chaired by the late Professor P.C. Mahalanobis. The basic aim behind setting up NSS was to fill up the large gaps in statistical data to calculate the national income aggregates (especiall 3 min read
- What is Census Method of Collecting Data? Collection of Data is the first step of the statistical investigation and can be gathered through two different sources, namely, primary sources and secondary sources. Besides primary and secondary sources of collecting data, there are two essential methods of collecting data; i.e., Census Method an 4 min read
- Sample Method of Collection of Data Meaning of Population:A population is a pool of similar objects, items, or events that are used to define the subject of study, which is related to some questions or events under study. In statistics, it means the aggregate of all items about which we want to collect information. The population can 6 min read
- Methods of Sampling The sampling method involves selecting a subset of individuals or observations from a larger population to collect data and make inferences about the entire population. It is a practical and efficient way to gather data when it is impractical or impossible to collect information from every member of 11 min read
- Father of Indian Census Who is the Father of Indian Census? Census, a systematic collection and recording of demographic, social, and economic data of a country's population, stands as one of the most crucial tools for understanding the dynamics of a society. In the context of India, the census has played an indispensable 5 min read
- What makes a Sampling Data Reliable? Data is the collection of measurement and facts and a tool that help an individual or a group of individuals reach a sound conclusion by providing them with some information. It helps the analyst understand, analyze, and interpret different socio-economic problems like unemployment, poverty, inflati 2 min read
- Difference between Census Method and Sampling Method of Collecting Data Collection of Data is the first step of the statistical investigation and can be gathered through two different sources, namely, primary sources and secondary sources. Besides primary and secondary sources of collecting data, there are two essential methods of collecting data; i.e., Census Method an 4 min read
- What are Statistical Errors? Data is the collection of measurement and facts and a tool that help an individual or a group of individuals reach a sound conclusion by providing them with some information. It helps the analyst understand, analyze, and interpret different socio-economic problems like unemployment, poverty, inflati 3 min read
Chapter 3: Organisation of Data
- Organization of Data What is Data Organization? The data collected by an investigator is in raw form and cannot offer any meaningful conclusion; hence, it needs to be organized properly. Therefore, the process of systematically arranging the collected data or raw data so that it can be easy to understand the data is kno 6 min read
- Objectives and Characteristics of Classification of Data Data can not always be found in an organised manner. Therefore, an analyst or investigator has to properly organise the collected data for a better analysis of information and to reach the desired results. One of the most important methods of organising such data is known as the classification of da 5 min read
- Classification of Data in Statistics | Meaning and Basis of Classification of Data Classification of data refers to the systematic organization of raw data into groups or categories based on shared characteristics or attributes. This process transforms unstructured data into a structured format, making it easier to analyze and draw meaningful conclusions. Data can be classified ba 5 min read
- Concept of Variable and Raw Data The data collected by an investigator is in raw form and cannot offer any meaningful conclusion; hence, it needs to be organized properly. Therefore, the process of systematically arranging the collected data or raw data so that it can be easy to understand is known as the organization of data. With 4 min read
- Types of Statistical Series In statistics, data is often organized in series to facilitate analysis and interpretation. A statistical series refers to a set of observations arranged in a particular order based on one or more criteria. Understanding the different types of statistical series is crucial for effectively analyzing 13 min read
- Difference between Frequency Array and Frequency Distribution The number of times a specific value appears in a distribution is known as its frequency. For instance, there are 30 students in a class, and fifteen of them have received 80 points, ten have received 90 points, and five have received 100 points. The frequencies will now be 15, 10, and 5. A table in 4 min read
- Types of Frequency Distribution Frequency distribution is a method of organizing and summarizing data to show the frequency (count) of each possible outcome of a dataset. It is an essential tool in statistics for understanding the distribution and pattern of data. There are several types of frequency distributions used based on th 11 min read
Chapter 4: Presentation of Data: Textual and Tabular
- Textual Presentation of Data: Meaning, Suitability, and Drawbacks Presentation of Data refers to the exhibition of data in such a clear and attractive way that it is easily understood and analysed. Data can be presented in different forms, including Textual or Descriptive Presentation, Tabular Presentation, and Diagrammatic Presentation. Textual Presentation Textu 3 min read
- Tabular Presentation of Data: Meaning, Objectives, Features and Merits What is Tabulation?The systematic presentation of numerical data in rows and columns is known as Tabulation. It is designed to make presentation simpler and analysis easier. This type of presentation facilitates comparison by putting relevant information close to one another, and it helps in further 8 min read
- Different Types of Tables The tables can be categorised into various categories depending upon different aspects, such as the purpose, the nature of data used for the investigation, and the extent of coverage of the table. The following are the various kinds of tables that are commonly used in studies of statistics. (I) Clas 4 min read
- Classification and Tabulation of Data Classification and Tabulation of Data are fundamental processes in the field of statistics, especially in the context of economics. They transform raw data into a structured form, enabling better analysis, interpretation, and presentation of economic data. Proper classification ensures that data is 8 min read
Chapter 5: Diagrammatic Presentation of Data
- Diagrammatic Presentation of Data: Meaning , Features, Guidelines, Advantages and Disadvantages Diagrammatic Presentation of Data The technique of presenting statistical data in the form of diagrams such as bar diagrams, cartograms, pie diagrams, and pictograms is known as the Diagrammatic Presentation of Data. Statistics performs an important function by presenting a complex mass of data in a 6 min read
- Types of Diagrams What is a Diagram?Statistics performs an important function by presenting a complex mass of data in a simple way that makes it easier to understand. Classification and tabulation are two techniques for presenting data in an understandable form. However, as the volume of data increases, it becomes in 7 min read
- Bar Graph | Meaning, Types, and Examples Bar graphs are one of the most common and versatile types of charts used to represent categorical data visually. They display data using rectangular bars, where the length or height of each bar corresponds to the value it represents. Bar graphs are widely used in various fields such as business, edu 12 min read
- Pie Diagrams | Meaning, Example and Steps to Construct What is Pie Chart or Pie Diagram?A circle can be divided into parts to show the ratios of different components. A pie diagram is one such representation. Pie charts are also referred to as Angular Circle Diagrams. The circle is divided into as many sections as there are elements by drawing straight 3 min read
- Histogram | Meaning, Example, Types and Steps to Draw What is Histogram?A histogram is a graphical representation of the frequency distribution of continuous series using rectangles. The x-axis of the graph represents the class interval, and the y-axis shows the various frequencies corresponding to different class intervals. A histogram is a two-dimens 5 min read
- Frequency Polygon | Meaning, Steps to Draw and Examples What is Frequency Polygon?A frequency polygon is another way to show a frequency distribution on a graph. In addition to being an alternate for the histogram, the frequency polygon is also an outcome of the histogram. While comparing two or more frequency distributions, a frequency polygon is more s 5 min read
- Ogive (Cumulative Frequency Curve) and its Types A method of presenting data in the form of graphs that provides a quick and easier way to understand the trends of the given set of data is known as Graphic Presentation. The two types of graphs through which a given set of data can be presented are Frequency Distribution Graphs and Time Series Grap 6 min read
- What is Arithmetic Line-Graph or Time-Series Graph? A time series is an arrangement in which the values of variables are recorded in relation to the time of occurrence. In the case of a long series of data, time series helps identify the trend, periodicity, etc. The time period can be defined as a year, quarter, month, week, days, hours, and so on. A 6 min read
- Diagrammatic and Graphic Presentation of Data Diagrammatic and graphic presentation of data means visual representation of the data. It shows a comparison between two or more sets of data and helps in the presentation of highly complex data in its simplest form. Diagrams and graphs are clear and easy to read and understand. In the diagrammatic 4 min read
Chapter 6: Measures of Central Tendency: Arithmetic Mean
- Measures of Central Tendency in Statistics Central Tendencies in Statistics are the numerical values that are used to represent mid-value or central value a large collection of numerical data. These obtained numerical values are called central or average values in Statistics. A central or average value of any statistical data or series is th 10 min read
- Arithmetic Mean: Meaning, Example, Types, Merits, and Demerits A single value used to symbolise a whole set of data is called the Measure of Central Tendency. In comparison to other values, it is a typical value to which the majority of observations are closer. The arithmetic mean is one approach to measure central tendency in statistics. This measure of centra 8 min read
- What is Simple Arithmetic Mean? Arithmetic Mean is one approach to measure central tendency in statistics. This measure of central tendency involves the condensation of a huge amount of data to a single value. Arithmetic mean can be determined using two methods; viz., Simple Arithmetic Mean and Weighted Arithmetic Mean. Meaning of 11 min read
- Calculation of Mean in Individual Series | Formula of Mean What is Mean? Mean is the sum of a set of numbers divided by the total number of values. It is also referred to as the average. For instance, if there are four items in a series, i.e. 2, 5, 8, 3, and 9. The simple arithmetic mean is (2 + 5 + 8 + 3 + 9) / 5 = 5.4. What is Individual Series? The serie 2 min read
- Calculation of Mean in Discrete Series | Formula of Mean What is Mean?Mean is the sum of a set of numbers divided by the total number of values. It is also referred to as the average. For instance, if there are four items in a series, i.e. 2, 5, 8, 3, and 9. The simple arithmetic mean is (2 + 5 + 8 + 3 + 9) / 5 = 5.4. What is Discrete Series?In discrete s 3 min read
- Calculation of Mean in Continuous Series | Formula of Mean The mean, also known as the average, is a measure of central tendency that summarizes a set of data by identifying the central point. In a continuous series, data is grouped into class intervals, and the mean is calculated differently than in a discrete series. The mean provides a comprehensive over 4 min read
- Calculation of Arithmetic Mean in Special Cases A single value used to symbolise a whole set of data is called the Measure of Central Tendency. In comparison to other values, it is a typical value to which the majority of observations are closer. The arithmetic mean is one approach to measure central tendency in statistics. This measure of centra 4 min read
- Weighted Arithmetic Mean Simple Arithmetic Mean gives equal importance to all the variables in a series. However, in some situations, a greater emphasis is given to one item and less to others, i.e., ranking of the variables is done according to their significance in that situation. For example, during inflation, the price 3 min read
Chapter 7: Measures of Central Tendency: Median and Mode
- Median(Measures of Central Tendency): Meaning, Formula, Merits, Demerits, and Examples What is Median?The median is a centrally located value that splits the distribution into two equal portions, one including all values more than or equal to the median and the other containing all values less than or equal to it. The median is the " middle " element when the data set is organized in 8 min read
- Calculation of Median for Different Types of Statistical Series What is Median?When elements in the data set are organised sequentially, that is, in either an ascending or descending order of magnitude, the median can be referred to as the middle value of the data set. Its value is located in a distribution in such a way that 50% of the items are below it and 50 8 min read
- Calculation of Median in Individual Series | Formula of Median What is Median?When elements in the data set are organised sequentially, that is, in either an ascending or descending order of magnitude, the median can be referred to as the middle value of the data set. Its value locates in a distribution in such a way that 50% of the items are below it and 50% a 3 min read
- Calculation of Median in Discrete Series | Formula of Median What is Median?When elements in the data set are organised sequentially, that is, in either an ascending or descending order of magnitude, the median can be referred to as the middle value of the data set. Its value locates in a distribution in such a way that 50% of the items are below it and 50% a 3 min read
- Calculation of Median in Continuous Series | Formula of Median The median is a measure of central tendency that represents the middle value in a dataset, dividing it into two equal halves. In a continuous series, data is grouped into class intervals, and the median is calculated differently than in a discrete series. The median provides valuable insights into t 6 min read
- Graphical determination of Median A measure of central tendency that determines the centrally located value of a given series is known as the Median. The number of values of the series below and above the given series is always equal. To determine the median value of a given series, it is first managed in increasing or decreasing or 5 min read
- Mode: Meaning, Formula, Merits, Demerits, and Examples The word mode is derived from the French word 'La Mode', meaning anything that is in fashion or vogue. A measure of central tendency in statistical series that determines the value occurring most frequently in a given series is known as mode. In other words, the modal value of the series has the hig 9 min read
- Calculation of Mode in Individual Series | Formula of Mode The word mode comes from the Latin word ‘Modus’, meaning measurements, quantity, way, or manner. In statistics, Mode refers to the variable that occurs most of the time or repeats itself most frequently in a given series of variables (say X). It is a maximum occurrence at a particular point or a val 5 min read
- Calculation of Mode in Discrete Series | Formula of Mode The word mode comes from the Latin word 'Modus', meaning measurements, quantity, way, or manner. In statistics, Mode refers to the variable that occurs most of the time or repeats itself most frequently in a given series of variables (say X). It is a maximum occurrence at a particular point or a val 6 min read
- Grouping Method of Calculating Mode in Discrete Series | Formula of Mode Mode is the value from a data set that has occurred the most number of times. It is one of the most crucial measures of central tendency and is represented by Z. For example, if, in a class of 35 students, 10 students are 10 years old, 20 students are 11 years old, and the rest 5 students are 9 year 5 min read
- Calculation of Mode in Continuous Series | Formula of Mode Mode, in statistics, refers to the variable that occurs most of the time in the given series. In simple words, a mode is a variable that repeats itself most frequently in a given series of variables (say X). We can determine the mode in two series; viz., individual and discrete series. Mode is denot 7 min read
- Calculation of Mode in Special Cases The word mode is derived from the French word ‘La Mode’, meaning anything that is in fashion or vogue. A measure of central tendency in statistical series that determines the value occurring most frequently in the given series is known as mode. In other words, the modal value of the series has the h 6 min read
- Calculation of Mode by Graphical Method The word mode is derived from the French word 'La Mode', meaning anything that is in fashion or vogue. A measure of central tendency in statistical series that determines the value occurring most frequently in the given series is known as mode. In other words, the modal value of the series has the h 4 min read
- Mean, Median and Mode| Comparison, Relationship and Calculation A single value used to symbolise a whole set of data is called the Measure of Central Tendency. In comparison to other values, it is a typical value to which the majority of observations are closer. Average and Measure of Location are other names for the Measure of Central Tendency. In statistical a 7 min read
Chapter 8: Measures of Dispersion
- Measures of Dispersion | Meaning, Absolute and Relative Measures of Dispersion Averages like mean, median, and mode can be used to represent any series by a single number. However, averages are not enough to describe the characteristics of statistical data. So, it is necessary to define some additional summary measures to adequately represent the characteristics of a distribut 5 min read
- Range | Meaning, Coefficient of Range, Merits and Demerits, Calculation of Range What is Range?Range is the easiest to understand of all the measures of dispersion. The difference between the largest and smallest item in a distribution is called range. It can be written as: Range (R) = Largest item (L) – Smallest item (S) For example, If the marks of 5 students of class Xth are 4 min read
- Calculation of Range and Coefficient of Range What is Range?Range is the easiest to understand of all the measures of dispersion. The difference between the largest and smallest item in a distribution is called range. It can be written as: Range (R) = Largest item (L) – Smallest item (S) For example, If the marks of 5 students of class XIth are 5 min read
- Interquartile Range and Quartile Deviation The extent to which the values of a distribution differ from the average of that distribution is known as Dispersion. The measures of dispersion can be either absolute or relative. The Measures of Absolute Dispersion consist of Range, Quartile Deviation, Mean Deviation, Standard Deviation, and Loren 3 min read
- Partition Value | Quartiles, Deciles and Percentiles Partition values are statistical measures that divide a dataset into equal parts. They help in understanding the distribution and spread of data by indicating where certain percentages of the data fall. The most commonly used partition values are quartiles, deciles, and percentiles. Table of Content 9 min read
- Quartile Deviation and Coefficient of Quartile Deviation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation, and Examples The extent to which the values of a distribution differ from the average of that distribution is known as Dispersion. The measures of dispersion can be either absolute or relative. The Measures of Absolute Dispersion consist of Range, Quartile Deviation, Mean Deviation, Standard Deviation, and Loren 3 min read
- Quartile Deviation in Discrete Series | Formula, Calculation and Examples What is Quartile Deviation?Quartile Deviation (absolute measure) divides the distribution into multiple quarters. Quartile Deviation is calculated as the average of the difference of the upper quartile (Q3) and the lower quartile (Q1). [Tex]Quartile~Deviation=\frac{Q_3-Q_1}{2} [/Tex] Where, Q3 = Upp 2 min read
- Quartile Deviation in Continuous Series | Formula, Calculation and Examples What is Quartile Deviation?Quartile Deviation (absolute measure) divides the distribution into multiple quarters. Quartile Deviation is calculated as the average of the difference of the upper quartile (Q3) and the lower quartile (Q1). [Tex]Quartile~Deviation=\frac{Q_3-Q_1}{2} [/Tex] Where, Q3 = Upp 3 min read
- Mean Deviation: Coefficient of Mean Deviation, Merits, and Demerits Range, Interquartile range, and Quartile deviation all have the same defect; i.e., they are determined by considering only two values of a series: either the extreme values (as in range) or the values of the quartiles (as in quartile deviation). This approach of analysing dispersion by determining t 5 min read
- Calculation of Mean Deviation for different types of Statistical Series What is Mean Deviation?The arithmetic average of the deviations of various items from a measure of central tendency (mean, median, or mode) is known as the Mean Deviation of a series. Other names for Mean Deviation are the First Moment of Dispersion and Average Deviation. Mean deviation is calculate 3 min read
- Mean Deviation from Mean | Individual, Discrete, and Continuous Series Mean Deviation of a series can be defined as the arithmetic average of the deviations of various items from a measure of central tendency (mean, median, or mode). Mean Deviation is also known as the First Moment of Dispersion or Average Deviation. Mean Deviation is based on all the items of the seri 4 min read
- Mean Deviation from Median | Individual, Discrete, and Continuous Series What is Mean Deviation from Median?Mean Deviation of a series can be defined as the arithmetic average of the deviations of various items from a measure of central tendency (mean, median, or mode). Mean Deviation is also known as the First Moment of Dispersion or Average Deviation. Mean Deviation is 5 min read
- Standard Deviation: Meaning, Coefficient of Standard Deviation, Merits, and Demerits The methods of measuring dispersion such as quartile deviation, range, mean deviation, etc., are not universally adopted as they do not provide much accuracy. Range does not provide required satisfaction as in the entire group, range's magnitude is determined by most extreme cases. Quartile Deviatio 6 min read
- Standard Deviation in Individual Series A scientific measure of dispersion that is widely used in statistical analysis of a given set of data is known as Standard Deviation. Another name for standard deviation is Root Mean Square Deviation. Standard Deviation is denoted by a Greek Symbol σ (sigma). Under this method, the deviation of valu 3 min read
- Standard Deviation in Discrete Series A scientific measure of dispersion that is widely used in statistical analysis of a given set of data is known as Standard Deviation. Another name for standard deviation is Root Mean Square Deviation. Standard Deviation is denoted by a Greek Symbol σ (sigma). Under this method, the deviation of valu 5 min read
- Standard Deviation in Frequency Distribution Series A scientific measure of dispersion that is widely used in statistical analysis of a given set of data is known as Standard Deviation. Another name for standard deviation is Root Mean Square Deviation. It is denoted by a Greek Symbol σ (sigma). Under this method, the deviation of values is taken from 4 min read
- Combined Standard Deviation: Meaning, Formula, and Example A scientific measure of dispersion, which is widely used in statistical analysis of a given set of data is known as Standard Deviation. Another name for standard deviation is Root Mean Square Deviation. Standard Deviation is denoted by a Greek Symbol σ (sigma). Under this method, the deviation of va 2 min read
- How to calculate Variance? What is Variance?Variance is another measure of dispersion and is based on standard deviation. The term variance was first used by R.A. Fisher in 1913 and means the square of the standard deviation of the given distribution. Symbolically, Variance is denoted by σ2. Variance = σ2 [Tex]Standard~Deviat 1 min read
- Coefficient of Variation: Meaning, Formula and Examples What is Coefficient of Variation? As Standard Deviation is an absolute measure of dispersion, one cannot use it for comparing the variability of two or more series when they are expressed in different units. Therefore, in order to compare the variability of two or more series with different units it 2 min read
- Lorenz Curveb : Meaning, Construction, and Application What is Lorenz Curve?The variability of a statistical series can be measured through different measures, Lorenz Curve is one of them. It is a Cumulative Percentage Curve and was first used by Max Lorenz. Generally, Lorenz Curves are used to measure the variability of the distribution of income and w 4 min read
Chapter 9: Correlation
- Correlation: Meaning, Significance, Types and Degree of Correlation The previous statistical approaches (such as central tendency and dispersion) are limited to analysing a single variable or statistical analysis. This type of statistical analysis in which one variable is involved is known as Univariate Distribution. However, there are instances in real-world situat 9 min read
- Methods of Measurements of Correlation What is Correlation?A statistical tool that helps in the study of the relationship between two variables is known as Correlation. It also helps in understanding the economic behaviour of the variables. However, correlation does not tell anything about the cause-and-effect relationship between the tw 4 min read
- Scatter Diagram Correlation | Meaning, Interpretation, Example What is a Scatter Diagram?A simple and attractive method of measuring correlation by diagrammatically representing bivariate distribution for determination of the nature of the correlation between the variables is known as the Scatter Diagram Method. This method gives the investigator/analyst a visu 6 min read
- Spearman's Rank Correlation Coefficient in Statistics Spearman's Rank Correlation Coefficient or Spearman's Rank Difference Method or Formula is a method of calculating the correlation coefficient of qualitative variables and was developed in 1904 by Charles Edward Spearman. In other words, the formula determines the correlation coefficient of variable 6 min read
- Karl Pearson's Coefficient of Correlation | Assumptions, Merits and Demerits What is Karl Pearson's Coefficient of Correlation?The first person to give a mathematical formula for the measurement of the degree of relationship between two variables in 1890 was Karl Pearson. Karl Pearson's Coefficient of Correlation is also known as Product Moment Correlation or Simple Correlat 9 min read
- Karl Pearson's Coefficient of Correlation | Methods and Examples What is Karl Pearson's Coefficient of Correlation?The first person to give a mathematical formula for the measurement of the degree of relationship between two variables in 1890 was Karl Pearson. Karl Pearson's Coefficient of Correlation is also known as Product Moment Correlation or Simple Correlat 6 min read
Chapter 10: Index Number
- Index Number | Meaning, Characteristics, Uses and Limitations What is Index Number?We are a part of a fast-paced economy. Numerous changes in the size of the population, output, money supply, income, and price of commodities are taking place continuously in an ever-changing environment. Economic changes have their effects on the volume of economic activity, in 8 min read
- Methods of Construction of Index Number What is Index Number? A statistical measure that helps in finding out the percentage change in the values of different variables, such as the price of different goods, production of different goods, etc., over time is known as the Index Number. The percentage change is determined by taking a base ye 5 min read
- Unweighted or Simple Index Numbers: Meaning and Methods A statistical measure that helps in finding out the percentage change in the values of different variables, such as the price of different goods, production of different goods, etc., over time is known as the Index Number. The percentage change is determined by taking a base year as a reference. Thi 5 min read
- Methods of calculating Weighted Index Numbers A statistical measure that helps in finding out the percentage change in the values of different variables, such as the price of different goods, production of different goods, etc., over time is known as the Index Number. The percentage change is determined by taking a base year as a reference. Thi 4 min read
- Fisher's Index Number as an Ideal Method A statistical measure that helps in finding out the percentage change in the values of different variables, such as the price of different goods, production of different goods, etc., over time is known as the Index Number. The percentage change is determined by taking a base year as a reference. Thi 3 min read
- Fisher's Method of calculating Weighted Index Number A statistical measure that helps in finding out the percentage change in the values of different variables, such as the price of different goods, production of different goods, etc., over time is known as the Index Number. The percentage change is determined by taking a base year as a reference. Thi 2 min read
- Paasche's Method of calculating Weighted Index Number A statistical measure that helps in finding out the percentage change in the values of different variables, such as the price of different goods, production of different goods, etc., over time is known as the Index Number. The percentage change is determined by taking a base year as a reference. Thi 2 min read
- Laspeyre's Method of calculating Weighted Index Number A statistical measure that helps in finding out the percentage change in the values of different variables, such as the price of different goods, production of different goods, etc., over time is known as the Index Number. The percentage change is determined by taking a base year as a reference. Thi 2 min read
- Laspeyre's, Paasche's, and Fisher's Methods of Calculating Index Number A statistical measure that helps in finding out the percentage change in the values of different variables, such as the price of different goods, production of different goods, etc., over time is known as the Index Number. The percentage change is determined by taking a base year as a reference. Thi 3 min read
- Consumer Price Index (CPI) or Cost of Living Index Number: Construction of Consumer Price Index|Difficulties and Uses of Consumer Price Index A statistical measure that helps in finding out the percentage change in the values of different variables, such as the price of different goods, production of different goods, etc., over time is known as the Index Number. The percentage change is determined by taking a base year as a reference. Thi 9 min read
- Methods of Constructing Consumer Price Index (CPI) The index reflecting the average increase in the cost of the commodities consumed by a class of people and helping them maintain the same standard of living in the current year as in the base year is known as Consumer Price Index (CPI). The main aim behind their design is the measurement of the effe 3 min read
- Wholesale Price Index (WPI) | Meaning, Uses, Merits, and Demerits What is Wholesale Price Index(WPI)?The two most practical and widely used metrics used to assess market inflation in a country are the Wholesale Price Index and the Consumer Price Index. The WPI concentrates on the wholesale level, whereas the CPI concept concentrates on the retail level. The Wholes 6 min read
- Index Number of Industrial Production : Characteristics, Construction & Example The index number was first constructed by an Indian Statistician, Carli in 1764. It was used for the first time to compare the prices of the year 1750 with that of the year 1500. An index number is a statistical tool used to measure changes in the magnitude of a group of related variables. An index 3 min read
- Inflation and Index Number The index number was first constructed by an Indian Statistician, Carli in 1764. It was used for the first time to compare the prices of the year 1750 with that of the year 1500. An index number is a statistical tool for measuring changes in the magnitude of a group of related variables. An index nu 5 min read
Important Formulas in Statistics for Economics
- Important Formulas in Statistics for Economics | Class 11 Statistics for Economics is a field that helps in the study, collection, analysis, interpretation, and organization of data for different ultimate objectives. Statistics help a user in gathering and analyzing huge numerical data easily and efficiently. For this, it provides various statistical tools 15 min read
- Statistics for Economics
- Commerce - 11th
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Data presentation: A comprehensive guide
Learn how to create data presentation effectively and communicate your insights in a way that is clear, concise, and engaging.
Raja Bothra
Building presentations

Table of contents
Hey there, fellow data enthusiast!
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on data presentation.
Whether you're an experienced presenter or just starting, this guide will help you present your data like a pro. We'll dive deep into what data presentation is, why it's crucial, and how to master it. So, let's embark on this data-driven journey together.
What is data presentation?
Data presentation is the art of transforming raw data into a visual format that's easy to understand and interpret. It's like turning numbers and statistics into a captivating story that your audience can quickly grasp. When done right, data presentation can be a game-changer, enabling you to convey complex information effectively.
Why are data presentations important?
Imagine drowning in a sea of numbers and figures. That's how your audience might feel without proper data presentation. Here's why it's essential:
- Clarity : Data presentations make complex information clear and concise.
- Engagement : Visuals, such as charts and graphs, grab your audience's attention.
- Comprehension : Visual data is easier to understand than long, numerical reports.
- Decision-making : Well-presented data aids informed decision-making.
- Impact : It leaves a lasting impression on your audience.
Types of data presentation:
Now, let's delve into the diverse array of data presentation methods, each with its own unique strengths and applications. We have three primary types of data presentation, and within these categories, numerous specific visualization techniques can be employed to effectively convey your data.
1. Textual presentation
Textual presentation harnesses the power of words and sentences to elucidate and contextualize your data. This method is commonly used to provide a narrative framework for the data, offering explanations, insights, and the broader implications of your findings. It serves as a foundation for a deeper understanding of the data's significance.
2. Tabular presentation
Tabular presentation employs tables to arrange and structure your data systematically. These tables are invaluable for comparing various data groups or illustrating how data evolves over time. They present information in a neat and organized format, facilitating straightforward comparisons and reference points.
3. Graphical presentation
Graphical presentation harnesses the visual impact of charts and graphs to breathe life into your data. Charts and graphs are powerful tools for spotlighting trends, patterns, and relationships hidden within the data. Let's explore some common graphical presentation methods:
- Bar charts: They are ideal for comparing different categories of data. In this method, each category is represented by a distinct bar, and the height of the bar corresponds to the value it represents. Bar charts provide a clear and intuitive way to discern differences between categories.
- Pie charts: It excel at illustrating the relative proportions of different data categories. Each category is depicted as a slice of the pie, with the size of each slice corresponding to the percentage of the total value it represents. Pie charts are particularly effective for showcasing the distribution of data.
- Line graphs: They are the go-to choice when showcasing how data evolves over time. Each point on the line represents a specific value at a particular time period. This method enables viewers to track trends and fluctuations effortlessly, making it perfect for visualizing data with temporal dimensions.
- Scatter plots: They are the tool of choice when exploring the relationship between two variables. In this method, each point on the plot represents a pair of values for the two variables in question. Scatter plots help identify correlations, outliers, and patterns within data pairs.
The selection of the most suitable data presentation method hinges on the specific dataset and the presentation's objectives. For instance, when comparing sales figures of different products, a bar chart shines in its simplicity and clarity. On the other hand, if your aim is to display how a product's sales have changed over time, a line graph provides the ideal visual narrative.
Additionally, it's crucial to factor in your audience's level of familiarity with data presentations. For a technical audience, more intricate visualization methods may be appropriate. However, when presenting to a general audience, opting for straightforward and easily understandable visuals is often the wisest choice.
In the world of data presentation, choosing the right method is akin to selecting the perfect brush for a masterpiece. Each tool has its place, and understanding when and how to use them is key to crafting compelling and insightful presentations. So, consider your data carefully, align your purpose, and paint a vivid picture that resonates with your audience.
What to include in data presentation?
When creating your data presentation, remember these key components:
- Data points : Clearly state the data points you're presenting.
- Comparison : Highlight comparisons and trends in your data.
- Graphical methods : Choose the right chart or graph for your data.
- Infographics : Use visuals like infographics to make information more digestible.
- Numerical values : Include numerical values to support your visuals.
- Qualitative information : Explain the significance of the data.
- Source citation : Always cite your data sources.
How to structure an effective data presentation?
Creating a well-structured data presentation is not just important; it's the backbone of a successful presentation. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you craft a compelling and organized presentation that captivates your audience:
1. Know your audience
Understanding your audience is paramount. Consider their needs, interests, and existing knowledge about your topic. Tailor your presentation to their level of understanding, ensuring that it resonates with them on a personal level. Relevance is the key.
2. Have a clear message
Every effective data presentation should convey a clear and concise message. Determine what you want your audience to learn or take away from your presentation, and make sure your message is the guiding light throughout your presentation. Ensure that all your data points align with and support this central message.
3. Tell a compelling story
Human beings are naturally wired to remember stories. Incorporate storytelling techniques into your presentation to make your data more relatable and memorable. Your data can be the backbone of a captivating narrative, whether it's about a trend, a problem, or a solution. Take your audience on a journey through your data.
4. Leverage visuals
Visuals are a powerful tool in data presentation. They make complex information accessible and engaging. Utilize charts, graphs, and images to illustrate your points and enhance the visual appeal of your presentation. Visuals should not just be an accessory; they should be an integral part of your storytelling.
5. Be clear and concise
Avoid jargon or technical language that your audience may not comprehend. Use plain language and explain your data points clearly. Remember, clarity is king. Each piece of information should be easy for your audience to digest.
6. Practice your delivery
Practice makes perfect. Rehearse your presentation multiple times before the actual delivery. This will help you deliver it smoothly and confidently, reducing the chances of stumbling over your words or losing track of your message.
A basic structure for an effective data presentation
Armed with a comprehensive comprehension of how to construct a compelling data presentation, you can now utilize this fundamental template for guidance:
In the introduction, initiate your presentation by introducing both yourself and the topic at hand. Clearly articulate your main message or the fundamental concept you intend to communicate.
Moving on to the body of your presentation, organize your data in a coherent and easily understandable sequence. Employ visuals generously to elucidate your points and weave a narrative that enhances the overall story. Ensure that the arrangement of your data aligns with and reinforces your central message.
As you approach the conclusion, succinctly recapitulate your key points and emphasize your core message once more. Conclude by leaving your audience with a distinct and memorable takeaway, ensuring that your presentation has a lasting impact.
Additional tips for enhancing your data presentation
To take your data presentation to the next level, consider these additional tips:
- Consistent design : Maintain a uniform design throughout your presentation. This not only enhances visual appeal but also aids in seamless comprehension.
- High-quality visuals : Ensure that your visuals are of high quality, easy to read, and directly relevant to your topic.
- Concise text : Avoid overwhelming your slides with excessive text. Focus on the most critical points, using visuals to support and elaborate.
- Anticipate questions : Think ahead about the questions your audience might pose. Be prepared with well-thought-out answers to foster productive discussions.
By following these guidelines, you can structure an effective data presentation that not only informs but also engages and inspires your audience. Remember, a well-structured presentation is the bridge that connects your data to your audience's understanding and appreciation.
Do’s and don'ts on a data presentation
- Use visuals : Incorporate charts and graphs to enhance understanding.
- Keep it simple : Avoid clutter and complexity.
- Highlight key points : Emphasize crucial data.
- Engage the audience : Encourage questions and discussions.
- Practice : Rehearse your presentation.
Don'ts:
- Overload with data : Less is often more; don't overwhelm your audience.
- Fit Unrelated data : Stay on topic; don't include irrelevant information.
- Neglect the audience : Ensure your presentation suits your audience's level of expertise.
- Read word-for-word : Avoid reading directly from slides.
- Lose focus : Stick to your presentation's purpose.
Summarizing key takeaways
- Definition : Data presentation is the art of visualizing complex data for better understanding.
- Importance : Data presentations enhance clarity, engage the audience, aid decision-making, and leave a lasting impact.
- Types : Textual, Tabular, and Graphical presentations offer various ways to present data.
- Choosing methods : Select the right method based on data, audience, and purpose.
- Components : Include data points, comparisons, visuals, infographics, numerical values, and source citations.
- Structure : Know your audience, have a clear message, tell a compelling story, use visuals, be concise, and practice.
- Do's and don'ts : Do use visuals, keep it simple, highlight key points, engage the audience, and practice. Don't overload with data, include unrelated information, neglect the audience's expertise, read word-for-word, or lose focus.
FAQ's on a data presentation
1. what is data presentation, and why is it important in 2024.
Data presentation is the process of visually representing data sets to convey information effectively to an audience. In an era where the amount of data generated is vast, visually presenting data using methods such as diagrams, graphs, and charts has become crucial. By simplifying complex data sets, presentation of the data may helps your audience quickly grasp much information without drowning in a sea of chart's, analytics, facts and figures.
2. What are some common methods of data presentation?
There are various methods of data presentation, including graphs and charts, histograms, and cumulative frequency polygons. Each method has its strengths and is often used depending on the type of data you're using and the message you want to convey. For instance, if you want to show data over time, try using a line graph. If you're presenting geographical data, consider to use a heat map.
3. How can I ensure that my data presentation is clear and readable?
To ensure that your data presentation is clear and readable, pay attention to the design and labeling of your charts. Don't forget to label the axes appropriately, as they are critical for understanding the values they represent. Don't fit all the information in one slide or in a single paragraph. Presentation software like Prezent and PowerPoint can help you simplify your vertical axis, charts and tables, making them much easier to understand.

4. What are some common mistakes presenters make when presenting data?
One common mistake is trying to fit too much data into a single chart, which can distort the information and confuse the audience. Another mistake is not considering the needs of the audience. Remember that your audience won't have the same level of familiarity with the data as you do, so it's essential to present the data effectively and respond to questions during a Q&A session.
5. How can I use data visualization to present important data effectively on platforms like LinkedIn?
When presenting data on platforms like LinkedIn, consider using eye-catching visuals like bar graphs or charts. Use concise captions and e.g., examples to highlight the single most important information in your data report. Visuals, such as graphs and tables, can help you stand out in the sea of textual content, making your data presentation more engaging and shareable among your LinkedIn connections.
Create your data presentation with prezent
Prezent can be a valuable tool for creating data presentations. Here's how Prezent can help you in this regard:
- Time savings : Prezent saves up to 70% of presentation creation time, allowing you to focus on data analysis and insights.
- On-brand consistency : Ensure 100% brand alignment with Prezent's brand-approved designs for professional-looking data presentations.
- Effortless collaboration : Real-time sharing and collaboration features make it easy for teams to work together on data presentations.
- Data storytelling : Choose from 50+ storylines to effectively communicate data insights and engage your audience.
- Personalization : Create tailored data presentations that resonate with your audience's preferences, enhancing the impact of your data.
In summary, Prezent streamlines the process of creating data presentations by offering time-saving features, ensuring brand consistency, promoting collaboration, and providing tools for effective data storytelling. Whether you need to present data to clients, stakeholders, or within your organization, Prezent can significantly enhance your presentation-making process.
So, go ahead, present your data with confidence, and watch your audience be wowed by your expertise.
Thank you for joining us on this data-driven journey. Stay tuned for more insights, and remember, data presentation is your ticket to making numbers come alive! Sign up for our free trial or book a demo !
More zenpedia articles

Employee training and development presentation guide

Clinical trial investment decision: A presentation guide

How to start a resentation: 8 Powerful Approaches
Get the latest from Prezent community
Join thousands of subscribers who receive our best practices on communication, storytelling, presentation design, and more. New tips weekly. (No spam, we promise!)
the intact one
Read MBA, BBA, B.COM Notes
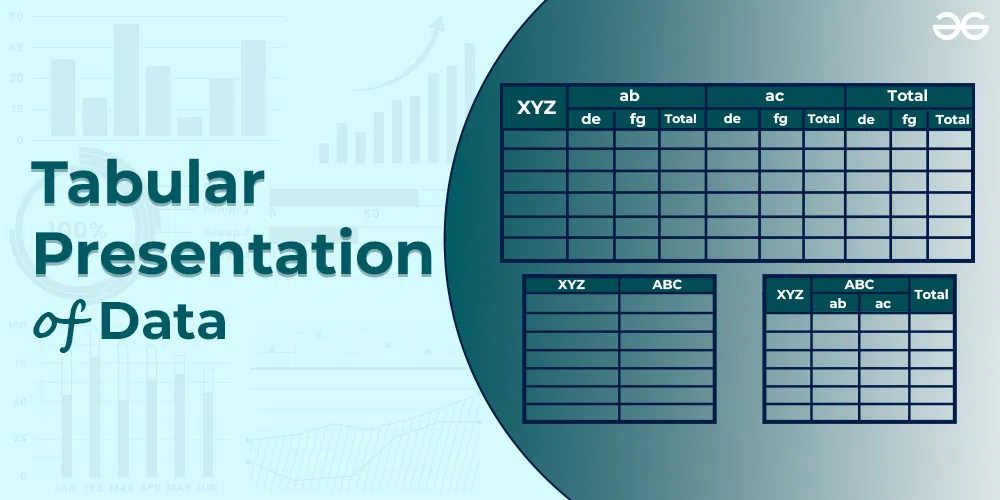
Tabulation and Presentation: Meaning, objectives and Types of Classification
Tabulation is the systematic arrangement of the statistical data in columns or rows. It involves the orderly and systematic presentation of numerical data in a form designed to explain the problem under consideration. Tabulation helps in drawing the inference from the statistical figures.
Tabulation prepares the ground for analysis and interpretation. Therefore a suitable method must be decided carefully taking into account the scope and objects of the investigation, because it is very important part of the statistical methods.
Types of Tabulation
In general, the tabulation is classified in two parts, that is a simple tabulation, and a complex tabulation.
Simple tabulation, gives information regarding one or more independent questions. Complex tabulation gives information regarding two mutually dependent questions.
Two-Way Table
These types of table give information regarding two mutually dependent questions. For example, question is, how many millions of the persons are in the Divisions; the One-Way Table will give the answer. But if we want to know that in the population number, who are in the majority, male, or female. The Two-Way Tables will answer the question by giving the column for female and male. Thus the table showing the real picture of divisions sex wise is as under:
Three-Way Table
Three-Way Table gives information regarding three mutually dependent and inter-related questions.
For example, from one-way table, we get information about population, and from two-way table, we get information about the number of male and female available in various divisions. Now we can extend the same table to a three way table, by putting a question, “How many male and female are literate?” Thus the collected statistical data will show the following, three mutually dependent and inter-related questions:
- Population in various division.
- Their sex-wise distribution.
- Their position of literacy.
Presentation of Data
Presentation of data is of utter importance nowadays. Afterall everything that’s pleasing to our eyes never fails to grab our attention. Presentation of data refers to an exhibition or putting up data in an attractive and useful manner such that it can be easily interpreted. The three main forms of presentation of data are:
- Textual presentation
- Data tables
- Diagrammatic presentation
Textual Presentation
The discussion about the presentation of data starts off with it’s most raw and vague form which is the textual presentation. In such form of presentation, data is simply mentioned as mere text, that is generally in a paragraph. This is commonly used when the data is not very large.
This kind of representation is useful when we are looking to supplement qualitative statements with some data. For this purpose, the data should not be voluminously represented in tables or diagrams. It just has to be a statement that serves as a fitting evidence to our qualitative evidence and helps the reader to get an idea of the scale of a phenomenon.
For example, “the 2002 earthquake proved to be a mass murderer of humans. As many as 10,000 citizens have been reported dead”. The textual representation of data simply requires some intensive reading. This is because the quantitative statement just serves as an evidence of the qualitative statements and one has to go through the entire text before concluding anything.
Further, if the data under consideration is large then the text matter increases substantially. As a result, the reading process becomes more intensive, time-consuming and cumbersome.
Data Tables or Tabular Presentation
A table facilitates representation of even large amounts of data in an attractive, easy to read and organized manner. The data is organized in rows and columns. This is one of the most widely used forms of presentation of data since data tables are easy to construct and read.
Components of Data Tables
- Table Number : Each table should have a specific table number for ease of access and locating. This number can be readily mentioned anywhere which serves as a reference and leads us directly to the data mentioned in that particular table.
- Title: A table must contain a title that clearly tells the readers about the data it contains, time period of study, place of study and the nature of classification of data.
- Headnotes: A headnote further aids in the purpose of a title and displays more information about the table. Generally, headnotes present the units of data in brackets at the end of a table title.
- Stubs: These are titles of the rows in a table. Thus a stub display information about the data contained in a particular row.
- Caption: A caption is the title of a column in the data table. In fact, it is a counterpart if a stub and indicates the information contained in a column.
- Body or field: The body of a table is the content of a table in its entirety. Each item in a body is known as a ‘cell’.
- Footnotes: Footnotes are rarely used. In effect, they supplement the title of a table if required.
- Source: When using data obtained from a secondary source, this source has to be mentioned below the footnote.
Construction of Data Tables
There are many ways for construction of a good table. However, some basic ideas are:
- The title should be in accordance with the objective of study: The title of a table should provide a quick insight into the table.
- Comparison: If there might arise a need to compare any two rows or columns then these might be kept close to each other.
- Alternative location of stubs: If the rows in a data table are lengthy, then the stubs can be placed on the right-hand side of the table.
- Headings: Headings should be written in a singular form. For example, ‘good’ must be used instead of ‘goods’.
- Footnote: A footnote should be given only if needed.
- Size of columns: Size of columns must be uniform and symmetrical.
- Use of abbreviations: Headings and sub-headings should be free of abbreviations.
- Units: There should be a clear specification of units above the columns.
The Advantages of Tabular Presentation
- Ease of representation: A large amount of data can be easily confined in a data table. Evidently, it is the simplest form of data presentation.
- Ease of analysis: Data tables are frequently used for statistical analysis like calculation of central tendency, dispersion etc.
- Helps in comparison: In a data table, the rows and columns which are required to be compared can be placed next to each other. To point out, this facilitates comparison as it becomes easy to compare each value.
- Economical: Construction of a data table is fairly easy and presents the data in a manner which is really easy on the eyes of a reader. Moreover, it saves time as well as space.
Classification of Data and Tabular Presentation
Qualitative classification.
In this classification, data in a table is classified on the basis of qualitative attributes. In other words, if the data contained attributes that cannot be quantified like rural-urban, boys-girls etc. it can be identified as a qualitative classification of data.
Quantitative Classification
In quantitative classification, data is classified on basis of quantitative attributes.
Temporal Classification
Here data is classified according to time. Thus when data is mentioned with respect to different time frames, we term such a classification as temporal.
Spatial Classification
When data is classified according to a location, it becomes a spatial classification.
Advantages of Tabulation
- The large mass of confusing data is easily reduced to reasonable form that is understandable to kind.
- The data once arranged in a suitable form, gives the condition of the situation at a glance, or gives a bird eye view.
- From the table it is easy to draw some reasonable conclusion or inferences.
- Tables gave grounds for analysis of the data.
- Errors, and omission if any are always detected in tabulation.
Therefore the importance of a carefully drawn table is vital for the preparation of data for analysis and interpretation.
Share this:
You might also like, international commercial arbitration, blogs promotion tool, benefits, challenges, audit evidences, 2 thoughts on “ tabulation and presentation: meaning, objectives and types of classification ”.
- Pingback: BBAN206 Business Statistics – HOME | BBA & MBA NOTES
- Pingback: CCSU(BBA) 204 Business Statistics – Home | Management
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Presentation of Data

Statistics deals with the collection, presentation and analysis of the data, as well as drawing meaningful conclusions from the given data. Generally, the data can be classified into two different types, namely primary data and secondary data. If the information is collected by the investigator with a definite objective in their mind, then the data obtained is called the primary data. If the information is gathered from a source, which already had the information stored, then the data obtained is called secondary data. Once the data is collected, the presentation of data plays a major role in concluding the result. Here, we will discuss how to present the data with many solved examples.
What is Meant by Presentation of Data?
As soon as the data collection is over, the investigator needs to find a way of presenting the data in a meaningful, efficient and easily understood way to identify the main features of the data at a glance using a suitable presentation method. Generally, the data in the statistics can be presented in three different forms, such as textual method, tabular method and graphical method.
Presentation of Data Examples
Now, let us discuss how to present the data in a meaningful way with the help of examples.
Consider the marks given below, which are obtained by 10 students in Mathematics:
36, 55, 73, 95, 42, 60, 78, 25, 62, 75.
Find the range for the given data.
Given Data: 36, 55, 73, 95, 42, 60, 78, 25, 62, 75.
The data given is called the raw data.
First, arrange the data in the ascending order : 25, 36, 42, 55, 60, 62, 73, 75, 78, 95.
Therefore, the lowest mark is 25 and the highest mark is 95.
We know that the range of the data is the difference between the highest and the lowest value in the dataset.
Therefore, Range = 95-25 = 70.
Note: Presentation of data in ascending or descending order can be time-consuming if we have a larger number of observations in an experiment.
Now, let us discuss how to present the data if we have a comparatively more number of observations in an experiment.
Consider the marks obtained by 30 students in Mathematics subject (out of 100 marks)
10, 20, 36, 92, 95, 40, 50, 56, 60, 70, 92, 88, 80, 70, 72, 70, 36, 40, 36, 40, 92, 40, 50, 50, 56, 60, 70, 60, 60, 88.
In this example, the number of observations is larger compared to example 1. So, the presentation of data in ascending or descending order is a bit time-consuming. Hence, we can go for the method called ungrouped frequency distribution table or simply frequency distribution table . In this method, we can arrange the data in tabular form in terms of frequency.
For example, 3 students scored 50 marks. Hence, the frequency of 50 marks is 3. Now, let us construct the frequency distribution table for the given data.
Therefore, the presentation of data is given as below:
The following example shows the presentation of data for the larger number of observations in an experiment.
Consider the marks obtained by 100 students in a Mathematics subject (out of 100 marks)
95, 67, 28, 32, 65, 65, 69, 33, 98, 96,76, 42, 32, 38, 42, 40, 40, 69, 95, 92, 75, 83, 76, 83, 85, 62, 37, 65, 63, 42, 89, 65, 73, 81, 49, 52, 64, 76, 83, 92, 93, 68, 52, 79, 81, 83, 59, 82, 75, 82, 86, 90, 44, 62, 31, 36, 38, 42, 39, 83, 87, 56, 58, 23, 35, 76, 83, 85, 30, 68, 69, 83, 86, 43, 45, 39, 83, 75, 66, 83, 92, 75, 89, 66, 91, 27, 88, 89, 93, 42, 53, 69, 90, 55, 66, 49, 52, 83, 34, 36.
Now, we have 100 observations to present the data. In this case, we have more data when compared to example 1 and example 2. So, these data can be arranged in the tabular form called the grouped frequency table. Hence, we group the given data like 20-29, 30-39, 40-49, ….,90-99 (As our data is from 23 to 98). The grouping of data is called the “class interval” or “classes”, and the size of the class is called “class-size” or “class-width”.
In this case, the class size is 10. In each class, we have a lower-class limit and an upper-class limit. For example, if the class interval is 30-39, the lower-class limit is 30, and the upper-class limit is 39. Therefore, the least number in the class interval is called the lower-class limit and the greatest limit in the class interval is called upper-class limit.
Hence, the presentation of data in the grouped frequency table is given below:
Hence, the presentation of data in this form simplifies the data and it helps to enable the observer to understand the main feature of data at a glance.
Practice Problems
- The heights of 50 students (in cms) are given below. Present the data using the grouped frequency table by taking the class intervals as 160 -165, 165 -170, and so on. Data: 161, 150, 154, 165, 168, 161, 154, 162, 150, 151, 162, 164, 171, 165, 158, 154, 156, 172, 160, 170, 153, 159, 161, 170, 162, 165, 166, 168, 165, 164, 154, 152, 153, 156, 158, 162, 160, 161, 173, 166, 161, 159, 162, 167, 168, 159, 158, 153, 154, 159.
- Three coins are tossed simultaneously and each time the number of heads occurring is noted and it is given below. Present the data using the frequency distribution table. Data: 0, 1, 2, 2, 1, 2, 3, 1, 3, 0, 1, 3, 1, 1, 2, 2, 0, 1, 2, 1, 3, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 2, 2, 0.
To learn more Maths-related concepts, stay tuned with BYJU’S – The Learning App and download the app today!
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
- Textual And Tabular Presentation Of Data
Think about a scenario where your report cards are printed in a textual format. Your grades and remarks about you are presented in a paragraph format instead of data tables. Would be very confusing right? This is why data must be presented correctly and clearly. Let us take a look.
Suggested Videos
Presentation of data.
Presentation of data is of utter importance nowadays. Afterall everything that’s pleasing to our eyes never fails to grab our attention. Presentation of data refers to an exhibition or putting up data in an attractive and useful manner such that it can be easily interpreted. The three main forms of presentation of data are:
- Textual presentation
- Data tables
- Diagrammatic presentation
Here we will be studying only the textual and tabular presentation, i.e. data tables in some detail.
Textual Presentation
The discussion about the presentation of data starts off with it’s most raw and vague form which is the textual presentation. In such form of presentation, data is simply mentioned as mere text, that is generally in a paragraph. This is commonly used when the data is not very large.
This kind of representation is useful when we are looking to supplement qualitative statements with some data. For this purpose, the data should not be voluminously represented in tables or diagrams. It just has to be a statement that serves as a fitting evidence to our qualitative evidence and helps the reader to get an idea of the scale of a phenomenon .
For example, “the 2002 earthquake proved to be a mass murderer of humans . As many as 10,000 citizens have been reported dead”. The textual representation of data simply requires some intensive reading. This is because the quantitative statement just serves as an evidence of the qualitative statements and one has to go through the entire text before concluding anything.
Further, if the data under consideration is large then the text matter increases substantially. As a result, the reading process becomes more intensive, time-consuming and cumbersome.
Data Tables or Tabular Presentation
A table facilitates representation of even large amounts of data in an attractive, easy to read and organized manner. The data is organized in rows and columns. This is one of the most widely used forms of presentation of data since data tables are easy to construct and read.
Components of Data Tables
- Table Number : Each table should have a specific table number for ease of access and locating. This number can be readily mentioned anywhere which serves as a reference and leads us directly to the data mentioned in that particular table.
- Title: A table must contain a title that clearly tells the readers about the data it contains, time period of study, place of study and the nature of classification of data .
- Headnotes: A headnote further aids in the purpose of a title and displays more information about the table. Generally, headnotes present the units of data in brackets at the end of a table title.
- Stubs: These are titles of the rows in a table. Thus a stub display information about the data contained in a particular row.
- Caption: A caption is the title of a column in the data table. In fact, it is a counterpart if a stub and indicates the information contained in a column.
- Body or field: The body of a table is the content of a table in its entirety. Each item in a body is known as a ‘cell’.
- Footnotes: Footnotes are rarely used. In effect, they supplement the title of a table if required.
- Source: When using data obtained from a secondary source, this source has to be mentioned below the footnote.
Construction of Data Tables
There are many ways for construction of a good table. However, some basic ideas are:
- The title should be in accordance with the objective of study: The title of a table should provide a quick insight into the table.
- Comparison: If there might arise a need to compare any two rows or columns then these might be kept close to each other.
- Alternative location of stubs: If the rows in a data table are lengthy, then the stubs can be placed on the right-hand side of the table.
- Headings: Headings should be written in a singular form. For example, ‘good’ must be used instead of ‘goods’.
- Footnote: A footnote should be given only if needed.
- Size of columns: Size of columns must be uniform and symmetrical.
- Use of abbreviations: Headings and sub-headings should be free of abbreviations.
- Units: There should be a clear specification of units above the columns.
The Advantages of Tabular Presentation
- Ease of representation: A large amount of data can be easily confined in a data table. Evidently, it is the simplest form of data presentation.
- Ease of analysis: Data tables are frequently used for statistical analysis like calculation of central tendency, dispersion etc.
- Helps in comparison: In a data table, the rows and columns which are required to be compared can be placed next to each other. To point out, this facilitates comparison as it becomes easy to compare each value.
- Economical: Construction of a data table is fairly easy and presents the data in a manner which is really easy on the eyes of a reader. Moreover, it saves time as well as space.
Classification of Data and Tabular Presentation
Qualitative classification.
In this classification, data in a table is classified on the basis of qualitative attributes. In other words, if the data contained attributes that cannot be quantified like rural-urban, boys-girls etc. it can be identified as a qualitative classification of data.
Quantitative Classification
In quantitative classification, data is classified on basis of quantitative attributes.
Temporal Classification
Here data is classified according to time. Thus when data is mentioned with respect to different time frames, we term such a classification as temporal.
Spatial Classification
When data is classified according to a location, it becomes a spatial classification.
A Solved Example for You
Q: The classification in which data in a table is classified according to time is known as:
- Qualitative
- Quantitative
Ans: The form of classification in which data is classified based on time frames is known as the temporal classification of data and tabular presentation.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Diagrammatic Presentation of Data
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Tabular Presentation of Data Explained

What is Tabular Presentation of Data in Detail
The presentation of data is essential. A tabular presentation of data helps the viewer to understand and to interpret the information better. Take, for example, your annual report card that is presented in a tabular format. You have your subjects written in one column of the table and your grades on the other. The third column mentions any teachers’ remarks. A single glance at your report card lets you read through the grades and subjects as well as the remarks with ease.
Now think, what would have happened if the same information was presented to you in the form of a paragraph. You would have to go through each line to know the grade that you got and the teachers’ remarks on a particular subject. This would make it tedious and also confusing to understand the report card.
Presentation of Data
Data must be presented properly. If the information is pleasing to the eyes, then it immediately gets attention. Data presentation is about using the same information to exhibit it in an attractive and useful way that can be read and interpreted easily. Data presentation is of three broad kinds. These are:
Textual presentation.
Data tables.
Diagrammatic presentation.
On this presentation of data Class 11 page, you will get to understand the textual and tabular data presentation or the data tables.
Textual Presentation
Data is first obtained in a textual format. It is a vague and raw format of the data. The data is mentioned in the text form, which is usually written in a paragraph. The textual presentation of data is used when the data is not large and can be easily comprehended by the reader just when he reads the paragraph.
This data format is useful when some qualitative statement is to be supplemented with data. The reader does not want to read volumes of data to be represented in the tabular format. Does he want to understand the data in a diagrammatic form? All that the reader wants to know is the data that provides evidence to the statement written. This is enough to let the reader gauge the intensity of the statement.
The textual data is evidence of the qualitative statement, and one needs to go through the complete text before he concludes anything.
For example, the coronavirus death toll in India today is 447. The reader does not need a lot of data here. The entire text of the state-wise breakup is accumulated to arrive at the national death figure. This is enough information for the reader.
Data Tables or Tabular Presentation
Data Tables or Tabular presentation of data is known to be the arrangement of certain values recorded in tables such that they are easy to manage and read. It is mostly done for a reader to gain the idea about the data without making it too complicated. The data presentation can be used for proper matter which is informative and creative at the same time.
What is Data Presentation?
If the reader has to interpret a lot of data, then this has to be organized in an easy to read format. The data should be laid out in rows and columns so that the reader can get what he wants at a single glance. Data tables are easy to construct and also easy to read, which makes them popular.
Components of Data Tables
Below are the key components of the data table.
Table Number - Each table has a table number that makes it easy to locate it. This number serves as a reference and leads one to a particular table.
Title - The table should also have a title that lets the reader understand what information the table provides. The place of study, the period, and the nature of data classification are also mentioned in the title.
Headnotes - The headnotes give further information. It provides the unit of data in brackets which is mentioned at the end of the title. The headnote aids the title to offer more information that the reader would need to interpret the data.
Stubs - These are the titles that tell you what the row represents. In other words, the stubs give information about what data is contained in each row.
Caption - The caption is the column title in the data table. It gives information about what is contained in each column.
Body or Field - The body or the field is the entire content in the table. Each item that is present in the body is the cell.
Footnotes - Footnotes are not commonly used, but these are used to supplement the table title if needed.
Source - If the data used in the table is taken from a secondary source, then that has to be mentioned in the footnote.
Construction of Data Tables
Tabular presentation can be constructed in many ways. Here are some ways that are commonly followed.
The title of the table should be able to reflect on the table content.
If two rows or columns have to be compared, then these should be placed adjacent to each other.
If the rows in the table are lengthy, then the stub can be placed on the right-hand part of the table.
Headings should always be in the singular.
Footnotes are not compulsory and should be provided only if required.
The column size should be symmetrical and uniform.
There should be no abbreviations in the headings and the subheadings.
The units should be specified above the column.
The Advantages of Tabular Presentation
Makes representation of data easy.
Makes it easy to analyze the data.
Makes it easy to compare data.
The data is represented in a readable manner which saves space and the reader’s time.
Classification of Data and Tabular Presentation
Classification of data and Tabular presentation is needed to arrange complex, heterogeneous data into a more simple and sophisticated manner. This is done for the convenience of the audience studying the data so the values are easy to distinguish. There are four ways in which one can classify the data and Tabular presentation. These are as follows.
Qualitative Classification
In qualitative classification, the data is classified based on its qualitative attributes. This is when the data has attributes that cannot be quantified. These could be boys-girls, rural-urban, etc.
Quantitative Classification
In quantitative classification, the data is classified based on the quantitative attributes. These could be marks where the data is categorized into 0-50, 51-100, etc.
Temporal Classification
In this tabular presentation, the data is classified according to the time. Here the data is represented in varied time frames like in the year 2016, 2018, etc.
Spatial Classification
In this method of classification, the data is classified according to location, like India, Pakistan, Russia, etc.
FAQs on Tabular Presentation of Data Explained
1. What do you Mean by the Tabular Presentation of Data?
When data is presented in a tabular form, it makes the information easy to read and to engage. The data is arranged in rows and columns. The tabular method of presenting data is the most widely used. The tabular representation of data coordinates the information for decision making, and any presentation of data in statistics use. Data in the tabular format is divided into 4 kinds. These are the Qualitative (based on traits), Quantitative (based on quantitative features), Temporal (based on time), and spatial (based on location) presentation of data.
2. Explain the Difference Between the Tabular and Textual Presentation of Data ?
In the tabular representation of data, the data is presented in the form of tables and diagrams. The textual presentation uses words to present the data.Tabular data is self-explanatory as there are segments that depict what the data wants to convey. The textual data need to be explained with words.The key difference thus is that the textual representation of data is subjective. In a tabular format, the data is mentioned in the form of tables. This makes tabular data perfect for the vast amount of data which makes it easy for the reader to read and interpret the information.
3. Where can I get the most appropriate Textual and Tabular Presentation of Data - Advantages, Classification and FAQs?
At Vedantu, the students can find different types of study material which help them ace their exams. Whether it is sample tests, mock tests, important questions, notes you want, Vedantu has it all. All of these are curated by our master teachers who make sure that you score the highest of marks. For finding the Textual and Tabular Presentation of data - Advantages, Classification and FAQs, all students have to do is sign in Vedantu.com using the Vedantu app or website.
4. What is meant by textual and Tabular Presentation?
Data around us is represented in different ways to us on an everyday basis. Two of these methods are either presenting it via texts which are known as textual presentation and the other one is known as Tabular Presentation by which the data is presented using tables. The tabular presentation is attractive and helps one to visualize the given data, although some may consider textual presentation for a detailed and proper explanation. It depends entirely on the individual how they want their data to be produced, however, most people consider the tabular presentation.
5. Why should I know about textual and Tabular Presentation?
We need data to share information with others, for this, it is important for the students to know how to use the different ways of data presentation. Knowing about Textual and Tabular presentation of data helps an individual to choose how they need their information to be conveyed. Textual data representation is basic and it is important that a student already knows about it completely when they move on to studying the tabular presentation of data. This makes sure that you have your concepts clear and for your progress to attain great heights.
Refer to Vedantu for free solutions chapter wise and get free access to other online resources to improve your learning in several folds.


IMAGES
COMMENTS
Jun 20, 2023 · Presentation of Data refers to the exhibition of data in such a clear and attractive way that it is easily understood and analysed. Data can be presented in different forms, including Textual or Descriptive Presentation, Tabular Presentation, and Diagrammatic Presentation. Textual Presentation Textu
The objectives of tabular data presentation are as follows. The tabular data presentation helps in simplifying the complex data. It also helps to compare different data sets thereby bringing out the important aspects. The tabular presentation provides the foundation for statistical analysis. The tabular data presentation further helps in the ...
Tabulation, i.e., tabular presentation of data is a method of presentation of data. It is a systematic and logical arrangement of data in the form of rows and columns with respect to the characteristics of data. It is an orderly arrangement which is compact and self-explanatory.
Define Data Presentation. Data presentation is defined as the process of using various graphical formats to visually represent the relationship between two or more data sets so that an informed decision can be made based on them. Types of Data Presentation. Broadly speaking, there are three methods of data presentation: Textual. Tabular ...
2. Tabular presentation. Tabular presentation employs tables to arrange and structure your data systematically. These tables are invaluable for comparing various data groups or illustrating how data evolves over time. They present information in a neat and organized format, facilitating straightforward comparisons and reference points. 3.
May 8, 2019 · The three main forms of presentation of data are: Textual presentation; Data tables; Diagrammatic presentation; Textual Presentation. The discussion about the presentation of data starts off with it’s most raw and vague form which is the textual presentation. In such form of presentation, data is simply mentioned as mere text, that is ...
So, the presentation of data in ascending or descending order is a bit time-consuming. Hence, we can go for the method called ungrouped frequency distribution table or simply frequency distribution table. In this method, we can arrange the data in tabular form in terms of frequency. For example, 3 students scored 50 marks.
Presentation of data refers to an exhibition or putting up data in an attractive and useful manner such that it can be easily interpreted. The three main forms of presentation of data are: Textual presentation; Data tables; Diagrammatic presentation; Here we will be studying only the textual and tabular presentation, i.e. data tables in some ...
Classification of Data and Tabular Presentation. Classification of data and Tabular presentation is needed to arrange complex, heterogeneous data into a more simple and sophisticated manner. This is done for the convenience of the audience studying the data so the values are easy to distinguish. There are four ways in which one can classify the ...
Jun 21, 2024 · Tabular Presentation of Data is a table that helps to represent even a large amount of data in an engaging, easy to read, and coordinated manner. The data is arranged in rows and columns. This is one of the most popularly used forms of presentation of data as data tables are simple to prepare and read.