What is quantitative research?
Patricia Petrat
19 min read


What is the purpose of quantitative research?
Types of quantitative research methods and techniques, data collection methodologies, advantages of quantitative research, disadvantages of quantitative research, secondary quantitative research methods, what’s the difference between quantitative and qualitative research.
- Learn More About Cint’s Quantitative Research Tools
1. Descriptive research
2. correlational research, 3. causal-comparative research, 4. experimental research, 1. surveys or questionnaires, 2. interviews, 3. observation.

- A description of teenagers’ alcohol habits: Researchers can issue surveys asking teens how much they drink, when they drink, and who they drink with. They can conduct the surveys over a period of years to see how teenage alcohol consumption changes with time.
- A description of how people in assisted-living facilities spend their time: Researchers can conduct surveys asking people who live or work at assisted-living facilities how much time they spend on certain activities. A researcher might also visit a facility to observe residents and workers, timing their activities.
- A description of how the housing market in a particular city has changed over the years: A researcher can collect data on housing prices, sales volume, and time-on-the-market to see how real estate in a city has changed over a defined period, such as the past 10 years. Since the researcher aims to describe the data, they aren’t looking for factors that could have affected homes’ prices, such as economic recessions or new amenities in the city.
- A description of how opinions on a subject have changed over a period: Researchers can describe how opinions on a subject, such as climate change or driving while intoxicated, have changed over time. They can collect data by conducting surveys that ask people to rank their feelings or beliefs on a subject on a scale from one to 10. They can follow up with the same people year after year to describe the evolution of opinions.

- An examination of the relationship between depression and diet: A researcher might ask people to rate their depression on a scale from one to 10 and provide details about what types of food they eat and how much of each food. For example, a researcher might notice a correlation between eating less than one serving of vegetables or fruit each day and more severe depression. They might notice that people who rate their depression as a one or two tend to eat multiple servings of sweets during the day.
- An examination of the relationship between SAT scores and grades during the first year of college: A researcher might be curious to see if there is a connection between standardized test scores and grades once a student is in college. They might look at the grades of first-year college students who received scores of 2200 or higher on the SATs to see if there is a relationship.
- An examination of people’s lifestyle habits and the prevalence of certain diseases: Researchers can ask people about their lifestyle habits, such as how much alcohol they drink daily or weekly or how many cigarettes they smoke, to see if there is a connection between habits and the prevalence of diseases. People who smoke more might have higher lung cancer rates or more respiratory issues than people who don’t smoke.
- An examination of types of classroom exercises and the grades students receive: A researcher might be interested in discovering if there is a connection between the types of exercises a teacher leads in a classroom setting and the grades students earn on tests. The research might measure how much time students spend listening to lectures, performing group work, or working individually, then compare that information to the grades students receive.

- Examining the effect taking vitamins has on children’s school attendance: A researcher might examine the attendance record of a group of elementary school students who take a multi-vitamin each day to see if the students taking the vitamin are more likely to go to school regularly compared to a group of students who don’t take the vitamin.
- Examining the connection between gender and scores on math tests: A researcher might ask students in the same grade to take a math test, then examine the scores the students received to see if one gender scored higher than the other overall.
- Examining the effect exercise habits have on heart health: A researcher compares blood pressure levels, cholesterol levels, and resting heart rates of people who exercise daily and people who don’t exercise to see if there is a connection between exercise and heart health.
- Examining the effect going to preschool has on high school graduation rates: A researcher might look at preschool attendance rates and compare them to graduation rates later on to see if students who started their education earlier were more likely to finish high school.

- Examining the effect of a new medication on chronic illness: Researchers divide patients with the same illness into three groups. One group receives no treatment, one receives a placebo, and the third receives a new medication. At the end of the experiment, the researchers assess the patients to determine if the new medication was more effective than a placebo or no treatment at all.
- Examining the effect of personalized instruction on students’ grades: Researchers divide a class of students into two. Both groups receive in-class instruction. One group also gets an hour of one-on-one tutoring three times a week. At the end of the trial, the students take a test. The researchers examine the students’ grades to see if those who received tutoring performed better than those who didn’t.
- Examining the effect of race or gender on crime: Researchers hire actors to pretend to commit a crime in broad daylight, such as stealing a bike or breaking into a car. The experiment’s goal is to determine if bystanders react differently based on the gender or race of the actor.

- Cross-sectional surveys gather data from multiple demographic groups at the same point in time. The method lets you compare answers across demographics and also lets you track multiple variables.
- Longitudinal surveys gather data from one demographic group at multiple periods. A longitudinal survey might follow up with participants one month later, one year later, and five years later. This type of survey aims to see how habits can change over time or what impact habits have on a particular group of people over the course of months or years.

- Reliability: Quantitative research is objective, meaning the variables and data you collect are reliable and accurate. When you ask someone how many cups of coffee they drink every day, you get a direct, objective answer.
- Reproducibility: Since you are collecting numerical or computational data when you perform quantitative research, it’s easy to reproduce the surveys or interviews when needed. Replication is a key component of a quantitative approach.
- Impartiality: Numbers and statistics don’t have a bias. There’s no way for a research team to influence the results or otherwise make the results biased when using a quantitative approach.
- Scalability: You can scale quantitative research up or down as needed without affecting the quality of the surveys or the data’s validity.

- Might not tell the whole story: The variables you collect through quantitative methods can be superficial or limited. For example, asking people how much coffee they drink doesn’t tell you very much. It can also be the case that other factors you are surveying affect the responses people give.
- Sample sizes can be small: Small sample sizes can limit the impact research has. Asking 10 people about their coffee drinking habits won’t give you a good idea of how coffee consumption plays out across the country, for example.
- Data can be over-manipulated: It’s possible for the setting of a research study to be manipulated and controlled to such an extent that it affects the accuracy of the results or for a range of other, unaccounted-for variables to affect the study.
- Universities and colleges
- Public and private libraries
- Government institutions
- Non-government organizations
- Commercial information sources

Learn More About Cint’s Quantitative Research Tools

More from our blog

Building the right tech partnerships: KFC U.S. and Cint’s ‘Finger lickin’ good’ recipe for success
At TMRE 2024 in Orlando, KFC’s Renee Reeves joined Cint’s Ryan Fletcher for a fireside chat on how building the right tech partnerships is the (not-so-secret) recipe for fostering a culture of innovation and setting your insights team up for success.

Surviving party season: CintSnap explores festive fatigue
Ready for a slew of parties, or dreading the prospect? Cint explores consumer attitudes toward a potentially massive month of social outings.

Eat, shop, repeat: CintSnap delves into Thanksgiving consumer trends
We examine the relationship between Thanksgiving and one of the biggest sales events of the year, Black Friday Cyber Monday (BFCM).
How Cint uses gender neutral language in job advertisements
We speak with Andy Perricone, Senior Talent Acquisition Manager at Cint to find out how Cint avoids gendered language in job ads, why it matters, and how we foster inclusivity that attracts the top talent from all genders and backgrounds.

Preparing for 2025: Insights on marketing and data collaborations
In 2025, global advertising spend is predicted to surpass $1 trillion—a milestone so monumental it could stretch dollar bills to the sun and back. However, beneath this record-breaking number lies a complex reality: while data is abundant, marketers and agencies still face significant challenges in unlocking its full potential. A recent research collaboration between Lotame…
CintSnap survey uncovers 2024 holiday travel trends and the use of AI in travel planning
As the festive season approaches, travelers worldwide are packing their bags for one of the busiest travel periods of the year – but not without a little help from technology. If the idea of using AI as your personal travel assistant sounds appealing, you’re not alone. This year, holiday travel trends reveal not only a…

John Lewis tops the tree in the Christmas ads anticipation stakes
The advertising industry’s biggest few weeks of the year are here. What do UK viewers and consumers want from their Xmas ads?

How popular is the poppy in 2024?
Ahead of Remembrance Day, Cint asks whether or not wearing a poppy is still a big deal in the UK.

Get to know our latest tool for brand lift studies: Study Creator
Find the full lowdown on Cint’s Study Creator tool, including the workflow process, benefits, and our latest video tutorial.

CintSnap explores US viewing habits ahead of the election
A huge election is also a huge moment for broadcasters. How will Americans be tuning into election night 2024?

TikTok, Deepfakes, and Political Ads: A study on the relationship between media and the upcoming election
Cint and Advertising Week partnered on research looking into the relationship between media influence and voter behavior leading up to this year’s US and UK elections.
Cint Trust Score – Inside the thinking AI brain
Cint’s experts break down the importance of our Trust Score model

CintSnap uncovers US and UK consumer Halloween 2024 spending habits and traditions
We take a look at the difference in spooky, seasonal spending habits and traditions in the US and the UK.

Step into a new era of the Cint brand with us
Find out how the Brand team used visual cues and language to bring the new brand vision to life.

The festive shift: How Diwali is driving India’s digital transformation across four key sectors
From ordering food online to the rise in quick commerce, our comprehensive Diwali survey reveals how technology is reshaping the way people prepare for and celebrate Diwali.

Getting the work-life balance right: Cinters share their hobbies outside of work this World Mental Health Day 2024
From carnival chasing to pilates, and kitesurfing to kickboxing, our international employees at Cint talk about how their hobbies keep stress under control.

Introducing Women@Cint
Cint is committed to making ourselves a more diverse and inclusive workforce. Here’s how we’re making that happen.

CintSnap takes a deep dive into the 2024 Formula One World Championship frenzy.
It might be the world’s premiere motorsport, but has F1 truly caught the attention of audiences in the US, UK and Australia?

How data-driven decision making is revolutionizing industries
A conversation with France Lasnier, SVP, for UK, France, Central Europe and Louis Nix, Senior Analyst, Product Operations, on the importance of a data-driven approach for companies.

How Cint keeps your data safe — and secure
A conversation with Cint experts Dhruv Mathur, Vice President, Information Security and Caroline Tahon, Data Protection Officer, on keeping data as safe and secure as possible.

Cint helps Push Digital uncover gaps in voter support and form insights to optimize targeting
Push Digital, a campaign agency active in America’s highest stakes races and debates by leveraging their digital expertise to start conversations, persuade audiences, and turn out voters, partnered with Cint on a study to uncover gaps in voter support.

Did you have a Brat summer?
Charli XCX might have dominated airwaves this summer, but how did the Brat campaign impact consumer habits?
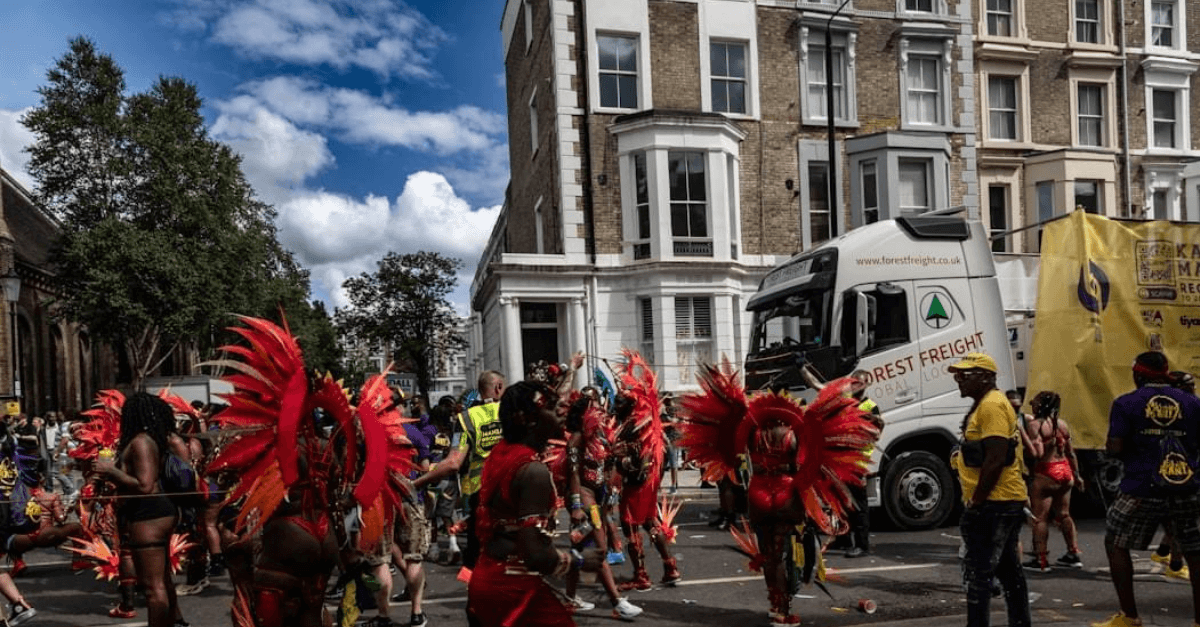

Notting Hill Carnival 2024: CintSnap reveals UK sentiments around main attractions, sustainability, and diversity initiatives
Using CintSnap, we surveyed 300 UK respondents on how they plan to engage with the iconic celebration and what aspects of the event excite them the most.
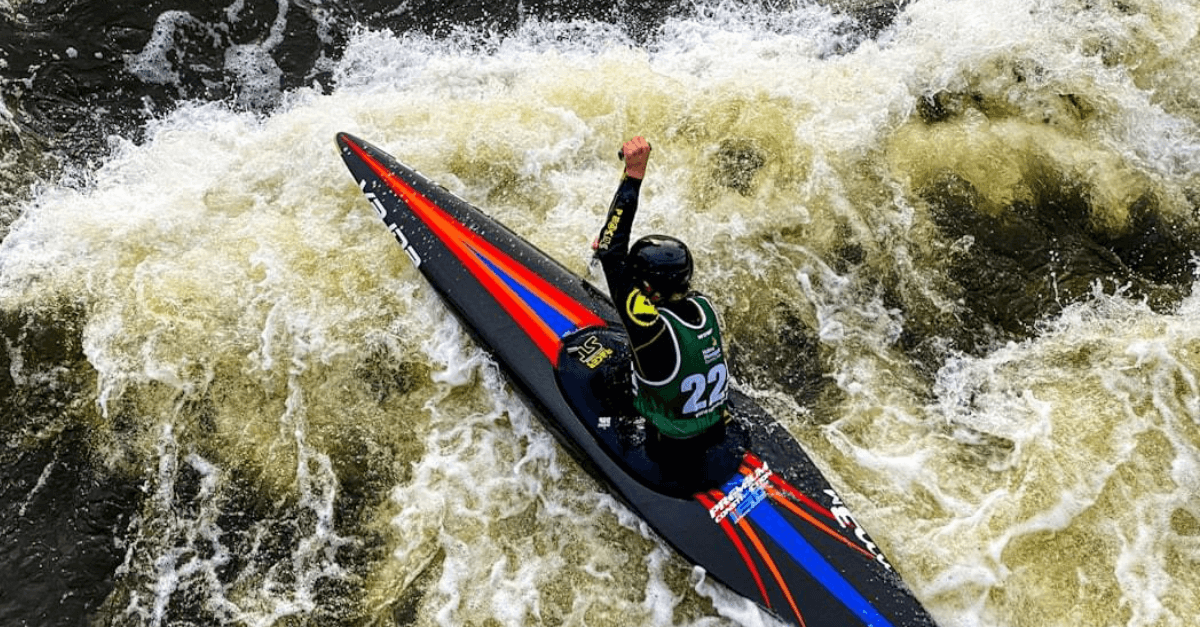

Paralympics 2024: CintSnap reveals UK consumer insights on viewing habits, the most popular sporting events, and brand sponsorship
Using CintSnap we surveyed 300 people in the UK on how they plan to engage with the Games, most watched sports, and how brand sponsorship is perceived.

Back-to-school Survey: How Americans are preparing for the new school year ahead
Using CintSnap, we surveyed 300 Americans to reveal some trends and preferences on how they gear up for the academic year ahead.

The Booker Effect: Do literary prizes influence reading — and spending — habits?
Using CintSnap, we conducted a poll with approximately 300 people from the UK to explore what they read, how they read, and what persuades them to take a punt on a new title.

Guide to measuring political advertisements with Lucid Impact Measurement
Explore our guide to measuring political advertisements by Cint’s in-house expert Chris Pope, Senior Director of Measurement.

‘We Hear You’ – Cint Exchange launch with Lindsay Fordham
Discover the latest platform developments at Cint with Lindsay Fordham, SVP, Product.
2024 Paris Summer Games
With the 2024 Paris Summer Games underway, Cint surveyed 400 French people to gauge sentiments around the world’s largest sporting event.

The TikTok effect: How the video-sharing platform is shaping voter behavior
As the UK headed to the polls on July 4th, Cint conducted a study to reveal TikTok’s influence of voters.

How researchers at Employment Hero explored the potential power of automated payroll procedures
HR, payroll and recruitment solution specialists Employment Hero conducted a survey with Cint to delve deep into how AI assistance could be a boon for payroll professionals across Australasia.

How pumped are people for Amazon Prime Day? CintSnap finds out.
As one of retail’s biggest events rolls around, we gather insights into consumer spending habits in the US, UK and Australia.

The Market Research Industry Isn’t Focusing Enough on Data Ethics; How to Solve It
Lindsay Fordham, SVP Product at Cint shares her thoughts on ethics in our industry

CintSnap reveals top reasons people in the UK flock to music festivals
With Glastonbury around the corner and a summer of festivals in full swing, we delve into everything from sustainability to the allure of secret sets.
CintSnap explores what consumers think about Father’s Day
As Father’s Day looms, Cint gets to grips with how people in the US and UK plan to celebrate – and how much they’re prepared to spend.

With Euro 2024 round the corner, we use CintSnap to assess just how football crazy the UK is
Our most recent CintSnap explores how much of the tournament people plan on watching and who they’ll be doing it with.
How a researcher at Harvard University successfully decoded the opinions of independent voters
Political scientists Andrew O’Donohue and Daniel Markovits conducted a survey with Cint to understand how prosecution of Donald Trump affected public opinion among independent voters.

Ariel Madway, Associate Director, Marketing Events on the upcoming events season
From London to Malaga and Cairns, Ariel Madway takes us on a journey through Cint’s busy events season, her planning inspiration and what she’s most excited about.

TV upfronts and NewFronts – and CintSnap insights into the state of streaming 2024
Both CTV and linear TV advertising present big opportunities for advertisers. In particular, the booming demand for CTV ads. We look at what the TV upfront and NewFronts are all about and the state of streaming in 2024.

Exploring insights on consumer sentiments around sustainability
We look at two recent reports published in partnership with Cint, that focus on global consumer sentiments around sustainability.

How to successfully navigate niche audiences: A teaser to our Whitepaper
In the world of market research, finding and engaging with niche audiences can feel like navigating uncharted territories. Gaining insights demands innovative strategies and streamlined processes.

CintSnap unveils the divide: Tipping culture in the US vs UK
When it comes to social customs and norms, few practices are as divisive as tipping expectations. We use CintSnap to survey consumer behaviour around tipping in the US and UK.

Going behind the scenes of CintSnaps: Best practices and fielding questions
Today we give you a look at how we take the pulse of the public, so you don’t have to…
Advanced Strategies: Market research data for strategic excellence
We delve into techniques and strategies used by big-hitters for leveraging market research data.
“And the winner is..” CintSnap insights into the 2024 Oscars
With the prestigious Academy Awards marking its 96th year, we set out to discover if the glitz and glam of ceremony still holds weight in determining viewing habits of filmgoers, as well as why people tune in, how predictions played out and who they thought should have won the coveted golden globes.

International Women’s Day 2024. Cint’s Women in leadership share their career insights
To celebrate International Women’s Day, we asked some of our incredible women in leadership share their best career advice.

Insights into International Women’s Day 2024
International Women’s Day is an opportunity to celebrate wins, raise awareness and get conversations going. We’ve dived into the narrative at Cint by uncovering the insights around International Women’s Day.

Independent study names Cint #1 supplier of accurate survey responses
We’re proud to share that Cint, a global leader in market research, emerged as the leader in sample quality for online polls in a third-party study. Sapio Research, a UK market research agency, conducted the study to understand if online surveys are accurate. Sapio surveyed 2,036 UK consumers – representative by age and gender of…

Taking a (cupid’s) shot at consumer spending habits on Valentine’s Day 2024
For Valentine’s Day 2024, the National Retail Federation predicts that consumers will spend $25.8 billion. We used CintSnap to find out how people in the US and the UK approach this romantic season, by surveying 300 respondents.

Ensuring high quality sample: Introducing Cint Trust Score
John Brackett, Director of Product, introduces our latest AI-powered innovation designed to elevate data quality

New Report: Unlocking insights on The Big Game
As football fever grips the nation, the anticipation for this year’s game is reaching unprecedented heights. We surveyed the nation to understand more about how people are planning to watch, and so much more.

Celebrating International Data Protection Day with Caroline Tahon, DPO at Cint
On the 28th of January every year, the importance of personal data, and of Personal Identifiable Information (PII) is celebrated across the world on Data Protection Day.
Game, set, match: Insights into The Happy Slam
The Australian Open is the first of the four Grand Slam tennis tournaments to occur. We uncovered spectator experience through preferences and behaviors of our 280 respondents across Australia.

Redefining your experience with Cint: An exclusive look at our API-first approach
Nick Richards, Director of Product, shares an update on the work his team have been doing to comprehensively integrate every corner of product offerings on the new platform.

Feeling blue? CintSnap investigates the “most depressing day of the year”
With the festive season well behind us, and gloomy skies looming above, January for a myriad of reasons, isn’t the most exhilarating of months. This sentiment is so nationally widespread that in 2005, a UK-based travel agency coined the term ‘Blue Monday’ to mark the most depressing day of the year.

2024 Leisure travel takes flight: CintSnap unpacks vacation plans
January is a popular time for reflection and what better month to get our plans organised for the year ahead of us? A new year represents new uncharted destinations we’ve yet to discover, and for some, the usual trusted spots bring familiar comfort to recharge weary batteries.
Embracing gender inclusivity: Empowering market research with accuracy and impact
Vishal Bhat – Program Manager, Susi Lindner – Vice President, and Sonali Kaushal – Senior Manager at Cint discuss the importance of being inclusive in language around gender.
AI in the Workplace
If Taylor Swift took up the greatest amount of air space and attention in pop culture this year; the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) – and its impact on jobs – took up the greatest amount of air space and attention in professional settings.

Ready for 2024? We look at your New Year resolutions
Saving money, eating less meat and going sober…Patricia Petrat takes a deep dive into how people across the world are ringing in the year ahead.

2023 in Review: Your favourite CintSnaps, ranked
Since there’s nothing we love more than a data driven trip down memory lane, we’ve rounded up the top 10 #CintSnaps which got the highest engagement from you this year.

The CEO view: “Think it over, think it under.”
When I took the reins from Tom Buehlmann on the 3rd of April of this year, the integration of Cint, Lucid, Gapfish and P2Sample was well under way – but there was still work to do. A lot of work.

Revolutionizing the Cint experience: A glimpse into the future
Our first video in our new interview series is with Jonathan Jaynes, Senior Director of Product Design, Cint, who shares an insider’s perspective on the groundbreaking developments underway.

Unwrapping the festive magic with CintSnap: A look into consumer feelings around Christmas ads
Our most recent CintSnap takes a festive peek into the sentiments the UK public to unveil their thoughts on this year’s Christmas ads. Join us in unwrapping the findings and discovering what makes these ads a seasonal staple for UK consumers.

Navigating the transition: behind the scenes of our new platform
When we talk about migrating customers and supply partners to our new platform, we understand that concerns may arise. In this blog post, we want to address some of the worries you may have, and give a little reassurance about the process. You’re in good hands, we promise!

Influencers, Inspiration, and Inflation: Key topics driving holiday shopping habits in 2023
The build up to the holiday season is almost palpable, Christmas lights illuminate city centers and cheese fondue and mulled wine start popping up on the menu. We pull out our coziest socks from the attic storage and gear up for hours of Home Alone movie marathons and engage in another big part of the yearly tradition -…

CintSnap delves into Black Friday and Cyber Monday shopping trends
As Black Friday and Cyber Monday (BFCM) sales continue to skyrocket and dominate global retailer revenues, Cint takes a deeper look into consumer behaviors in the US, UK, Canadian and Australian markets, and the shopping habits that drive this highly anticipated shopping season.

The Beatles ‘Now and Then’: CintSnap reveals consumer sentiments of AI’s impact on the music industry
Using Cint’s owned data – that we call CintSnap – we gathered some insights around sentiments surrounding consumer behavior of the implementation of AI in the music industry, specifically on the posthumous Beatles collaboration.

Answering your questions: what does it take to build a new platform?
Innovation is in our DNA, and our mission has always been to bridge the gap between real people and organizations striving to understand and serve them. With this in mind, we’ve embarked on an exciting journey of transformation – building a new platform that will redefine the way our customers can access and leverage consumer…
Measuring brand lift in real-time: Leveraging Lucid Impact Measurement by Cint for in-flight optimization on cross-platform campaigns
Stephanie Gall, Director of Measurement Products at Cint, examines the use of Lucid Impact Measurement to optimize advertising campaigns across linear and connected TV, digital and social channels

The next chapter of Cint: A new phase of innovation and creativity
Read on for a brief outline of the latest developments in our new platform as we continue on an exciting journey with our partners, led by our core purpose – to feed the world’s curiosity

Behind the scenes at Cint: with Events Director, Ariel Madway
In today’s blog we spend a bit of time getting to know one of our superstar team members – one who you may have met on the MR events circuit this fall.

Webinar: Improving data quality and mitigating fraud
Our recent webinar hosted by Oscar Carlsson, Chief Innovation Officer, provided an overview of industry data quality trends and outlined what Cint is doing to help.

5 pillars to success: In conversation with Jimmy Snyder, VP, Trust and Safety, Cint
Jimmy oversees an operational team focused on creating and implementing quality-related programs and policies. He shares how the team helps to ensure a healthy and efficient market research ecosystem.

How to monetize your community
Monetizing your community involves strategically leveraging its value to generate revenue. Let’s say you have an online forum, social media group or a thriving platform with active members. You can transform your online community into a profitable asset. You can monetize your community in various ways. This post explores the ins and outs of community…

Working to deliver best-of-breed consumer intelligence
John Brackett is Director of Product, working across supply, respondent experience, and trust and safety. Here he outlines some of the actions being taken to optimize one of the world’s largest digital marketplace for research sample.

Lucid awarded NBCU Brand Measurement certification
Lucid, a Cint Group company, has been chosen by NBCUniversal as a brand measurement certified partner. The selection was made based on solution readiness, deliverables, and market presence.

Cint Snap reveals what consumers want from US Open commercials
With the final Grand Slam tournament of the year fast approaching, Cint uncovers the most successful strategies for brand engagement by asking consumers their thoughts on the sporting extravaganza

How to recruit survey respondents
When conducting market research, finding participants for a survey is crucial to gather valuable insights. Survey respondents provide the data necessary to understand target audiences and build action plans for reaching them. Their input enables data-driven decision-making, improves product or service offerings, and helps tailor marketing strategies to meet customer needs effectively.

How media measurement can help the food and beverage industry
The food and beverage industry is highly dynamic and constantly evolving, with new trends and consumer preferences always emerging. In such a fast-paced and competitive landscape, staying ahead of the game is critical for success. That’s where media measurement comes in.

In the Rise of CTV, How Do You Effectively Measure It?
CTV’s customized strategies provide marketers with massive amounts of analytics. With all the viewership data CTV provides, it often seems complicated to measure specific goals for your campaign. Using CTV measurement is critical for understanding your ad performance and information about your viewers.

Why real-time measurement is crucial for back-to-school and holiday campaign success
The Back- to- School and Holiday Shopping seasons are changing rapidly, short in nature and extremely lucrative. This blog explains the power of leveraging real-time measurement to optimize your campaign; not after completion, but while consumers are still buying.
Improving Qualification Data and Screening Questions for High-Quality Survey Results
Learn how to enhance the quality of your survey results by optimizing qualification data and screening questions. Discover strategies to avoid respondent fatigue, keep data up to date, maintain specificity without bias, innovate targeting approaches, and minimize fraud. Act now and unlock the power of connected data for business success.

4 ways to use consumer surveys in the food and beverage industry
Surveys are powerful information sources across industries and organizations. With the data pulled from customer surveys, departments can drive actions and initiatives that better reflect audiences and market conditions. The food and beverage industry can benefit from using surveys in several applications to gain more information and knowledge about their organization, products, customers and market.

Why government agencies should do market research
U.S. government market research aims to allocate resources to prioritize social services and responsibilities. Using market research to create a more effective fiscal policy or make purchasing decisions is valuable.

Conducting market research for the healthcare industry
In this blog, we’ll explore the importance of market research in the healthcare industry and some of the key methods and techniques that can help gather and analyze data. We’ll also discuss specific ways healthcare providers can use market research to improve operations, expand their reach and enhance the overall patient experience. Whether you’re a…

How to ask sensitive survey questions effectively: tips and strategies
Surveys are an effective way to gather valuable data and insights from a group of people. However, some survey questions may touch on sensitive topics, and require additional care.

Why Global Benchmarking can drive campaign success
By comparing your campaign’s performance against industry standards on key performance indicators (KPIs), you gain valuable insights and context that can drive better outcomes. In this blog post, we’ll explore why benchmarking your advertising campaign is essential and how Lucid Impact Measurement, a product by Cint, can help you achieve this.

Identify consumer shopping struggles through surveys
With the help of customer experience research via surveys, you can locate and address pain points, in turn creating a better experience. This article will provide you with valuable insights into how to gather feedback from your customers and improve your operations as a result.

Unlocking the Power of Data Connection for Enhanced Research and Marketing Insights
Unlock the power of connected data to drive superior research & marketing. Learn how to access rich datasets, navigate legal considerations, and gain comprehensive insights. Discover four essential steps to connect data effectively.

How the public sector can use surveys to better inform decision making
Survey data can provide meaningful insights to public sector agencies. It’s one of the most powerful tools to serve your community. Public sector agencies have multiple objectives. Gathering actionable feedback is essential to help you reach your goals.
Behind the Numbers with eMarketer’s Marcus Johnson and Cint’s Stephanie Gall
How in-flight brand lift measurement helps brands do more with less

How the financial service industry can get ahead with survey data
The financial services industry has been experiencing significant changes in recent years due to the increasing demand for digital solutions and the emergence of a cashless society. As technology continues to advance, it has become essential for financial service providers to adapt and stay ahead of the game.

Cint found to have best sample quality in two independent studies
In the past few months, two independent studies found that Cint had the highest-quality sample for both consumer and B2B respondents.

How to do academic market research
Many industries use market research to help reach marketing or growth goals by connecting with audiences and receiving feedback. But, academic researchers utilize market research for their own unique applications. Conducting market research — whether in a college or university setting or otherwise — can improve studies, papers, theses and research projects.

How to identify target market through surveys
Because marketing is customer-centric and values-based, all marketers must have a thorough understanding of their audiences to succeed. To achieve this insight, you’ll need to identify your target audience in the first place. It’s best to learn about your respondents in their own words, so you should use a combination of online surveys and target…

3 things you can do to improve survey quality
Today, it is harder than ever to get high-quality survey responses. Cint is one of the world’s largest marketplaces for survey responses. We’ve consulted with experts on 3 ways users can improve survey quality.

4 ways in-flight measurement can help stretch your 2023 marketing budget
Knowing how to prioritize your limited budget while increasing the impact of your digital advertising will make the difference between success and just getting by this year.

The Story of Cint
Today, Cint has over 239 million engaged respondents and employs over 1000 people in 11 countries. So, how did we get here?

Common mistakes with media measurement – and how to avoid them
When measuring ad campaigns, it’s important to be aware of common pitfalls that can affect your advertising goals – especially if you want real-time campaign results.

Growing awareness of the Women’s Euros creates new opportunities for brand sponsorship
After England’s win over Germany, the value of sponsoring women’s football has changed in a monumental way.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and Analysis
Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and Analysis
Table of Contents
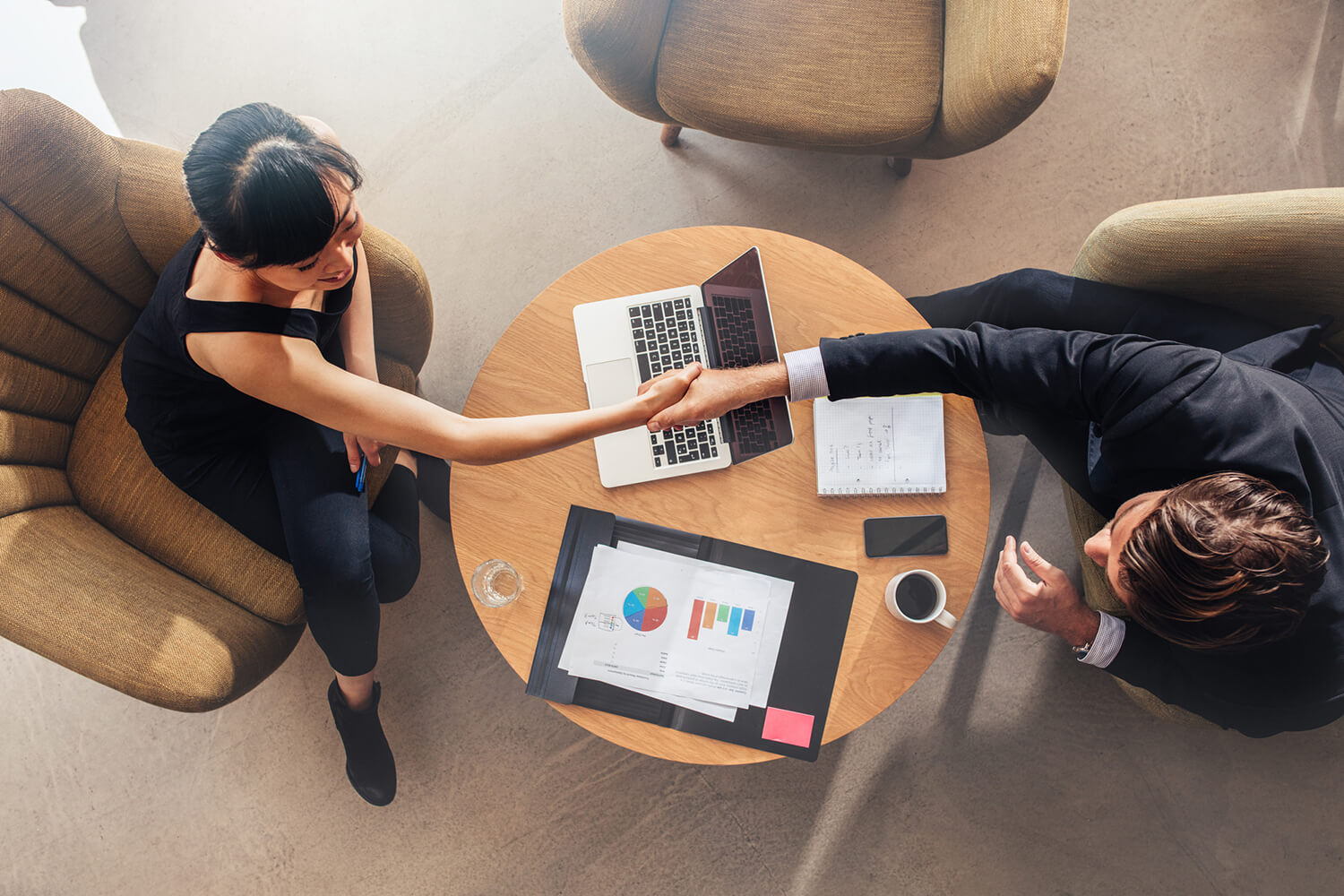
Quantitative research is a systematic investigation that primarily focuses on quantifying data, variables, and relationships. It involves the use of statistical, mathematical, and computational techniques to collect and analyze data. Quantitative research is often used to establish patterns, test hypotheses, and make predictions. It is widely applied in fields such as psychology, sociology, economics, health sciences, and education.

Quantitative Research
Quantitative research is a research approach that seeks to quantify data and generalize results from a sample to a larger population. It relies on structured data collection methods and employs statistical analysis to interpret results. This type of research is objective, and findings are typically presented in numerical form, allowing for comparison and generalization.
Key Characteristics of Quantitative Research :
- Objective : Focuses on numbers and measurable variables rather than subjective opinions.
- Structured : Employs well-defined research questions, hypotheses, and data collection methods.
- Statistical : Utilizes statistical tools to analyze data and validate findings.
- Replicable : Enables repetition of the study to verify results and increase reliability.
Example : A survey on the correlation between exercise frequency and stress levels among adults, using a Likert scale to measure responses.
Types of Quantitative Research
Quantitative research can be categorized into several types, each serving a specific purpose. The most common types include descriptive , correlational , experimental , and causal-comparative research.
1. Descriptive Research
Definition : Descriptive research describes characteristics or behaviors of a population without examining relationships or causes. It provides a snapshot of current conditions or attitudes.
Purpose : To gather information and create an overview of a particular phenomenon, population, or condition.
Example : A survey describing the demographics and academic performance of students at a university.

2. Correlational Research
Definition : Correlational research examines the relationship between two or more variables but does not imply causation. It analyzes patterns to determine if variables are associated or occur together.
Purpose : To identify associations or trends among variables without establishing cause and effect.
Example : Investigating the relationship between social media use and self-esteem among teenagers.
3. Experimental Research
Definition : Experimental research manipulates one or more independent variables to observe the effect on a dependent variable, establishing cause-and-effect relationships. This type of research involves control and experimental groups.
Purpose : To test hypotheses by isolating and controlling variables to establish causality.
Example : Testing the effect of a new medication on blood pressure by administering it to one group (experimental) and comparing it to a placebo group (control).
4. Causal-Comparative (Ex Post Facto) Research
Definition : Causal-comparative research investigates the cause-effect relationship between variables when experimental manipulation is not possible. It compares groups that differ on a particular variable to determine the effect of that variable.
Purpose : To explore cause-and-effect relationships retrospectively by comparing pre-existing groups.
Example : Studying the impact of different teaching methods on student performance by comparing classes taught with traditional versus technology-assisted instruction.
Quantitative Research Methods
Quantitative research methods focus on systematic data collection and analysis using structured techniques. Common methods include surveys , experiments , and observations .
Definition : Surveys are a popular quantitative method that involves asking participants standardized questions to collect data on their opinions, behaviors, or demographics. Surveys can be conducted via questionnaires, interviews, or online forms.
Purpose : To gather data from a large sample, allowing researchers to make inferences about the larger population.
Example : Conducting a survey to collect customer satisfaction data from a random sample of customers in a retail store.
Advantages :
- Cost-effective and time-efficient for large sample sizes.
- Provides structured data that is easy to analyze statistically.
Disadvantages :
- Limited depth, as responses are often restricted to specific options.
- Potential for response bias, where participants may not answer truthfully.
2. Experiments
Definition : Experiments involve manipulating one or more variables in a controlled environment to observe the effect on another variable. Experiments are often conducted in laboratories or controlled settings to maintain precision and limit external influences.
Purpose : To test hypotheses and establish cause-and-effect relationships.
Example : Conducting a laboratory experiment to test the effect of light exposure on sleep patterns.
- High level of control over variables.
- Establishes causality, which can support theory-building.
- Limited external validity, as findings may not always apply outside of the controlled setting.
- Ethical considerations may limit experimentation on certain subjects or groups.
3. Observations
Definition : Observational research involves systematically observing and recording behavior or events as they occur naturally, without interference. While often used in qualitative research, structured observational methods can yield quantitative data.
Purpose : To gather real-world data in a non-intrusive manner.
Example : Observing customer behavior in a store to track time spent in different areas and identify shopping patterns.
- Provides data on actual behaviors rather than self-reported responses.
- Useful for gathering data on situations where surveys or experiments may not be feasible.
- Observer bias may affect results.
- Can be time-consuming, especially if behaviors are infrequent or complex.
Data Collection Tools in Quantitative Research
Quantitative research relies on various tools to collect and quantify data, including:
- Questionnaires : Standardized forms with close-ended questions, often using scales (e.g., Likert scale) for responses.
- Tests and Assessments : Used to measure knowledge, skills, or other measurable attributes.
- Digital Tracking Tools : Software or digital applications that collect data, such as website traffic metrics or physiological monitoring devices.
Data Analysis in Quantitative Research
Data analysis in quantitative research involves statistical techniques to interpret numerical data and determine relationships or trends. Key techniques include descriptive statistics , inferential statistics , and correlation analysis .
1. Descriptive Statistics
Definition : Descriptive statistics summarize and organize data, providing basic information such as mean, median, mode, standard deviation, and range.
Purpose : To give an overview of the dataset, allowing researchers to understand general trends and distributions.
Example : Calculating the average test scores of students in a school to assess overall performance.
Common Measures :
- Mean : Average of all data points.
- Median : Middle value of an ordered dataset.
- Standard Deviation : Measure of variability around the mean.
2. Inferential Statistics
Definition : Inferential statistics allow researchers to make predictions or inferences about a population based on sample data. Techniques include hypothesis testing, t-tests, ANOVA, and regression analysis.
Purpose : To determine if observed results are statistically significant and can be generalized to a larger population.
Example : Using a t-test to compare average scores between two different teaching methods to see if one is significantly more effective.
Common Tests :
- t-Test : Compares the means of two groups to determine if they are statistically different.
- ANOVA (Analysis of Variance) : Compares means among three or more groups.
- Regression Analysis : Examines the relationship between independent and dependent variables.
3. Correlation Analysis
Definition : Correlation analysis measures the strength and direction of the relationship between two variables. It is used to determine if changes in one variable are associated with changes in another.
Purpose : To identify associations between variables without implying causation.
Example : Calculating the correlation coefficient between screen time and academic performance to determine if there is an association.
- Pearson Correlation Coefficient (r) : Measures linear correlation between two continuous variables.
- Spearman’s Rank Correlation : Measures correlation between two ranked variables.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Quantitative Research
- Objective : Minimizes researcher bias by focusing on numerical data.
- Generalizable : Findings from large, random samples can often be applied to a broader population.
- Replicable : Structured methods make it possible for other researchers to replicate studies and verify results.
Disadvantages
- Limited Depth : Quantitative research often lacks the depth of qualitative insights.
- Rigid Structure : Limited flexibility in data collection and analysis.
- Potential Bias : Response or sampling biases can affect results, especially in survey-based studies.
Tips for Conducting Effective Quantitative Research
- Define Clear Objectives : Develop specific research questions or hypotheses to guide the study.
- Choose the Right Method : Select a quantitative method that aligns with the research goals and type of data needed.
- Ensure Sample Representativeness : Use appropriate sampling techniques to ensure results can be generalized.
- Employ Proper Statistical Tools : Choose analysis techniques that match the nature of the data and research questions.
- Interpret Results Accurately : Avoid overgeneralizing findings and consider limitations when interpreting results.
Quantitative research provides a structured, objective approach to investigating research questions, allowing for statistical analysis, pattern recognition, and hypothesis testing. With methods like surveys, experiments, and observational studies, quantitative research offers valuable insights across diverse fields, from social sciences to healthcare. By applying rigorous statistical analysis, researchers can draw meaningful conclusions, contributing to the body of scientific knowledge and helping inform data-driven decisions.
- Creswell, J. W., & Creswell, J. D. (2018). Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches (5th ed.). SAGE Publications.
- Punch, K. F. (2014). Introduction to Social Research: Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches (3rd ed.). SAGE Publications.
- Field, A. (2013). Discovering Statistics Using IBM SPSS Statistics (4th ed.). SAGE Publications.
- Trochim, W. M., & Donnelly, J. P. (2008). The Research Methods Knowledge Base (3rd ed.). Cengage Learning.
- Babbie, E. R. (2021). The Practice of Social Research (15th ed.). Cengage Learning.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Qualitative Research – Methods, Analysis Types...

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide

Applied Research – Types, Methods and Examples

Focus Groups – Steps, Examples and Guide

Mixed Methods Research – Types & Analysis

Experimental Design – Types, Methods, Guide

What is the Purpose of Quantitative Research?

If you are involved in any kind of research, you have probably heard of quantitative research. It is a method of research that involves collecting and analyzing data in a systematic and objective way. But what is the purpose of quantitative research?
The purpose of quantitative research is to gather numerical data that can be analyzed using statistical methods. This type of research is used to answer questions that require numerical data, such as “How many people prefer product A over product B?” or “What is the average age of people who buy our product?” Quantitative research is often used in fields such as marketing, psychology, and education.
To conduct quantitative research, researchers use a structured approach to collect data. This may involve surveys, experiments, or other methods that are designed to gather numerical data. The data is then analyzed using statistical methods to identify patterns and relationships. The goal of this analysis is to draw conclusions that can be used to make informed decisions.
Key Takeaways
- Quantitative research involves collecting and analyzing numerical data using statistical methods.
- The purpose of quantitative research is to answer questions that require numerical data.
- This type of research is used in fields such as marketing, psychology, and education.
Understanding Quantitative Research
If you are interested in conducting research, you might have come across the term “quantitative research” and wondered what it means. Quantitative research is a scientific method that involves collecting and analyzing numerical data to generate knowledge and create understanding. It is a method commonly used in the social sciences to investigate relationships between variables and test hypotheses.
The purpose of quantitative research is to provide empirical evidence that can be used to support or refute a theory. This type of research involves collecting data through structured methods, such as surveys, experiments, or observations, and analyzing it using statistical techniques. The results of quantitative research are typically presented in the form of tables, graphs, or charts, which allow researchers to draw conclusions and make predictions based on the data.
Quantitative research methods can be used to answer a wide range of questions in the social sciences, including questions about human behavior, attitudes, and beliefs. For example, a researcher might use quantitative methods to investigate the relationship between income and happiness, or to determine the effectiveness of a particular educational program.
To conduct quantitative research, you need to have a good understanding of the scientific method and research methodology. You also need to be familiar with statistical techniques and software, such as SPSS or Excel, that are commonly used to analyze quantitative data.
In conclusion, quantitative research is a powerful scientific method that can be used to generate knowledge and create understanding in the social sciences. By collecting and analyzing numerical data, researchers can test hypotheses and draw conclusions based on empirical evidence. If you are interested in conducting research in the social sciences, it is essential to have a good understanding of quantitative research methods and their applications.
Key Elements of Quantitative Research
Quantitative research is a scientific method that involves collecting and analyzing numerical data to test hypotheses and make predictions. It is widely used in many fields, including social sciences, natural sciences, and business. In this section, we will explore the key elements of quantitative research.
Variables in Research
In quantitative research, variables are the concepts or characteristics that are being measured. They can be classified into two types: independent variables and dependent variables. The independent variable is the variable that is manipulated by the researcher, while the dependent variable is the one that is being measured.
Quantitative Data
Quantitative data is numerical data that can be measured and analyzed statistically. It is collected through various methods, such as surveys, experiments, and observations. This type of data is used to test hypotheses and make predictions.
Research Questions
Research questions are the questions that guide the research process. They are formulated based on the research objectives and the hypotheses that are being tested. Research questions should be specific, measurable, and relevant to the research objectives.
In quantitative research, the research questions should be designed to test hypotheses and explore the relationships among variables. The hypotheses are specific predictions about the relationships among variables. They are formulated based on the existing literature and the research objectives.
Quantitative research involves collecting and analyzing data to test hypotheses and make predictions. It is based on the cause-and-effect relationship between variables. The results of the research are analyzed using statistical methods to determine the relationships among variables and to test the hypotheses.
Quantitative research is widely used in experimental research, where the researcher manipulates the independent variable to test its effect on the dependent variable. The operational definitions of the variables are used to ensure that the variables are measured consistently and accurately.
In conclusion, quantitative research is a scientific method that involves collecting and analyzing numerical data to test hypotheses and make predictions. The key elements of quantitative research include variables, quantitative data, and research questions. By understanding these elements, you can design and conduct effective quantitative research studies.
Quantitative Research Methods
Quantitative research is a method of collecting and analysing numerical data to answer research questions. It involves a structured approach to data collection and analysis, which allows researchers to draw conclusions based on statistical evidence. There are several methods used in quantitative research, including surveys and questionnaires, observations, experiments, and secondary research.
Surveys and Questionnaires
Surveys and questionnaires are one of the most common methods used in quantitative research. They involve collecting data from a sample population using a set of structured questions. The questions can be open-ended or closed-ended, and the data can be collected through face-to-face interviews, telephone interviews, or online surveys. Surveys and questionnaires are useful for collecting data on attitudes, opinions, and behaviours.
Observations
Observations involve collecting data by watching and recording people’s behaviour. This can be done through structured observations, where the researcher observes specific behaviours, or unstructured observations, where the researcher records all behaviours. Observations are useful for collecting data on behaviours that people may not be able to report accurately, such as non-verbal communication or social interactions.
Experiments
Experiments involve manipulating one or more variables to see how they affect the outcome. They are used to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables. Experimental design involves selecting a sample population, randomly assigning participants to groups, and manipulating the independent variable. The dependent variable is then measured to see if there is a significant difference between the groups. Experiments are useful for testing hypotheses and establishing causal relationships.
Secondary Research
Secondary research involves using existing data to answer research questions. This can include data from previous studies, government reports, or other sources. Secondary research can be useful for answering research questions that have already been addressed or for providing context for primary research.
In conclusion, quantitative research methods involve a structured approach to data collection and analysis. Surveys and questionnaires, observations, experiments, and secondary research are all useful methods for collecting and analysing numerical data. Each method has its strengths and weaknesses, and the choice of method will depend on the research question, sample population, and other factors.
Data Analysis in Quantitative Research
When conducting quantitative research, data analysis is a crucial step in the research process. It involves the use of statistical methods to identify patterns, trends, and relationships within the data. The purpose of data analysis in quantitative research is to draw meaningful and accurate conclusions from the data collected.
Descriptive Statistics
Descriptive statistics is a type of statistical analysis used to describe and summarize the data collected in a study. It involves the use of measures of central tendency, such as mean, median, and mode, to describe the typical value of a variable. Other measures, such as standard deviation and variance, are used to describe the spread of the data.
Inferential Statistics
Inferential statistics is a type of statistical analysis used to make inferences about a population based on the data collected in a sample. It involves the use of hypothesis testing and confidence intervals to determine the likelihood that a particular result is due to chance.
Correlation and Causality
Correlation analysis is used to determine the strength and direction of a relationship between two variables. It involves calculating a correlation coefficient, which ranges from -1 to 1, with values closer to -1 or 1 indicating a stronger relationship. However, correlation does not imply causation, and it is important to establish a cause-and-effect relationship through experimental design or other methods.
In summary, data analysis is a critical component of quantitative research, and it involves the use of statistical methods to identify patterns and relationships within the data. Descriptive statistics are used to summarize the data, while inferential statistics are used to make inferences about the population. Correlation analysis is used to determine the strength and direction of a relationship between two variables.
Reliability and Validity in Quantitative Research
In quantitative research, it is essential to ensure that the data collected is reliable and valid. Reliability refers to the consistency of the results obtained from the research. If the research is reliable, then the results can be replicated consistently. On the other hand, validity refers to the accuracy of the results obtained from the research. If the research is valid, then the results are accurate and can be trusted.
To ensure reliability in quantitative research, researchers use different methods such as test-retest reliability, inter-rater reliability, and internal consistency. Test-retest reliability involves administering the same test to the same group of participants at different times. Inter-rater reliability involves having different researchers rate the same phenomenon to ensure that the results are consistent. Internal consistency involves ensuring that the different items in the questionnaire or survey measure the same construct.
To ensure validity in quantitative research, researchers use different methods such as content validity, criterion validity, and construct validity. Content validity involves ensuring that the items in the questionnaire or survey measure the construct of interest. Criterion validity involves comparing the results obtained from the research to a known standard. Construct validity involves ensuring that the items in the questionnaire or survey measure the construct of interest and not any other construct.
In summary, reliability and validity are essential in quantitative research to ensure that the results obtained are consistent and accurate. Researchers use different methods to ensure reliability and validity, and these methods depend on the research design and the type of data collected.
Limitations of Quantitative Research
Quantitative research has its limitations, and it is important to acknowledge them in order to ensure that the research is conducted appropriately and that the results are interpreted correctly. In this section, we will discuss some of the limitations of quantitative research, including sampling issues, structural bias and narrow focus, missing data and lack of context, and superficiality.
Sampling Issues
One of the main limitations of quantitative research is that inappropriate sampling methods can lead to biased results. For example, if the sample size is too small, the results may not be representative of the population being studied. Similarly, if the sample is not randomly selected, the results may be biased towards a particular group or demographic. It is therefore important to ensure that the sample is representative of the population being studied and that appropriate sampling methods are used.
Structural Bias and Narrow Focus
Another limitation of quantitative research is that it can be subject to structural bias and narrow focus. Structural bias occurs when the research design or methodology is biased towards a particular outcome or conclusion. This can be particularly problematic in fields such as medicine, where research funding may be biased towards certain treatments or pharmaceuticals. Narrow focus occurs when the research is focused on a specific aspect of a problem, rather than considering the problem as a whole. This can limit the scope of the research and lead to incomplete or inaccurate conclusions.
Missing Data and Lack of Context
Quantitative research is also limited by missing data and lack of context. Incomplete data sets or missing data can lead to inaccurate conclusions or biased results. Similarly, quantitative research can lack context, which can limit the interpretation of the results. For example, a study that focuses solely on numerical data may miss important qualitative aspects of a problem, such as cultural or social factors.
Superficiality
Finally, quantitative research can be limited by superficiality. This occurs when the research is focused solely on numerical data and does not consider the underlying causes or complexities of a problem. Superficial research can lead to incomplete or inaccurate conclusions and may fail to provide a comprehensive understanding of the problem being studied.
In conclusion, while quantitative research is a valuable tool for understanding complex problems, it is important to acknowledge its limitations. By being aware of these limitations and ensuring that appropriate research methods are used, researchers can ensure that their findings are accurate and meaningful.
Applications of Quantitative Research
Quantitative research is widely used in various fields, including social sciences, health and biology, economics, and marketing. In this section, we will explore the applications of quantitative research in these fields.
In Social Sciences
Quantitative research is commonly used in social sciences, such as sociology and psychology. It involves the collection and analysis of numerical data to identify patterns and trends in human behaviour. Researchers use quantitative methods to study large groups of individuals, such as surveying a representative sample of a population. This helps to ensure that the results are representative of the entire population, making it easier to draw general conclusions.
In Health and Biology
Quantitative research is also frequently used in health and biology. For example, doctors and researchers may use quantitative methods to study the effectiveness of a particular treatment or medication. This might involve conducting a randomized controlled trial, where patients are randomly assigned to receive either the treatment or a placebo. By collecting numerical data on the outcomes of each group, researchers can determine whether the treatment is effective.
In Economics and Marketing
Quantitative research is also widely used in economics and marketing. In these fields, researchers use quantitative methods to study consumer behaviour, market trends, and economic indicators. For example, a market research firm might conduct a survey to gather data on consumer preferences for a particular product. By analyzing this data, they can identify trends and make predictions about future demand.
In conclusion, quantitative research is a powerful tool for studying a wide range of phenomena, from human behaviour to market trends. By collecting and analyzing numerical data, researchers can gain valuable insights into complex systems and make informed decisions.
Qualitative Vs Quantitative Research
When it comes to research, there are two main types: qualitative and quantitative. Both types of research have their own purposes and are used to answer different types of questions. In this section, we will explore the differences between qualitative and quantitative research.
Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is a type of research that is used to explore and understand people’s experiences, beliefs, and attitudes. It is often used in social sciences and humanities. Qualitative research relies on non-numerical data such as interviews, observations, and case studies. The data collected in qualitative research is often subjective and open-ended, which allows researchers to gain a deeper understanding of the topic being studied.
Quantitative Research
Quantitative research, on the other hand, is used to quantify data and test hypotheses. It is often used in natural sciences and social sciences. Quantitative research relies on numerical data such as surveys, experiments, and statistical analyses. The data collected in quantitative research is often objective and structured, which allows researchers to make statistical inferences and draw conclusions.
Comparisons
The main difference between qualitative and quantitative research is the type of data that is collected. Qualitative research collects non-numerical data, while quantitative research collects numerical data. Qualitative research is often used to explore and understand a topic, while quantitative research is used to test hypotheses and quantify data.
Direct comparisons between the two types of research can be difficult, as they are used to answer different types of questions. However, some researchers choose to use both types of research in their studies. This is known as mixed-methods research, which allows researchers to gain a deeper understanding of the topic being studied.
In summary, qualitative and quantitative research have different purposes and are used to answer different types of questions. Qualitative research is used to explore and understand a topic, while quantitative research is used to test hypotheses and quantify data. Mixed-methods research can be used to gain a deeper understanding of a topic by using both types of research.
Quantitative research is an important tool used by scientists to generate knowledge and create understanding. The objective of quantitative research is to collect numerical data and use logical or statistical observations to draw conclusions. This type of research involves a systematic and objective process, which is used to test theories and models.
Quantitative research relies heavily on numbers and statistical analysis to draw conclusions. The data collected is usually presented in tables, graphs, and charts, which makes it easy to understand and interpret. The use of numbers and statistical analysis also helps to eliminate bias and subjectivity in the research process.
The modeling process is an important aspect of quantitative research. Scientists use models to test theories and make predictions about the future. These models can be used to simulate real-world scenarios and predict the outcomes of different scenarios.
The discussion section of a quantitative research paper is where the results are presented and analyzed. The discussion section should be objective and clear, and should provide a detailed analysis of the results. The discussion section should also provide a critical evaluation of the research problem and the methods used to collect data.
In conclusion, quantitative research is an important tool used by scientists to generate knowledge and create understanding. This type of research relies heavily on numbers and statistical analysis to draw conclusions. The modeling process is an important aspect of quantitative research, and the discussion section is where the results are presented and analyzed.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the advantages of using quantitative research methods.
Quantitative research methods are advantageous because they provide empirical evidence that is objective and reliable. The use of statistical analysis in quantitative research allows researchers to make generalizations about a population based on a sample. This means that the findings of a well-designed quantitative research study can be applied to a larger population, which increases the study’s external validity. Additionally, quantitative research methods are often used to investigate cause-and-effect relationships between variables, which can inform policy decisions.
What are the limitations of quantitative research?
One of the main limitations of quantitative research is that it can oversimplify complex phenomena. Quantitative research methods typically involve the use of closed-ended questions and standardized measures, which may not capture the full range of individuals’ experiences or perspectives. Additionally, quantitative research methods may not be appropriate for investigating topics that are difficult to measure, such as emotions or attitudes. Finally, quantitative research methods may be costly and time-consuming, especially if a large sample size is required.
How do researchers design a quantitative research study?
Researchers typically begin by identifying a research question or hypothesis that they want to investigate. They then select a sample of participants that is representative of the population they are interested in studying. Next, they collect data using standardized measures, such as surveys or experiments. Finally, they analyze the data using statistical methods, such as regression analysis or ANOVA.
What are some common examples of quantitative research in social science?
Common examples of quantitative research in social science include surveys, experiments, and observational studies. Surveys are often used to collect data on individuals’ attitudes, beliefs, and behaviours. Experiments are used to investigate cause-and-effect relationships between variables. Observational studies are used to investigate relationships between variables without manipulating them.
What are the key characteristics of a well-designed quantitative research study?
A well-designed quantitative research study should have a clear research question or hypothesis, a representative sample, standardized measures, appropriate statistical analysis, and a discussion of the study’s limitations. Additionally, a well-designed quantitative research study should be ethical and transparent in its methods and reporting.
What is the role of statistical analysis in quantitative research?
Statistical analysis is a key component of quantitative research because it allows researchers to make inferences about a population based on a sample. Statistical analysis can also be used to investigate cause-and-effect relationships between variables, control for confounding variables, and test hypotheses. However, it is important to use appropriate statistical methods and to report statistical results accurately and transparently.
Similar Posts

Why Surveys are Essential for Quantitative Research
If you are conducting quantitative research, surveys can be an incredibly valuable tool. Surveys are a popular method of data collection that allows researchers to gather large amounts of information from a diverse group of participants. They are useful for gathering both factual and attitudinal information and can be used to measure a wide range…

What Is the Difference Between Qualitative and Quantitative Research?
If you’re new to research, you may have heard the terms qualitative and quantitative research thrown around. While both types of research are used to gather information, they differ in their approaches and methods. Qualitative research is often used to explore and understand complex phenomena, while quantitative research is used to measure and quantify data….

Why Use Quantitative Research
If you’re looking to conduct research that produces numerical data, then quantitative research is the way to go. Quantitative research is a type of research that uses mathematical, statistical, and computational methods to collect and analyze data. This type of research is often used in social sciences, marketing, and business, among other fields. One of…

What is a Good Sample Size for Quantitative Research?
When conducting quantitative research, one of the most important decisions you’ll make is determining the appropriate sample size. A good sample size ensures that your results are statistically significant and representative of the population you’re studying. However, determining what constitutes a “good” sample size can be a challenge, as it depends on a variety of…

How to Critique a Quantitative Research Study
If you are a student or researcher in the social sciences, you will likely come across quantitative research studies. These studies use statistical analysis to measure and interpret data, and they are often used to answer research questions about the relationship between variables. However, it is important to critically evaluate these studies to determine their…

What is Quantitative Research in Marketing?
Quantitative research in marketing is a method of collecting data that involves statistical, mathematical or numerical analysis. This type of research is used to measure consumer behaviour, attitudes, and preferences. It involves the use of questionnaires, surveys, and experiments to gather data. The data is then analysed using statistical methods to determine patterns and relationships…

Your online go-to resource for knowledge digital skills and digital products.
COPYRIGHT © Zorgle.co.uk 2024
“Empowering your business to implement change .”
Review Cart
No products in the basket.
- Chapter 1: Home
- Narrowing Your Topic
- Problem Statement
Purpose Statement Overview
Best practices for writing your purpose statement, writing your purpose statement, sample purpose statements.
- Student Experience Feedback Buttons
- Conceptual Framework
- Theoretical Framework
- Quantitative Research Questions This link opens in a new window
- Qualitative Research Questions This link opens in a new window
- Qualitative & Quantitative Research Support with the ASC This link opens in a new window
- Library Research Consultations This link opens in a new window
Jump to DSE Guide
The purpose statement succinctly explains (on no more than 1 page) the objectives of the research study. These objectives must directly address the problem and help close the stated gap. Expressed as a formula:

Good purpose statements:
- Flow from the problem statement and actually address the proposed problem
- Are concise and clear
- Answer the question ‘Why are you doing this research?’
- Match the methodology (similar to research questions)
- Have a ‘hook’ to get the reader’s attention
- Set the stage by clearly stating, “The purpose of this (qualitative or quantitative) study is to ...
In PhD studies, the purpose usually involves applying a theory to solve the problem. In other words, the purpose tells the reader what the goal of the study is, and what your study will accomplish, through which theoretical lens. The purpose statement also includes brief information about direction, scope, and where the data will come from.
A problem and gap in combination can lead to different research objectives, and hence, different purpose statements. In the example from above where the problem was severe underrepresentation of female CEOs in Fortune 500 companies and the identified gap related to lack of research of male-dominated boards; one purpose might be to explore implicit biases in male-dominated boards through the lens of feminist theory. Another purpose may be to determine how board members rated female and male candidates on scales of competency, professionalism, and experience to predict which candidate will be selected for the CEO position. The first purpose may involve a qualitative ethnographic study in which the researcher observes board meetings and hiring interviews; the second may involve a quantitative regression analysis. The outcomes will be very different, so it’s important that you find out exactly how you want to address a problem and help close a gap!
The purpose of the study must not only align with the problem and address a gap; it must also align with the chosen research method. In fact, the DP/DM template requires you to name the research method at the very beginning of the purpose statement. The research verb must match the chosen method. In general, quantitative studies involve “closed-ended” research verbs such as determine , measure , correlate , explain , compare , validate , identify , or examine ; whereas qualitative studies involve “open-ended” research verbs such as explore , understand , narrate , articulate [meanings], discover , or develop .
A qualitative purpose statement following the color-coded problem statement (assumed here to be low well-being among financial sector employees) + gap (lack of research on followers of mid-level managers), might start like this:
In response to declining levels of employee well-being, the purpose of the qualitative phenomenology was to explore and understand the lived experiences related to the well-being of the followers of novice mid-level managers in the financial services industry. The levels of follower well-being have been shown to correlate to employee morale, turnover intention, and customer orientation (Eren et al., 2013). A combined framework of Leader-Member Exchange (LMX) Theory and the employee well-being concept informed the research questions and supported the inquiry, analysis, and interpretation of the experiences of followers of novice managers in the financial services industry.
A quantitative purpose statement for the same problem and gap might start like this:
In response to declining levels of employee well-being, the purpose of the quantitative correlational study was to determine which leadership factors predict employee well-being of the followers of novice mid-level managers in the financial services industry. Leadership factors were measured by the Leader-Member Exchange (LMX) assessment framework by Mantlekow (2015), and employee well-being was conceptualized as a compound variable consisting of self-reported turnover-intent and psychological test scores from the Mental Health Survey (MHS) developed by Johns Hopkins University researchers.
Both of these purpose statements reflect viable research strategies and both align with the problem and gap so it’s up to the researcher to design a study in a manner that reflects personal preferences and desired study outcomes. Note that the quantitative research purpose incorporates operationalized concepts or variables ; that reflect the way the researcher intends to measure the key concepts under study; whereas the qualitative purpose statement isn’t about translating the concepts under study as variables but instead aim to explore and understand the core research phenomenon.
Always keep in mind that the dissertation process is iterative, and your writing, over time, will be refined as clarity is gradually achieved. Most of the time, greater clarity for the purpose statement and other components of the Dissertation is the result of a growing understanding of the literature in the field. As you increasingly master the literature you will also increasingly clarify the purpose of your study.
The purpose statement should flow directly from the problem statement. There should be clear and obvious alignment between the two and that alignment will get tighter and more pronounced as your work progresses.
The purpose statement should specifically address the reason for conducting the study, with emphasis on the word specifically. There should not be any doubt in your readers’ minds as to the purpose of your study. To achieve this level of clarity you will need to also insure there is no doubt in your mind as to the purpose of your study.
Many researchers benefit from stopping your work during the research process when insight strikes you and write about it while it is still fresh in your mind. This can help you clarify all aspects of a dissertation, including clarifying its purpose.
Your Chair and your committee members can help you to clarify your study’s purpose so carefully attend to any feedback they offer.
The purpose statement should reflect the research questions and vice versa. The chain of alignment that began with the research problem description and continues on to the research purpose, research questions, and methodology must be respected at all times during dissertation development. You are to succinctly describe the overarching goal of the study that reflects the research questions. Each research question narrows and focuses the purpose statement. Conversely, the purpose statement encompasses all of the research questions.
Identify in the purpose statement the research method as quantitative, qualitative or mixed (i.e., “The purpose of this [qualitative/quantitative/mixed] study is to ...)
Avoid the use of the phrase “research study” since the two words together are redundant.
Follow the initial declaration of purpose with a brief overview of how, with what instruments/data, with whom and where (as applicable) the study will be conducted. Identify variables/constructs and/or phenomenon/concept/idea. Since this section is to be a concise paragraph, emphasis must be placed on the word brief. However, adding these details will give your readers a very clear picture of the purpose of your research.
Developing the purpose section of your dissertation is usually not achieved in a single flash of insight. The process involves a great deal of reading to find out what other scholars have done to address the research topic and problem you have identified. The purpose section of your dissertation could well be the most important paragraph you write during your academic career, and every word should be carefully selected. Think of it as the DNA of your dissertation. Everything else you write should emerge directly and clearly from your purpose statement. In turn, your purpose statement should emerge directly and clearly from your research problem description. It is good practice to print out your problem statement and purpose statement and keep them in front of you as you work on each part of your dissertation in order to insure alignment.
It is helpful to collect several dissertations similar to the one you envision creating. Extract the problem descriptions and purpose statements of other dissertation authors and compare them in order to sharpen your thinking about your own work. Comparing how other dissertation authors have handled the many challenges you are facing can be an invaluable exercise. Keep in mind that individual universities use their own tailored protocols for presenting key components of the dissertation so your review of these purpose statements should focus on content rather than form.
Once your purpose statement is set it must be consistently presented throughout the dissertation. This may require some recursive editing because the way you articulate your purpose may evolve as you work on various aspects of your dissertation. Whenever you make an adjustment to your purpose statement you should carefully follow up on the editing and conceptual ramifications throughout the entire document.
In establishing your purpose you should NOT advocate for a particular outcome. Research should be done to answer questions not prove a point. As a researcher, you are to inquire with an open mind, and even when you come to the work with clear assumptions, your job is to prove the validity of the conclusions reached. For example, you would not say the purpose of your research project is to demonstrate that there is a relationship between two variables. Such a statement presupposes you know the answer before your research is conducted and promotes or supports (advocates on behalf of) a particular outcome. A more appropriate purpose statement would be to examine or explore the relationship between two variables.
Your purpose statement should not imply that you are going to prove something. You may be surprised to learn that we cannot prove anything in scholarly research for two reasons. First, in quantitative analyses, statistical tests calculate the probability that something is true rather than establishing it as true. Second, in qualitative research, the study can only purport to describe what is occurring from the perspective of the participants. Whether or not the phenomenon they are describing is true in a larger context is not knowable. We cannot observe the phenomenon in all settings and in all circumstances.
It is important to distinguish in your mind the differences between the Problem Statement and Purpose Statement.
The Problem Statement is why I am doing the research
The Purpose Statement is what type of research I am doing to fit or address the problem
The Purpose Statement includes:
- Method of Study
- Specific Population
Remember, as you are contemplating what to include in your purpose statement and then when you are writing it, the purpose statement is a concise paragraph that describes the intent of the study, and it should flow directly from the problem statement. It should specifically address the reason for conducting the study, and reflect the research questions. Further, it should identify the research method as qualitative, quantitative, or mixed. Then provide a brief overview of how the study will be conducted, with what instruments/data collection methods, and with whom (subjects) and where (as applicable). Finally, you should identify variables/constructs and/or phenomenon/concept/idea.
Qualitative Purpose Statement
Creswell (2002) suggested for writing purpose statements in qualitative research include using deliberate phrasing to alert the reader to the purpose statement. Verbs that indicate what will take place in the research and the use of non-directional language that do not suggest an outcome are key. A purpose statement should focus on a single idea or concept, with a broad definition of the idea or concept. How the concept was investigated should also be included, as well as participants in the study and locations for the research to give the reader a sense of with whom and where the study took place.
Creswell (2003) advised the following script for purpose statements in qualitative research:
“The purpose of this qualitative_________________ (strategy of inquiry, such as ethnography, case study, or other type) study is (was? will be?) to ________________ (understand? describe? develop? discover?) the _________________(central phenomenon being studied) for ______________ (the participants, such as the individual, groups, organization) at __________(research site). At this stage in the research, the __________ (central phenomenon being studied) will be generally defined as ___________________ (provide a general definition)” (pg. 90).
Quantitative Purpose Statement
Creswell (2003) offers vast differences between the purpose statements written for qualitative research and those written for quantitative research, particularly with respect to language and the inclusion of variables. The comparison of variables is often a focus of quantitative research, with the variables distinguishable by either the temporal order or how they are measured. As with qualitative research purpose statements, Creswell (2003) recommends the use of deliberate language to alert the reader to the purpose of the study, but quantitative purpose statements also include the theory or conceptual framework guiding the study and the variables that are being studied and how they are related.
Creswell (2003) suggests the following script for drafting purpose statements in quantitative research:
“The purpose of this _____________________ (experiment? survey?) study is (was? will be?) to test the theory of _________________that _________________ (compares? relates?) the ___________(independent variable) to _________________________(dependent variable), controlling for _______________________ (control variables) for ___________________ (participants) at _________________________ (the research site). The independent variable(s) _____________________ will be generally defined as _______________________ (provide a general definition). The dependent variable(s) will be generally defined as _____________________ (provide a general definition), and the control and intervening variables(s), _________________ (identify the control and intervening variables) will be statistically controlled in this study” (pg. 97).
- The purpose of this qualitative study was to determine how participation in service-learning in an alternative school impacted students academically, civically, and personally. There is ample evidence demonstrating the failure of schools for students at-risk; however, there is still a need to demonstrate why these students are successful in non-traditional educational programs like the service-learning model used at TDS. This study was unique in that it examined one alternative school’s approach to service-learning in a setting where students not only serve, but faculty serve as volunteer teachers. The use of a constructivist approach in service-learning in an alternative school setting was examined in an effort to determine whether service-learning participation contributes positively to academic, personal, and civic gain for students, and to examine student and teacher views regarding the overall outcomes of service-learning. This study was completed using an ethnographic approach that included observations, content analysis, and interviews with teachers at The David School.
- The purpose of this quantitative non-experimental cross-sectional linear multiple regression design was to investigate the relationship among early childhood teachers’ self-reported assessment of multicultural awareness as measured by responses from the Teacher Multicultural Attitude Survey (TMAS) and supervisors’ observed assessment of teachers’ multicultural competency skills as measured by the Multicultural Teaching Competency Scale (MTCS) survey. Demographic data such as number of multicultural training hours, years teaching in Dubai, curriculum program at current school, and age were also examined and their relationship to multicultural teaching competency. The study took place in the emirate of Dubai where there were 14,333 expatriate teachers employed in private schools (KHDA, 2013b).
- The purpose of this quantitative, non-experimental study is to examine the degree to which stages of change, gender, acculturation level and trauma types predicts the reluctance of Arab refugees, aged 18 and over, in the Dearborn, MI area, to seek professional help for their mental health needs. This study will utilize four instruments to measure these variables: University of Rhode Island Change Assessment (URICA: DiClemente & Hughes, 1990); Cumulative Trauma Scale (Kira, 2012); Acculturation Rating Scale for Arabic Americans-II Arabic and English (ARSAA-IIA, ARSAA-IIE: Jadalla & Lee, 2013), and a demographic survey. This study will examine 1) the relationship between stages of change, gender, acculturation levels, and trauma types and Arab refugees’ help-seeking behavior, 2) the degree to which any of these variables can predict Arab refugee help-seeking behavior. Additionally, the outcome of this study could provide researchers and clinicians with a stage-based model, TTM, for measuring Arab refugees’ help-seeking behavior and lay a foundation for how TTM can help target the clinical needs of Arab refugees. Lastly, this attempt to apply the TTM model to Arab refugees’ condition could lay the foundation for future research to investigate the application of TTM to clinical work among refugee populations.
- The purpose of this qualitative, phenomenological study is to describe the lived experiences of LLM for 10 EFL learners in rural Guatemala and to utilize that data to determine how it conforms to, or possibly challenges, current theoretical conceptions of LLM. In accordance with Morse’s (1994) suggestion that a phenomenological study should utilize at least six participants, this study utilized semi-structured interviews with 10 EFL learners to explore why and how they have experienced the motivation to learn English throughout their lives. The methodology of horizontalization was used to break the interview protocols into individual units of meaning before analyzing these units to extract the overarching themes (Moustakas, 1994). These themes were then interpreted into a detailed description of LLM as experienced by EFL students in this context. Finally, the resulting description was analyzed to discover how these learners’ lived experiences with LLM conformed with and/or diverged from current theories of LLM.
- The purpose of this qualitative, embedded, multiple case study was to examine how both parent-child attachment relationships are impacted by the quality of the paternal and maternal caregiver-child interactions that occur throughout a maternal deployment, within the context of dual-military couples. In order to examine this phenomenon, an embedded, multiple case study was conducted, utilizing an attachment systems metatheory perspective. The study included four dual-military couples who experienced a maternal deployment to Operation Iraqi Freedom (OIF) or Operation Enduring Freedom (OEF) when they had at least one child between 8 weeks-old to 5 years-old. Each member of the couple participated in an individual, semi-structured interview with the researcher and completed the Parenting Relationship Questionnaire (PRQ). “The PRQ is designed to capture a parent’s perspective on the parent-child relationship” (Pearson, 2012, para. 1) and was used within the proposed study for this purpose. The PRQ was utilized to triangulate the data (Bekhet & Zauszniewski, 2012) as well as to provide some additional information on the parents’ perspective of the quality of the parent-child attachment relationship in regards to communication, discipline, parenting confidence, relationship satisfaction, and time spent together (Pearson, 2012). The researcher utilized the semi-structured interview to collect information regarding the parents' perspectives of the quality of their parental caregiver behaviors during the deployment cycle, the mother's parent-child interactions while deployed, the behavior of the child or children at time of reunification, and the strategies or behaviors the parents believe may have contributed to their child's behavior at the time of reunification. The results of this study may be utilized by the military, and by civilian providers, to develop proactive and preventive measures that both providers and parents can implement, to address any potential adverse effects on the parent-child attachment relationship, identified through the proposed study. The results of this study may also be utilized to further refine and understand the integration of attachment theory and systems theory, in both clinical and research settings, within the field of marriage and family therapy.
Was this resource helpful?
- << Previous: Problem Statement
- Next: Alignment >>
- Last Updated: Oct 30, 2024 5:45 PM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/c.php?g=1006886

© Copyright 2024 National University. All Rights Reserved.
Privacy Policy | Consumer Information
- How it works
"Christmas Offer"
Terms & conditions.
As the Christmas season is upon us, we find ourselves reflecting on the past year and those who we have helped to shape their future. It’s been quite a year for us all! The end of the year brings no greater joy than the opportunity to express to you Christmas greetings and good wishes.
At this special time of year, Research Prospect brings joyful discount of 10% on all its services. May your Christmas and New Year be filled with joy.
We are looking back with appreciation for your loyalty and looking forward to moving into the New Year together.
"Claim this offer"
In unfamiliar and hard times, we have stuck by you. This Christmas, Research Prospect brings you all the joy with exciting discount of 10% on all its services.
Offer valid till 5-1-2024
We love being your partner in success. We know you have been working hard lately, take a break this holiday season to spend time with your loved ones while we make sure you succeed in your academics
Discount code: RP0996Y

Your content here...

What Is Quantitative Research? | Definition, Methods & Examples
Published by Ellie Cross at October 24th, 2024 , Revised On October 24, 2024
Quantitative research involves gathering and analysing numerical data to make predictions and describe the relationship between two variables. It deals with more than just numbers and integrates theory, hypothesis , proper methodological approach and statistical analysis to answer research questions.
It is a crucial part of market research that relies on numerical data and other computational techniques to gain insights into consumer preferences and opinions. Unlike qualitative research which uses hard evidence to answer a research question, quantitative research is more data-based and uses objective measurements to answer research questions.
What is Quantitative Research?
The meaning of quantitative research can be understood from the word quantitative, which focuses on data such as numbers that can be easily quantified, compared and analysed. This type of research uses both primary and secondary sources to gain data through closed-question poll results, demographic data and census information.
While quantitative data can be gathered through surveys and other methods, it can also be gained from the research studies of third parties. Additionally, this research is widely used in the fields of psychology, economics, accounting, finance and marketing.
Types Of Quantitative Research
There are several kinds of quantitative research with different methodologies and purposes. Each type has its own characteristics and can be used to calculate data in different ways. Here are numerous types of quantitative research:
Correlational Research
Correlational research defines the possibility of a relation existing between two variables. It identifies a relationship to define patterns and trends between two or more study variables.
Example : Cross-sectional studies and cross-section analysis
- Experimental Research
In experimental research , you investigate if two variables affect each other. This mostly includes studying the effect of independent variables on dependent variables. Experiments are carried out to study the cause and effect between them to establish relationships.
Example: Field and laboratory experiments
- Descriptive Research
In this type of research, a researcher often studies the characteristics of a dataset. This includes applying mean, median and standard deviation equations to understand the data.
Example: Surveys and observational studies
It is necessary to know that both experimental and correlational research use sampling methods to test hypotheses and generate findings that are applicable to a large population.
Hire an Expert Researcher
Orders completed by our expert writers are
- Formally drafted in academic style
- 100% Plagiarism free & 100% Confidential
- Never resold
- Include unlimited free revisions
- Completed to match exact client requirements

Quantitative Research Methods
Quantitative research methods include both primary and secondary research methods to analyse and gather numerical data. Here is an overview of the various methods employed for quantitative research:
Quantitative Research Advantages & Disadvantages
Quantitative research focuses on gathering numerical data to explain a particular topic, subject or research question. Like any other research, there are strengths of qualitative research. However, there are disadvantages as well which should be considered:
Quantitative Research Vs Qualitative Research
There are two types of research, qualitative research and quantitative research . Unlike quantitative research, qualitative research is exploratory and does not use mathematical and statistical methods to analyse the data gathered. The table below outlines the key differences between qualitative and quantitative research:
Quantitative Research Examples
Here are a few examples of quantitative research that can help understand how the studies are carried out:
A fast-food restaurant notices that there has been a significant drop in their sales. To understand the reasons behind this, they conduct a descriptive research study to gather insights. Numerical data is collected through customer surveys with close-ended questions asking about food quality, customer service, and service speed. This helps them pinpoint that the service speed is a major issue.
A smartphone company has launched a new smartphone with added features and benefits. They display a new marketing campaign in their outlets at every mall. To determine the success of their product, they launched a social media survey based on the Likert scale, where the customers have to rate the features and overall campaign on a scale of 1 to 5 reflecting the level of satisfaction or dissatisfaction. These responses help the brand determine customer’s perceptions, opinions and overall experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is research design for quantitative study .
A research design for a quantitative study is a framework that highlights how the research will be carried out. It specifies the research question, variables, sampling method to be used, data analysis methods and the ethical considerations to be taken into view.
What is a CASP quantitative research tool?
CASP (Critical Appraisal Skills Programme) is a quantitative research tool that is used to evaluate the effectiveness and quality of quantitative research studies. It checks the authenticity, accuracy and reliability of the data collected and assists policymakers and researchers in ensuring that it meets the highest standards of research.
What are the different kinds of quantitative research?
Quantitative research can be categorised into several types such as:
- Cross-sectional Research
- Correlational Research
- Comparative Research
- Longitudinal Research
You May Also Like
If you are looking for a quick guide on how to write a good literature review, then our blog provides all the essential tips you need.
A perfectly written research paper discussion section increases the study’s credibility, which is only possible by following the 5 steps.
Qualitative research uses surveys, interviews, observations, and case studies to gather and analyse data to create meaningful conclusions.
As Featured On

USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

Splash Sol LLC
- How It Works
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

What is Quantitative Research? Definition, Methods, Types, and Examples

If you’re wondering what is quantitative research and whether this methodology works for your research study, you’re not alone. If you want a simple quantitative research definition , then it’s enough to say that this is a method undertaken by researchers based on their study requirements. However, to select the most appropriate research for their study type, researchers should know all the methods available.
Selecting the right research method depends on a few important criteria, such as the research question, study type, time, costs, data availability, and availability of respondents. There are two main types of research methods— quantitative research and qualitative research. The purpose of quantitative research is to validate or test a theory or hypothesis and that of qualitative research is to understand a subject or event or identify reasons for observed patterns.
Quantitative research methods are used to observe events that affect a particular group of individuals, which is the sample population. In this type of research, diverse numerical data are collected through various methods and then statistically analyzed to aggregate the data, compare them, or show relationships among the data. Quantitative research methods broadly include questionnaires, structured observations, and experiments.
Here are two quantitative research examples:
- Satisfaction surveys sent out by a company regarding their revamped customer service initiatives. Customers are asked to rate their experience on a rating scale of 1 (poor) to 5 (excellent).
- A school has introduced a new after-school program for children, and a few months after commencement, the school sends out feedback questionnaires to the parents of the enrolled children. Such questionnaires usually include close-ended questions that require either definite answers or a Yes/No option. This helps in a quick, overall assessment of the program’s outreach and success.

Table of Contents
What is quantitative research ? 1,2
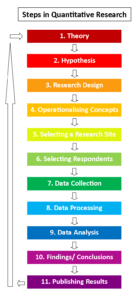
The steps shown in the figure can be grouped into the following broad steps:
- Theory : Define the problem area or area of interest and create a research question.
- Hypothesis : Develop a hypothesis based on the research question. This hypothesis will be tested in the remaining steps.
- Research design : In this step, the most appropriate quantitative research design will be selected, including deciding on the sample size, selecting respondents, identifying research sites, if any, etc.
- Data collection : This process could be extensive based on your research objective and sample size.
- Data analysis : Statistical analysis is used to analyze the data collected. The results from the analysis help in either supporting or rejecting your hypothesis.
- Present results : Based on the data analysis, conclusions are drawn, and results are presented as accurately as possible.
Quantitative research characteristics 4
- Large sample size : This ensures reliability because this sample represents the target population or market. Due to the large sample size, the outcomes can be generalized to the entire population as well, making this one of the important characteristics of quantitative research .
- Structured data and measurable variables: The data are numeric and can be analyzed easily. Quantitative research involves the use of measurable variables such as age, salary range, highest education, etc.
- Easy-to-use data collection methods : The methods include experiments, controlled observations, and questionnaires and surveys with a rating scale or close-ended questions, which require simple and to-the-point answers; are not bound by geographical regions; and are easy to administer.
- Data analysis : Structured and accurate statistical analysis methods using software applications such as Excel, SPSS, R. The analysis is fast, accurate, and less effort intensive.
- Reliable : The respondents answer close-ended questions, their responses are direct without ambiguity and yield numeric outcomes, which are therefore highly reliable.
- Reusable outcomes : This is one of the key characteristics – outcomes of one research can be used and replicated in other research as well and is not exclusive to only one study.

Quantitative research methods 5
Quantitative research methods are classified into two types—primary and secondary.
Primary quantitative research method:
In this type of quantitative research , data are directly collected by the researchers using the following methods.
– Survey research : Surveys are the easiest and most commonly used quantitative research method . They are of two types— cross-sectional and longitudinal.
->Cross-sectional surveys are specifically conducted on a target population for a specified period, that is, these surveys have a specific starting and ending time and researchers study the events during this period to arrive at conclusions. The main purpose of these surveys is to describe and assess the characteristics of a population. There is one independent variable in this study, which is a common factor applicable to all participants in the population, for example, living in a specific city, diagnosed with a specific disease, of a certain age group, etc. An example of a cross-sectional survey is a study to understand why individuals residing in houses built before 1979 in the US are more susceptible to lead contamination.
->Longitudinal surveys are conducted at different time durations. These surveys involve observing the interactions among different variables in the target population, exposing them to various causal factors, and understanding their effects across a longer period. These studies are helpful to analyze a problem in the long term. An example of a longitudinal study is the study of the relationship between smoking and lung cancer over a long period.
– Descriptive research : Explains the current status of an identified and measurable variable. Unlike other types of quantitative research , a hypothesis is not needed at the beginning of the study and can be developed even after data collection. This type of quantitative research describes the characteristics of a problem and answers the what, when, where of a problem. However, it doesn’t answer the why of the problem and doesn’t explore cause-and-effect relationships between variables. Data from this research could be used as preliminary data for another study. Example: A researcher undertakes a study to examine the growth strategy of a company. This sample data can be used by other companies to determine their own growth strategy.

– Correlational research : This quantitative research method is used to establish a relationship between two variables using statistical analysis and analyze how one affects the other. The research is non-experimental because the researcher doesn’t control or manipulate any of the variables. At least two separate sample groups are needed for this research. Example: Researchers studying a correlation between regular exercise and diabetes.
– Causal-comparative research : This type of quantitative research examines the cause-effect relationships in retrospect between a dependent and independent variable and determines the causes of the already existing differences between groups of people. This is not a true experiment because it doesn’t assign participants to groups randomly. Example: To study the wage differences between men and women in the same role. For this, already existing wage information is analyzed to understand the relationship.
– Experimental research : This quantitative research method uses true experiments or scientific methods for determining a cause-effect relation between variables. It involves testing a hypothesis through experiments, in which one or more independent variables are manipulated and then their effect on dependent variables are studied. Example: A researcher studies the importance of a drug in treating a disease by administering the drug in few patients and not administering in a few.
The following data collection methods are commonly used in primary quantitative research :
- Sampling : The most common type is probability sampling, in which a sample is chosen from a larger population using some form of random selection, that is, every member of the population has an equal chance of being selected. The different types of probability sampling are—simple random, systematic, stratified, and cluster sampling.
- Interviews : These are commonly telephonic or face-to-face.
- Observations : Structured observations are most commonly used in quantitative research . In this method, researchers make observations about specific behaviors of individuals in a structured setting.
- Document review : Reviewing existing research or documents to collect evidence for supporting the quantitative research .
- Surveys and questionnaires : Surveys can be administered both online and offline depending on the requirement and sample size.
The data collected can be analyzed in several ways in quantitative research , as listed below:
- Cross-tabulation —Uses a tabular format to draw inferences among collected data
- MaxDiff analysis —Gauges the preferences of the respondents
- TURF analysis —Total Unduplicated Reach and Frequency Analysis; helps in determining the market strategy for a business
- Gap analysis —Identify gaps in attaining the desired results
- SWOT analysis —Helps identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of a product, service, or organization
- Text analysis —Used for interpreting unstructured data
Secondary quantitative research methods :
This method involves conducting research using already existing or secondary data. This method is less effort intensive and requires lesser time. However, researchers should verify the authenticity and recency of the sources being used and ensure their accuracy.
The main sources of secondary data are:
- The Internet
- Government and non-government sources
- Public libraries
- Educational institutions
- Commercial information sources such as newspapers, journals, radio, TV

When to use quantitative research 6
Here are some simple ways to decide when to use quantitative research . Use quantitative research to:
- recommend a final course of action
- find whether a consensus exists regarding a particular subject
- generalize results to a larger population
- determine a cause-and-effect relationship between variables
- describe characteristics of specific groups of people
- test hypotheses and examine specific relationships
- identify and establish size of market segments
A research case study to understand when to use quantitative research 7
Context: A study was undertaken to evaluate a major innovation in a hospital’s design, in terms of workforce implications and impact on patient and staff experiences of all single-room hospital accommodations. The researchers undertook a mixed methods approach to answer their research questions. Here, we focus on the quantitative research aspect.
Research questions : What are the advantages and disadvantages for the staff as a result of the hospital’s move to the new design with all single-room accommodations? Did the move affect staff experience and well-being and improve their ability to deliver high-quality care?
Method: The researchers obtained quantitative data from three sources:
- Staff activity (task time distribution): Each staff member was shadowed by a researcher who observed each task undertaken by the staff, and logged the time spent on each activity.
- Staff travel distances : The staff were requested to wear pedometers, which recorded the distances covered.
- Staff experience surveys : Staff were surveyed before and after the move to the new hospital design.
Results of quantitative research : The following observations were made based on quantitative data analysis:
- The move to the new design did not result in a significant change in the proportion of time spent on different activities.
- Staff activity events observed per session were higher after the move, and direct care and professional communication events per hour decreased significantly, suggesting fewer interruptions and less fragmented care.
- A significant increase in medication tasks among the recorded events suggests that medication administration was integrated into patient care activities.
- Travel distances increased for all staff, with highest increases for staff in the older people’s ward and surgical wards.
- Ratings for staff toilet facilities, locker facilities, and space at staff bases were higher but those for social interaction and natural light were lower.
Advantages of quantitative research 1,2
When choosing the right research methodology, also consider the advantages of quantitative research and how it can impact your study.
- Quantitative research methods are more scientific and rational. They use quantifiable data leading to objectivity in the results and avoid any chances of ambiguity.
- This type of research uses numeric data so analysis is relatively easier .
- In most cases, a hypothesis is already developed and quantitative research helps in testing and validatin g these constructed theories based on which researchers can make an informed decision about accepting or rejecting their theory.
- The use of statistical analysis software ensures quick analysis of large volumes of data and is less effort intensive.
- Higher levels of control can be applied to the research so the chances of bias can be reduced.
- Quantitative research is based on measured value s, facts, and verifiable information so it can be easily checked or replicated by other researchers leading to continuity in scientific research.
Disadvantages of quantitative research 1,2
Quantitative research may also be limiting; take a look at the disadvantages of quantitative research.
- Experiments are conducted in controlled settings instead of natural settings and it is possible for researchers to either intentionally or unintentionally manipulate the experiment settings to suit the results they desire.
- Participants must necessarily give objective answers (either one- or two-word, or yes or no answers) and the reasons for their selection or the context are not considered.
- Inadequate knowledge of statistical analysis methods may affect the results and their interpretation.
- Although statistical analysis indicates the trends or patterns among variables, the reasons for these observed patterns cannot be interpreted and the research may not give a complete picture.
- Large sample sizes are needed for more accurate and generalizable analysis .
- Quantitative research cannot be used to address complex issues.

Frequently asked questions on quantitative research
Q: What is the difference between quantitative research and qualitative research? 1
A: The following table lists the key differences between quantitative research and qualitative research, some of which may have been mentioned earlier in the article.
Q: What is the difference between reliability and validity? 8,9
A: The term reliability refers to the consistency of a research study. For instance, if a food-measuring weighing scale gives different readings every time the same quantity of food is measured then that weighing scale is not reliable. If the findings in a research study are consistent every time a measurement is made, then the study is considered reliable. However, it is usually unlikely to obtain the exact same results every time because some contributing variables may change. In such cases, a correlation coefficient is used to assess the degree of reliability. A strong positive correlation between the results indicates reliability.
Validity can be defined as the degree to which a tool actually measures what it claims to measure. It helps confirm the credibility of your research and suggests that the results may be generalizable. In other words, it measures the accuracy of the research.
The following table gives the key differences between reliability and validity.
Q: What is mixed methods research? 10
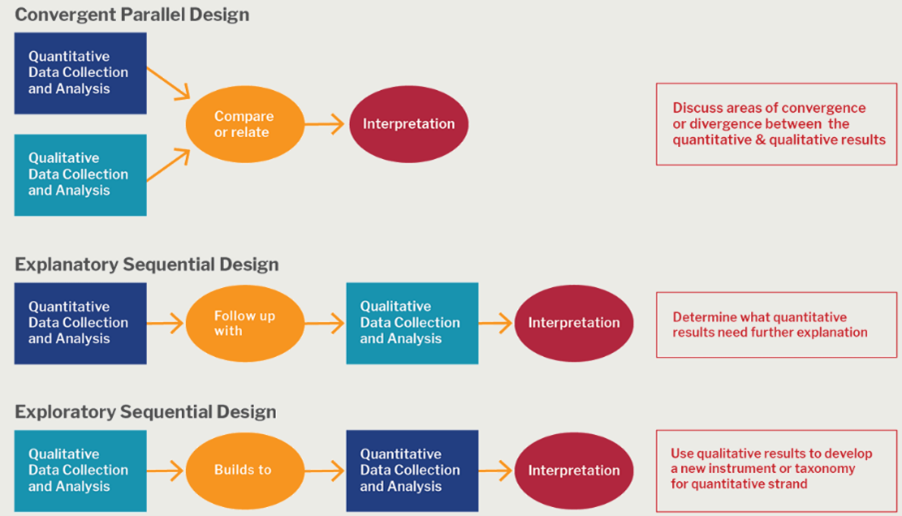
A: A mixed methods approach combines the characteristics of both quantitative research and qualitative research in the same study. This method allows researchers to validate their findings, verify if the results observed using both methods are complementary, and explain any unexpected results obtained from one method by using the other method. A mixed methods research design is useful in case of research questions that cannot be answered by either quantitative research or qualitative research alone. However, this method could be more effort- and cost-intensive because of the requirement of more resources. The figure 3 shows some basic mixed methods research designs that could be used.
Thus, quantitative research is the appropriate method for testing your hypotheses and can be used either alone or in combination with qualitative research per your study requirements. We hope this article has provided an insight into the various facets of quantitative research , including its different characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages, and a few tips to quickly understand when to use this research method.
References
- Qualitative vs quantitative research: Differences, examples, & methods. Simply Psychology. Accessed Feb 28, 2023. https://simplypsychology.org/qualitative-quantitative.html#Quantitative-Research
- Your ultimate guide to quantitative research. Qualtrics. Accessed February 28, 2023. https://www.qualtrics.com/uk/experience-management/research/quantitative-research/
- The steps of quantitative research. Revise Sociology. Accessed March 1, 2023. https://revisesociology.com/2017/11/26/the-steps-of-quantitative-research/
- What are the characteristics of quantitative research? Marketing91. Accessed March 1, 2023. https://www.marketing91.com/characteristics-of-quantitative-research/
- Quantitative research: Types, characteristics, methods, & examples. ProProfs Survey Maker. Accessed February 28, 2023. https://www.proprofssurvey.com/blog/quantitative-research/#Characteristics_of_Quantitative_Research
- Qualitative research isn’t as scientific as quantitative methods. Kmusial blog. Accessed March 5, 2023. https://kmusial.wordpress.com/2011/11/25/qualitative-research-isnt-as-scientific-as-quantitative-methods/
- Maben J, Griffiths P, Penfold C, et al. Evaluating a major innovation in hospital design: workforce implications and impact on patient and staff experiences of all single room hospital accommodation. Southampton (UK): NIHR Journals Library; 2015 Feb. (Health Services and Delivery Research, No. 3.3.) Chapter 5, Case study quantitative data findings. Accessed March 6, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK274429/
- McLeod, S. A. (2007). What is reliability? Simply Psychology. www.simplypsychology.org/reliability.html
- Reliability vs validity: Differences & examples. Accessed March 5, 2023. https://statisticsbyjim.com/basics/reliability-vs-validity/
- Mixed methods research. Community Engagement Program. Harvard Catalyst. Accessed February 28, 2023. https://catalyst.harvard.edu/community-engagement/mmr
Editage All Access is a subscription-based platform that unifies the best AI tools and services designed to speed up, simplify, and streamline every step of a researcher’s journey. The Editage All Access Pack is a one-of-a-kind subscription that unlocks full access to an AI writing assistant, literature recommender, journal finder, scientific illustration tool, and exclusive discounts on professional publication services from Editage.
Based on 22+ years of experience in academia, Editage All Access empowers researchers to put their best research forward and move closer to success. Explore our top AI Tools pack, AI Tools + Publication Services pack, or Build Your Own Plan. Find everything a researcher needs to succeed, all in one place – Get All Access now starting at just $14 a month !
Related Posts

What is Experimental Research Design? Definition, Examples, and Types of Designs

What is an SCI-indexed Journal?

- Agile & Development
- Prioritization
- Product Management
- Product Marketing & Growth
- Product Metrics
- Product Strategy
Home » Quantitative Research: Definition, Methods, and Examples
Quantitative Research: Definition, Methods, and Examples
June 13, 2023 max 8min read.

This article covers:
What Is Quantitative Research?
Quantitative research methods .
- Data Collection and Analysis
Types of Quantitative Research
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Quantitative Research
Examples of Quantitative Research
Picture this: you’re a product or project manager and must make a crucial decision. You need data-driven insights to guide your choices, understand customer preferences, and predict market trends. That’s where quantitative research comes into play. It’s like having a secret weapon that empowers you to make informed decisions confidently.
Quantitative research is all about numbers, statistics, and measurable data. It’s a systematic approach that allows you to gather and analyze numerical information to uncover patterns, trends, and correlations.
Quantitative research provides concrete, objective data to drive your strategies, whether conducting surveys, analyzing large datasets, or crunching numbers.
In this article, we’ll dive and learn all about quantitative research; get ready to uncover the power of numbers.
Quantitative Research Definition:
Quantitative research is a systematic and objective approach to collecting, analyzing, and interpreting numerical data. It measures and quantifies variables, employing statistical methods to uncover patterns, relationships, and trends.
Quantitative research gets utilized across a wide range of fields, including market research, social sciences, psychology, economics, and healthcare. It follows a structured methodology that uses standardized instruments, such as surveys, experiments, or polls, to collect data. This data is then analyzed using statistical techniques to uncover patterns and relationships.
The purpose of quantitative research is to measure and quantify variables, assess the connections between variables, and draw objective and generalizable conclusions. Its benefits are numerous:
- Rigorous and scientific approach : Quantitative research provides a comprehensive and scientific approach to studying phenomena. It enables researchers to gather empirical evidence and draw reliable conclusions based on solid data.
- Evidence-based decision-making : By utilizing quantitative research, researchers can make evidence-based decisions. It helps in developing informed strategies and evaluating the effectiveness of interventions or policies by relying on data-driven insights.
- Advancement of knowledge : Quantitative research contributes to the advancement of knowledge by building upon existing theories. It expands understanding in various fields and informs future research directions, allowing for continued growth and development.
Here are various quantitative research methods:
Survey research : This method involves collecting data from a sample of individuals through questionnaires, interviews, or online surveys. Surveys gather information about people’s attitudes, opinions, behaviors, and characteristics.
Experimentation: It is a research method that allows researchers to determine cause-and-effect relationships. In an experiment, participants randomly get assigned to different groups. While the other group does not receive treatment or intervention, one group does. The outcomes of the two groups then get measured to analyze the effects of the treatment or intervention.
Here are the steps involved in an experiment:
- Define the research question. What do you want to learn about?
- Develop a hypothesis. What do you think the answer to your research question is?
- Design the experiment. How will you manipulate the variables and measure the outcomes?
- Recruit participants. Who will you study?
- Randomly assign participants to groups. This ensures that the groups are as similar as possible.
- Apply the treatments or interventions. This is what the researcher is attempting to test the effects of.
- Measure the outcomes. This is how the researcher will determine whether the treatments or interventions had any effect.
- Analyze the data. This is how the researcher will determine whether the results support the hypothesis.
- Draw conclusions. What do the results mean?
- Content analysis : Content analysis is a systematic approach to analyzing written, verbal, or visual communication. Researchers identify and categorize specific content, themes, or patterns in various forms of media, such as books, articles, speeches, or social media posts.
- Secondary data analysis : It is a research method that involves analyzing data already collected by someone else. This data can be from various sources, such as government reports, previous research studies, or large datasets like surveys or medical records.
Researchers use secondary data analysis to answer new research questions or gain additional insights into a topic.
Data Collection and Analysis for Quantitative Research
Quantitative research is research that uses numbers and statistics to answer questions. It often measures things like attitudes, behaviors, and opinions.
There are three main methods for collecting quantitative data:
- Surveys and questionnaires: These are structured instruments used to gather data from a sample of people.
- Experiments and controlled observations: These are conducted in a controlled setting to measure variables and determine cause-and-effect relationships.
- Existing data sources (secondary data): This data gets collected from databases, archives, or previous studies.
Data preprocessing and cleaning is the first step in data analysis. It involves identifying and correcting errors, removing outliers, and ensuring the data is consistent.
Descriptive statistics is a branch of statistics that deals with the description of the data. It summarizes and describes the data using central tendency, variability, and shape measures.
Inferential statistics again comes under statistics which deals with the inference of properties of a population from a sample. It tests hypotheses, estimates parameters, and makes predictions.
Here are some of the most common inferential statistical techniques:
- Hypothesis testing : This assesses the significance of relationships or differences between variables.
- Confidence intervals : This estimates the range within which population parameters likely fall.
- Correlation and regression analysis : This examines relationships and predicts outcomes based on variables.
- Analysis of variance (ANOVA) : This compare means across multiple groups or conditions.
Statistical software and tools for data analysis can perform complex statistical analyses efficiently. Some of the most popular statistical software packages include SPSS, SAS, and R.
Here are some of the main types of quantitative research methodology:
- Descriptive research describes a particular population’s characteristics, trends, or behaviors. For example, a descriptive study might look at the average height of students in a school, the number of people who voted in an election, or the types of food people eat.
- Correlational research checks the relationship between two or more variables. For example, a correlational study might examine the relationship between income and happiness or stress and weight gain. Correlational research can show that two variables are related but cannot show that one variable causes the other.
- Experimental research is a type of research that investigates cause-and-effect relationships. In an experiment, researchers manipulate one variable (the independent variable) and measure the impact on another variable (the dependent variable). This allows researchers to make inferences about the relationship between the two variables.
- Quasi-experimental research is similar to experimental research. However, it does not involve random assignment of participants to groups. This can be due to practical or ethical considerations, such as when assigning people to receive a new medication randomly is impossible. In quasi-experimental research, researchers try to control for other factors affecting the results, such as the participant’s age, gender, or health status.
- Longitudinal research studies change patterns over an extended time. For example, a longitudinal study might examine how children’s reading skills develop over a few years or how people’s attitudes change as they age. But longitudinal research can be expensive and time-consuming. Still, it can offer valuable insights into how people and things change over time.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Quantitative Research
Here are the advantages and downsides of quantitative research:
Advantages of Quantitative Research:
- Objectivity: Quantitative research aims to be objective and unbiased. This is because it relies on numbers and statistical methods, which reduce the potential for researcher bias and subjective interpretation.
- Generalizability: Quantitative research often involves large sample sizes, which increases the likelihood of obtaining representative data. The study findings are more likely to apply to a wider population.
- Replicability: Using standardized procedures and measurement instruments in quantitative research enhances replicability. This means that other researchers can repeat the study using the same methods to test the reliability of the findings.
- Statistical analysis: Quantitative research employs various statistical techniques for data analysis. This allows researchers to identify data patterns, relationships, and associations. Additionally, statistical analysis can provide precision and help draw objective conclusions.
- Numerical precision: Quantitative research produces numerical data that can be analyzed using mathematical calculations. This numeric precision allows for clear comparisons and quantitative interpretations.
Disadvantages of Quantitative Research :
- Lack of Contextual Understanding : Quantitative research often focuses on measurable variables, which may limit the exploration of complex phenomena. It may overlook the social, cultural, and contextual factors that could influence the research findings.
- Limited Insight : While quantitative research can identify correlations and associations, it may not uncover underlying causes or explanations of these relationships. It may provide answers to “what” and “how much,” but not necessarily “why.”
- Potential for Simplification : The quantification of data can lead to oversimplification, as it may reduce complex phenomena into numerical values. This simplification may overlook nuances and intricacies important to understanding the research topic fully.
- Cost and Time-Intensive : Quantitative research requires significant resources. It includes time, funding, and specialized expertise. Researchers must collect and analyze large amounts of numerical data, which can be lengthy and expensive.
- Limited Flexibility : A systematic and planned strategy typically gets employed in quantitative research. It signifies the researcher’s use of a predetermined data collection and analysis approach. As a result, you may be more confident that your study gets conducted consistently and equitably. But it may also make it more difficult for the researcher to change the research plan or pose additional inquiries while gathering data. This could lead to missing valuable insights.
Here are some real-life examples of quantitative research:
- Market Research : Quantitative market research is a type of market research that uses numerical data to understand consumer preferences, buying behavior, and market trends. This data typically gets gathered through surveys and questionnaires, which are then analyzed to make informed business decisions.
- Health Studies : Quantitative research, such as clinical trials and epidemiological research, is vital in health studies. Researchers collect numerical data on treatment effectiveness, disease prevalence, risk factors, and patient outcomes. This data is then analyzed statistically to draw conclusions and make evidence-based recommendations for healthcare practices.
- Educational Research : Quantitative research is used extensively in educational studies to examine various aspects of learning, teaching methods, and academic achievement. Researchers collect data through standardized tests, surveys, or observations. The reason for this approach is to analyze factors influencing student performance, educational interventions, and educational policy effectiveness.
- Social Science Surveys : Social science researchers often employ quantitative research methods. The aim here is to study social phenomena and gather data on individuals’ or groups’ attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors. Large-scale surveys collect numerical data, then statistically analyze to identify patterns, trends, and associations within the population.
- Opinion Polls : Opinion polls and public opinion research rely heavily on quantitative research techniques. Polling organizations conduct surveys with representative samples of the population. The companies do this intending to gather numerical data on public opinions, political preferences, and social attitudes. The data then gets analyzed to gauge public sentiment and predict election outcomes or public opinion on specific issues.
- Economic Research : Quantitative research is widely used in economic studies to analyze economic indicators, trends, and patterns. Economists collect numerical data on GDP, inflation, employment, and consumer spending. Statistical analysis of this data helps understand economic phenomena, forecast future trends, and inform economic policy decisions.
More To Read :-
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Definition and Examples
- What Is Operations Management? Definition and Overview
Qualitative research is about understanding and exploring something in depth. It uses non-numerical data, like interviews, observations, and open-ended survey responses, to gather rich, descriptive insights. Quantitative research is about measuring and analyzing relationships between variables using numerical data.
Quantitative research gets characterized by the following:
- The collection of numerical information
- The use of statistical analysis
- The goal of measuring and quantifying phenomena
- The purpose of examining relationships between variables
- The purpose of generalizing findings to a larger population
- The use of large sample sizes
- The use of structured surveys or experiments
- The usage of statistical techniques to analyze data objectively
The primary goal of quantitative research is to gather numerical data and analyze it statistically to uncover patterns, relationships, and trends. It aims to provide objective and generalizable insights using systematic data collection methods, standardized instruments, and statistical analysis techniques. Quantitative research seeks to test hypotheses, make predictions, and inform decision-making in various fields.
Crafting great product requires great tools. Try Chisel today, it's free forever.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Jun 30, 2020 · Quantitative research design describes how a researcher arranges a study in an attempt to control the variables. At one end of the spectrum is a method to observe and describe data rather than control or manipulate variables.
Aug 1, 2024 · In quantitative research, the choice of design serves as the structural foundation that shapes the study’s direction, credibility, and impact. Making informed decisions in the design phase is imperative for the generation of rigorous and actionable insights.
Mar 26, 2024 · Replicable: Enables repetition of the study to verify results and increase reliability. Example: A survey on the correlation between exercise frequency and stress levels among adults, using a Likert scale to measure responses. Types of Quantitative Research. Quantitative research can be categorized into several types, each serving a specific ...
Jan 5, 2021 · The purpose of this study is to provide some important fundamental concepts of quantitative research to the common readers for the development of their future projects, articles and/or theses.
Nov 15, 2023 · Explore the purpose of quantitative research and how it plays a crucial role in data-driven decision-making. This article outlines the key objectives of quantitative research, including measuring variables, identifying patterns, and testing hypotheses. Learn how to effectively apply quantitative research methods to gain valuable insights that inform strategies and enhance outcomes across ...
Jun 14, 2021 · The purpose of quantitative research is to attain greater knowledge and understanding of the social world. Researchers use quantitative methods to observe situations or events that affect people. 1 Quantitative research produces objective data that can be clearly communicated through statistics and numbers.
Oct 30, 2024 · As with qualitative research purpose statements, Creswell (2003) recommends the use of deliberate language to alert the reader to the purpose of the study, but quantitative purpose statements also include the theory or conceptual framework guiding the study and the variables that are being studied and how they are related.
Oct 24, 2024 · Quantitative Research Examples. Here are a few examples of quantitative research that can help understand how the studies are carried out: Example 1. A fast-food restaurant notices that there has been a significant drop in their sales. To understand the reasons behind this, they conduct a descriptive research study to gather insights.
Mar 23, 2023 · The purpose of quantitative research is to validate or test a theory or hypothesis and that of qualitative research is to understand a subject or event or identify reasons for observed patterns. Quantitative research methods are used to observe events that affect a particular group of individuals, which is the sample population. In this type of ...
Jun 13, 2023 · The purpose of quantitative research is to measure and quantify variables, assess the connections between variables, and draw objective and generalizable conclusions. Its benefits are numerous: Rigorous and scientific approach : Quantitative research provides a comprehensive and scientific approach to studying phenomena.